Understanding Semi-Fowler’s Position: Benefits, Uses, and Proper Implementation
In healthcare, patient positioning is crucial for comfort, treatment, and recovery. One common and versatile position is the Semi-Fowler’s position. This article delves into what Semi-Fowler’s position entails, its benefits, appropriate uses, and how to implement it correctly. Understanding this position is essential for healthcare professionals and caregivers alike.
What is Semi-Fowler’s Position?
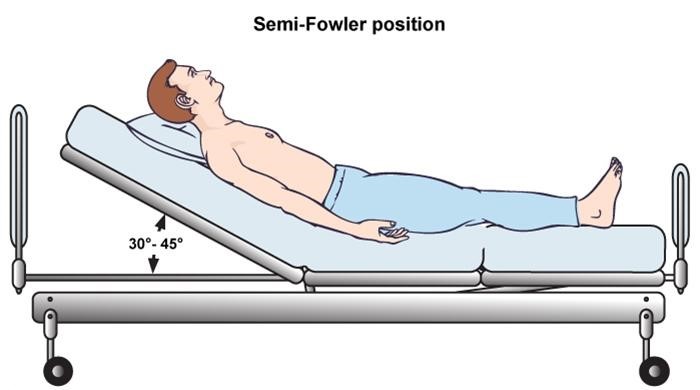
Semi-Fowler’s position involves placing a patient in a supine (lying on their back) position with the head of the bed raised to an angle of approximately 30 to 45 degrees. This elevation affects various physiological systems, making it suitable for a wide range of medical conditions and post-operative care scenarios. It differs from Fowler’s position (45-60 degrees) and High Fowler’s position (60-90 degrees) in the degree of elevation.
Benefits of Semi-Fowler’s Position
The Semi-Fowler’s position offers numerous advantages for patients. These benefits contribute to improved respiratory function, reduced risk of aspiration, and enhanced overall comfort. Let’s explore these in detail:
Improved Respiratory Function
Elevating the upper body in Semi-Fowler’s position facilitates better lung expansion. This is particularly beneficial for patients with respiratory conditions such as pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or those recovering from anesthesia. The position reduces pressure on the diaphragm, allowing for deeper and more efficient breathing. [See also: Respiratory Care Techniques]
Reduced Risk of Aspiration
Aspiration, the accidental inhalation of foreign material (such as food, fluids, or saliva) into the lungs, is a significant concern for patients with swallowing difficulties or decreased level of consciousness. Semi-Fowler’s position helps minimize this risk by using gravity to keep stomach contents down, preventing them from refluxing into the esophagus and potentially entering the airway. This is especially important during and after feeding.
Enhanced Comfort and Reduced Pressure Sores
For patients confined to bed for extended periods, comfort is paramount. Semi-Fowler’s position can alleviate pressure on the sacrum and buttocks, reducing the risk of pressure sore development. It also promotes better circulation and reduces muscle strain, leading to a more comfortable experience. Regular repositioning, even in Semi-Fowler’s position, is still necessary to prevent pressure ulcers.
Improved Cardiac Output
While not the primary benefit, the Semi-Fowler’s position can aid in improving cardiac output. By reducing venous return to the heart compared to a fully supine position, it can decrease the workload on the heart, making it beneficial for patients with certain cardiac conditions. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the suitability of this position for specific cardiac patients.
Uses of Semi-Fowler’s Position
The versatility of Semi-Fowler’s position makes it applicable in various clinical settings. Here are some common uses:
Post-Operative Care
After surgery, patients often benefit from being placed in Semi-Fowler’s position. It aids in easier breathing, reduces the risk of aspiration, and promotes overall comfort during the recovery period. This position is particularly useful after abdominal or thoracic surgeries. Monitoring the patient’s vital signs and comfort level is crucial during this time.
Respiratory Distress
Patients experiencing respiratory distress, whether due to asthma, pneumonia, or other conditions, often find relief in Semi-Fowler’s position. The elevated upper body allows for better lung expansion and easier breathing. Supplemental oxygen may also be administered in conjunction with this position to further improve oxygenation. [See also: Management of Respiratory Distress]
Feeding and Medication Administration
To minimize the risk of aspiration, Semi-Fowler’s position is recommended during and immediately after feeding or administering oral medications. This allows gravity to assist in swallowing and prevents food or medication from entering the airway. Patients should remain in this position for at least 30 minutes after eating or taking medication.
Patients with Nasogastric Tubes
For patients who have a nasogastric (NG) tube for feeding or medication administration, Semi-Fowler’s position is essential. It helps prevent reflux and aspiration of gastric contents. Regular monitoring of the tube placement and patient’s tolerance to the feeding is necessary.
Implementing Semi-Fowler’s Position Correctly
Proper implementation of Semi-Fowler’s position is essential to maximize its benefits and avoid potential complications. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Preparation
Gather the necessary equipment, including an adjustable bed, pillows, and blankets. Explain the procedure to the patient and ensure they are comfortable. Wash your hands and put on gloves if necessary. Ensure the patient understands the reason for the position and what to expect.
Positioning
Raise the head of the bed to an angle of 30 to 45 degrees. Use pillows to support the patient’s head, neck, and shoulders. Ensure the patient’s spine is aligned and that they are not slumped to one side. Adjust the bed and pillows as needed to maintain the correct angle and provide optimal support. The goal is to maintain the patient’s comfort and safety throughout the procedure.
Monitoring
Regularly assess the patient’s comfort level, skin integrity, and respiratory status. Watch for signs of pressure sores, shortness of breath, or discomfort. Reposition the patient every two hours to prevent pressure ulcers. Ensure the patient can easily reach the call bell if they need assistance. Monitor vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation, to ensure the patient is tolerating the position well. [See also: Pressure Ulcer Prevention]
Documentation
Document the position, the time it was initiated, and the patient’s response to the position. Note any concerns or complications that arise. Accurate documentation is crucial for continuity of care and legal purposes. Include any interventions performed, such as repositioning or medication administration.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While Semi-Fowler’s position is generally safe, there are some potential risks and considerations to keep in mind:
Pressure Sores
Prolonged positioning in Semi-Fowler’s position can increase the risk of pressure sores, especially on the sacrum and buttocks. Regular repositioning and the use of pressure-relieving devices are essential to prevent skin breakdown. Inspect the skin regularly for signs of redness or irritation.
Sliding Down
Patients may slide down in bed while in Semi-Fowler’s position, increasing the risk of shearing forces on the skin. Using a draw sheet or other assistive devices can help prevent this. Ensure the patient is properly supported and that the bed is adjusted to prevent sliding.
Discomfort
Some patients may find Semi-Fowler’s position uncomfortable, especially if they have back pain or other musculoskeletal issues. Provide adequate support and padding to minimize discomfort. Adjust the position as needed to ensure the patient’s comfort.
Contraindications
In certain situations, Semi-Fowler’s position may be contraindicated. For example, patients with unstable spinal injuries or severe hypotension may not be able to tolerate this position. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate positioning for each patient. It is important to assess the patient’s individual needs and medical history before implementing any positioning strategy.
Conclusion
Semi-Fowler’s position is a valuable and versatile tool in healthcare. Its benefits, including improved respiratory function, reduced risk of aspiration, and enhanced comfort, make it an essential component of patient care. By understanding the proper implementation and potential risks, healthcare professionals can effectively utilize this position to improve patient outcomes. Remember to always prioritize patient safety and comfort when implementing Semi-Fowler’s position. The position contributes significantly to patient well-being when used correctly in conjunction with other care interventions.
