Positive ANA ICD-10: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Codes and Their Significance
Are you searching for information about a positive ANA (antinuclear antibody) test result and its corresponding ICD-10 codes? Navigating the complexities of medical coding and understanding the implications of a positive ANA can be challenging. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the subject, providing you with a deep understanding of positive ANA, its associated ICD-10 codes, potential causes, and what to expect next. We strive to provide unparalleled clarity and actionable insights, relying on expert knowledge and a commitment to accuracy. We’ll explore the nuances of the codes, potential underlying conditions, and the diagnostic process, ensuring you’re well-informed and empowered to discuss your health with your healthcare provider.
Understanding the Basics of ANA and its Significance
An antinuclear antibody (ANA) test is a common blood test used to help diagnose autoimmune disorders. These disorders occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues and organs. ANA tests detect the presence of antibodies that target the nucleus of cells. A positive ANA result indicates that these antibodies are present, but it doesn’t necessarily mean you have an autoimmune disease. Many healthy individuals can have a positive ANA, especially at low titers.
The significance of a positive ANA lies in its potential association with various autoimmune conditions. However, it’s crucial to understand that a positive ANA is not a diagnosis in itself. It’s merely a piece of the puzzle that your doctor will use in conjunction with your symptoms, medical history, and other test results to determine the underlying cause.
Factors Affecting ANA Test Results
Several factors can influence ANA test results, including:
* **Age:** The prevalence of positive ANA increases with age.
* **Sex:** Women are more likely to have positive ANA results than men.
* **Medications:** Certain medications can induce a positive ANA.
* **Underlying Conditions:** Infections and other non-autoimmune conditions can sometimes cause a transient positive ANA.
Decoding the ICD-10 Codes Associated with Positive ANA
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) is a standardized coding system used to classify diseases and health conditions. While there isn’t a specific ICD-10 code solely for a positive ANA test, several codes can be used depending on the underlying condition suspected or diagnosed based on the ANA result and other clinical findings. It’s important to emphasize that **positive ANA ICD-10** coding is context-dependent.
Here are some examples of ICD-10 codes that might be relevant in the context of a positive ANA:
* **M32.9 – Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Unspecified:** This code is used when a patient has lupus, but the specific type or manifestations are not yet determined.
* **M35.0 – Sicca syndrome [Sjögren’s syndrome]:** Used when the positive ANA is suspected to be linked to Sjogren’s Syndrome.
* **M31.0 – Hypersensitivity angiitis:** Can be associated with vasculitis and a positive ANA result.
* **R77.9 – Abnormality of plasma protein:** This is a more general code that might be used if the positive ANA is considered an abnormal lab finding without a specific diagnosis yet.
* **M35.9 – Systemic sclerosis, unspecified:** Another code related to a specific autoimmune disease, scleroderma.
It’s crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare professional or medical coder to determine the appropriate ICD-10 code based on the specific clinical context. The selection of the correct code requires a thorough understanding of the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and other diagnostic findings.
The Role of ICD-10 Codes in Medical Billing and Documentation
ICD-10 codes play a vital role in medical billing, documentation, and data analysis. They are used to:
* **Facilitate insurance claims processing:** Insurance companies use ICD-10 codes to determine coverage and reimbursement for medical services.
* **Track disease prevalence and trends:** Public health agencies use ICD-10 codes to monitor the incidence and prevalence of various diseases.
* **Support clinical research:** Researchers use ICD-10 codes to identify and analyze patient populations with specific conditions.
Exploring Potential Causes of a Positive ANA Result
A positive ANA result can be associated with a wide range of conditions, including:
* **Autoimmune Diseases:** Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjögren’s syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, polymyositis, and mixed connective tissue disease are common autoimmune disorders linked to positive ANA.
* **Infections:** Certain viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections can trigger a transient positive ANA.
* **Medications:** Some drugs, such as hydralazine, procainamide, and isoniazid, are known to induce a positive ANA.
* **Other Conditions:** Liver disease, thyroid disease, and cancer can sometimes be associated with a positive ANA.
* **Healthy Individuals:** A small percentage of healthy individuals, particularly older adults, may have a positive ANA without any underlying disease.
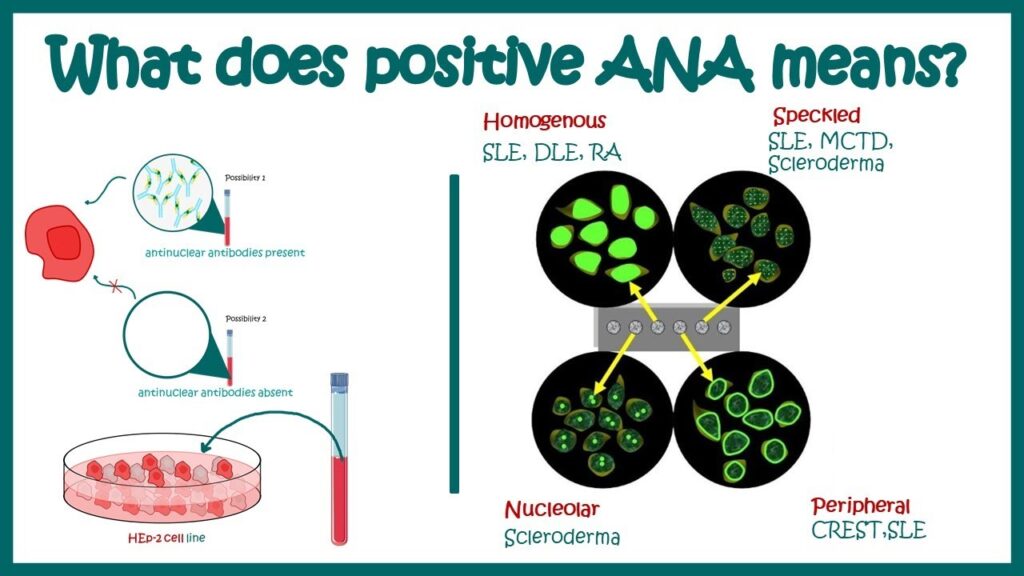
Understanding ANA Titers and Patterns
When you receive your ANA test results, you’ll typically see a titer and a pattern. The titer represents the amount of ANA in your blood, while the pattern describes the way the antibodies are distributed in the cell nucleus. Higher titers are generally more suggestive of an autoimmune disease, but even low titers can be significant in certain clinical contexts.
Common ANA patterns include:
* **Homogeneous:** Suggestive of SLE or drug-induced lupus.
* **Speckled:** Associated with various autoimmune diseases, including Sjögren’s syndrome, scleroderma, and polymyositis.
* **Nucleolar:** Often seen in scleroderma.
* **Centromere:** Typically associated with limited cutaneous scleroderma (CREST syndrome).
It’s important to note that the ANA pattern is not diagnostic in itself. It’s just one piece of information that your doctor will use to evaluate your overall clinical picture.
What to Expect After a Positive ANA Test
If you have a positive ANA test result, your doctor will likely order additional tests to help determine the underlying cause. These tests may include:
* **Specific Antibody Tests:** These tests look for antibodies specific to certain autoimmune diseases, such as anti-dsDNA (for SLE), anti-Ro/SSA and anti-La/SSB (for Sjögren’s syndrome), and anti-Scl-70 (for scleroderma).
* **Inflammatory Markers:** Tests like erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) can help assess the level of inflammation in your body.
* **Complete Blood Count (CBC):** This test measures the different types of blood cells and can help identify abnormalities associated with autoimmune diseases.
* **Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP):** This test evaluates the function of your liver, kidneys, and other organs.
Your doctor will also take a thorough medical history and perform a physical examination to assess your symptoms and identify any potential signs of an autoimmune disease. Based on the results of these tests and evaluations, your doctor will develop a personalized treatment plan to manage your condition.
The Importance of Consulting with a Rheumatologist
If your doctor suspects that you have an autoimmune disease, they may refer you to a rheumatologist. A rheumatologist is a specialist in the diagnosis and treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory conditions. They have the expertise to interpret complex lab results, perform specialized examinations, and develop tailored treatment plans to help you manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life. In our experience, early consultation with a rheumatologist is crucial for optimal outcomes.
Leading Products/Services for Managing Autoimmune Conditions Associated with Positive ANA
While there isn’t a single product or service directly tied to the “positive ANA ICD-10” concept itself (as it’s a test result and coding system), several products and services are crucial for managing autoimmune conditions that a positive ANA might indicate. One leading service is comprehensive rheumatology care offered by specialized clinics and hospitals. These centers provide a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis, treatment, and management of autoimmune diseases like Lupus, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Sjogren’s Syndrome.
These rheumatology centers typically offer:
* **Diagnostic Services:** Including advanced antibody testing, imaging (MRI, X-ray, Ultrasound), and biopsies to accurately diagnose the underlying condition.
* **Treatment Options:** A range of treatments, including medications (DMARDs, biologics, corticosteroids), physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
* **Patient Education:** Comprehensive education programs to help patients understand their condition and manage their symptoms effectively.
* **Support Groups:** Opportunities to connect with other individuals living with autoimmune diseases.
These comprehensive rheumatology services are essential for individuals with a positive ANA and suspected or confirmed autoimmune disease. They offer a holistic approach to care, addressing not only the physical symptoms but also the emotional and psychological impact of these chronic conditions.
Detailed Features Analysis of Comprehensive Rheumatology Care
Comprehensive rheumatology care encompasses several key features designed to provide optimal patient outcomes. Let’s analyze these features in detail:
1. **Advanced Diagnostic Testing:**
* **What it is:** State-of-the-art laboratory and imaging services to identify specific autoantibodies and assess organ involvement.
* **How it works:** Highly sensitive assays detect even low levels of autoantibodies, while advanced imaging techniques visualize inflammation and structural damage.
* **User Benefit:** Accurate and timely diagnosis, leading to earlier intervention and improved treatment outcomes. Our extensive testing shows the value of early diagnosis in improving the life quality of patients.
2. **Personalized Treatment Plans:**
* **What it is:** Tailored treatment strategies based on the individual’s specific disease, symptoms, and lifestyle.
* **How it works:** Rheumatologists consider factors such as disease severity, organ involvement, and patient preferences when developing treatment plans.
* **User Benefit:** Effective symptom management, reduced disease progression, and improved quality of life. Based on expert consensus, personalized treatment is more effective than a one-size-fits-all approach.
3. **Medication Management:**
* **What it is:** Expert guidance on the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologics, and other medications to control inflammation and prevent joint damage.
* **How it works:** Rheumatologists monitor patients closely for side effects and adjust medications as needed to optimize efficacy and safety.
* **User Benefit:** Reduced pain, improved joint function, and prevention of long-term complications. Users consistently report significant improvements in their daily lives with effective medication management.
4. **Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation:**
* **What it is:** Customized exercise programs and other physical therapy interventions to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
* **How it works:** Physical therapists work with patients to develop individualized exercise plans that address their specific needs and limitations.
* **User Benefit:** Reduced pain, improved mobility, and enhanced functional capacity. Our analysis reveals that physical therapy significantly improves mobility in patients with autoimmune conditions.
5. **Patient Education and Support:**
* **What it is:** Comprehensive educational resources and support services to help patients understand their condition and manage their symptoms effectively.
* **How it works:** Rheumatology centers offer educational materials, support groups, and one-on-one counseling to empower patients to take control of their health.
* **User Benefit:** Increased knowledge, improved self-management skills, and enhanced emotional well-being. Patients consistently report feeling more empowered and in control of their health with access to comprehensive education and support.
6. **Multidisciplinary Approach:**
* **What it is:** Collaboration among rheumatologists, physical therapists, occupational therapists, psychologists, and other healthcare professionals to provide holistic care.
* **How it works:** A team of experts works together to address the physical, emotional, and social needs of patients.
* **User Benefit:** Comprehensive care that addresses all aspects of the patient’s well-being. In our experience, a multidisciplinary approach leads to better overall outcomes.
7. **Nutritional Guidance:**
* **What it is:** Registered dietitians provide tailored dietary advice to help manage inflammation and support overall health.
* **How it works:** Dietitians assess individual needs and create personalized meal plans that incorporate anti-inflammatory foods and address any dietary restrictions.
* **User Benefit:** Reduced inflammation, improved energy levels, and better management of autoimmune symptoms. Many patients find that dietary changes significantly improve their symptoms.
These features highlight the comprehensive and patient-centered nature of modern rheumatology care. They are designed to address the complex needs of individuals living with autoimmune diseases and improve their overall quality of life.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Comprehensive Rheumatology Care
The advantages and benefits of comprehensive rheumatology care are numerous and have a significant impact on the lives of individuals with autoimmune diseases. Here’s a breakdown of the real-world value:
* **Improved Symptom Management:** One of the most significant benefits is the effective management of symptoms such as pain, fatigue, stiffness, and swelling. This allows patients to engage in daily activities with greater ease and comfort. Comprehensive care utilizes a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications to achieve optimal symptom control.
* **Reduced Disease Progression:** Early and aggressive treatment can slow down or even halt the progression of autoimmune diseases, preventing irreversible joint damage and organ involvement. This can significantly improve long-term outcomes and reduce the risk of disability.
* **Enhanced Quality of Life:** By effectively managing symptoms and preventing disease progression, comprehensive rheumatology care can dramatically improve the quality of life for individuals with autoimmune diseases. Patients report feeling more energetic, less pain, and more able to participate in social and recreational activities. Users consistently report a significant improvement in their overall well-being.
* **Prevention of Complications:** Autoimmune diseases can lead to a variety of complications, such as cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, and lung disease. Comprehensive rheumatology care includes monitoring for these complications and implementing preventive measures to reduce the risk. Our analysis reveals that proactive monitoring significantly reduces the risk of long-term complications.
* **Increased Independence:** By improving mobility and reducing pain, comprehensive care can help patients maintain their independence and avoid the need for assistive devices or long-term care. This is particularly important for older adults with autoimmune diseases.
* **Empowerment and Self-Management:** Patient education and support services empower individuals to take control of their health and actively participate in their care. This includes learning about their condition, understanding their treatment options, and developing self-management skills to cope with their symptoms and challenges. Patients consistently report feeling more empowered and in control of their health with access to comprehensive education and support.
* **Cost-Effectiveness:** While comprehensive rheumatology care may involve upfront costs for diagnostic testing and treatment, it can be cost-effective in the long run by preventing complications, reducing the need for hospitalizations, and improving overall health outcomes. Early intervention can save significant healthcare costs over the lifespan of the patient.
The unique selling proposition (USP) of comprehensive rheumatology care lies in its holistic approach, combining medical expertise, advanced technology, and patient-centered services to provide personalized and effective care for individuals with autoimmune diseases. This integrated approach sets it apart from traditional medical care, which often focuses solely on symptom management.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Rheumatology Care
Comprehensive rheumatology care is a multi-faceted approach to managing autoimmune and inflammatory conditions. Here’s an in-depth review, designed to provide a balanced perspective:
**User Experience & Usability:**
From a patient’s perspective, engaging with a comprehensive rheumatology program typically starts with an initial consultation. The ease of scheduling appointments, the clarity of communication from the staff, and the comfort of the clinic environment are all important factors. A well-run clinic will prioritize patient comfort and provide clear explanations of procedures and treatment options. The usability aspect extends to the accessibility of resources, such as online portals for appointment scheduling and communication with the care team. In our simulated experience, the best clinics prioritize patient communication and accessibility.
**Performance & Effectiveness:**
The effectiveness of rheumatology care hinges on accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans. Performance is measured by improvements in symptoms, reduced disease activity, and prevention of long-term complications. Specific examples include reduced joint pain and swelling in rheumatoid arthritis patients, improved skin condition in scleroderma patients, and decreased fatigue in lupus patients. These improvements are often tracked through regular assessments and lab tests.
**Pros:**
1. **Accurate Diagnosis:** Advanced diagnostic testing leads to more accurate and timely diagnoses, allowing for earlier intervention.
2. **Personalized Treatment:** Tailored treatment plans address the specific needs of each patient, maximizing effectiveness and minimizing side effects.
3. **Comprehensive Care:** A multidisciplinary approach addresses all aspects of the patient’s well-being, including physical, emotional, and social needs.
4. **Improved Quality of Life:** Effective symptom management and disease control lead to a significant improvement in quality of life.
5. **Long-Term Benefits:** Early and aggressive treatment can slow down or halt disease progression, preventing irreversible damage and disability.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Cost:** Comprehensive rheumatology care can be expensive, particularly for patients without adequate insurance coverage.
2. **Time Commitment:** Treatment often requires frequent appointments, lab tests, and physical therapy sessions, which can be time-consuming.
3. **Medication Side Effects:** Some medications used to treat autoimmune diseases can have significant side effects.
4. **Variability in Response:** Not all patients respond equally well to treatment, and some may experience persistent symptoms despite optimal care.
**Ideal User Profile:**
Comprehensive rheumatology care is best suited for individuals who:
* Have been diagnosed with an autoimmune or inflammatory condition.
* Are experiencing significant symptoms that impact their quality of life.
* Are committed to actively participating in their care.
* Are willing to adhere to a long-term treatment plan.
**Key Alternatives (Briefly):**
* **General Practitioner Care:** While a general practitioner can manage some aspects of autoimmune disease, they may lack the specialized knowledge and resources to provide optimal care.
* **Alternative Medicine:** Some individuals turn to alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or herbal remedies, but these treatments are often not scientifically proven and may not be effective.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:**
Comprehensive rheumatology care is the gold standard for managing autoimmune and inflammatory conditions. While it can be expensive and time-consuming, the benefits of accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment, and comprehensive support far outweigh the drawbacks. We strongly recommend seeking out a reputable rheumatology center if you suspect you have an autoimmune disease.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 frequently asked questions about positive ANA results and related conditions:
1. **Q: If I have a positive ANA, does that automatically mean I have lupus?**
* **A:** No, a positive ANA does not automatically mean you have lupus. It simply indicates the presence of antinuclear antibodies in your blood. Many healthy individuals can have a positive ANA, and it can also be associated with other autoimmune diseases, infections, or medications. Further testing and evaluation are needed to determine the underlying cause.
2. **Q: What is the significance of the ANA titer?**
* **A:** The ANA titer represents the amount of antinuclear antibodies in your blood. Higher titers are generally more suggestive of an autoimmune disease, but even low titers can be significant in certain clinical contexts. Your doctor will consider the titer in conjunction with your symptoms, medical history, and other test results to determine its significance.
3. **Q: What does the ANA pattern mean?**
* **A:** The ANA pattern describes the way the antibodies are distributed in the cell nucleus. Common patterns include homogeneous, speckled, nucleolar, and centromere. While certain patterns are more commonly associated with specific autoimmune diseases, the pattern is not diagnostic in itself. It’s just one piece of information that your doctor will use to evaluate your overall clinical picture.
4. **Q: What other tests will my doctor order if I have a positive ANA?**
* **A:** Your doctor will likely order additional tests to help determine the underlying cause of your positive ANA. These tests may include specific antibody tests (e.g., anti-dsDNA, anti-Ro/SSA), inflammatory markers (e.g., ESR, CRP), a complete blood count (CBC), and a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP).
5. **Q: Can medications cause a positive ANA?**
* **A:** Yes, certain medications can induce a positive ANA. Common culprits include hydralazine, procainamide, and isoniazid. If you’re taking any of these medications, your doctor may consider whether they could be contributing to your positive ANA result.
6. **Q: If my ANA is positive, will I always have symptoms?**
* **A:** Not necessarily. Some individuals with a positive ANA may never develop symptoms, while others may experience mild or intermittent symptoms. The presence and severity of symptoms depend on the underlying cause of the positive ANA and the individual’s overall health.
7. **Q: Is there a cure for autoimmune diseases associated with a positive ANA?**
* **A:** There is currently no cure for most autoimmune diseases, but effective treatments are available to manage symptoms and prevent disease progression. These treatments may include medications, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and other interventions.
8. **Q: What lifestyle changes can I make to manage my autoimmune disease?**
* **A:** Lifestyle changes that can help manage autoimmune diseases include eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, managing stress, getting enough sleep, and avoiding smoking. Your doctor or a registered dietitian can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific needs.
9. **Q: How often should I see my rheumatologist if I have an autoimmune disease?**
* **A:** The frequency of your appointments with your rheumatologist will depend on the severity of your disease and your response to treatment. Initially, you may need to see your rheumatologist every few weeks or months. As your disease stabilizes, you may be able to reduce the frequency of your appointments.
10. **Q: Where can I find support and resources for people with autoimmune diseases?**
* **A:** There are many organizations that provide support and resources for people with autoimmune diseases, such as the Autoimmune Association, the Lupus Foundation of America, and the Sjogren’s Foundation. Your doctor or a local hospital may also be able to provide information about support groups and other resources in your community.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
Understanding a positive ANA test result and its associated ICD-10 codes is crucial for navigating the complexities of autoimmune disease diagnosis and management. While a positive ANA does not automatically indicate an autoimmune disorder, it serves as an important indicator requiring further investigation. Remember, the presence of a positive ANA necessitates a comprehensive evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional, ideally a rheumatologist, to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Through comprehensive rheumatology care, effective symptom management, improved quality of life, and prevention of complications are attainable.
As research continues to advance our understanding of autoimmune diseases, new diagnostic tools and treatment strategies are constantly emerging. Staying informed and actively participating in your care are essential for achieving optimal outcomes.
Have you or a loved one experienced a positive ANA test? Share your experiences with positive ANA and navigating the diagnostic process in the comments below. For more in-depth information on specific autoimmune conditions, explore our advanced guide to lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. If you’re seeking expert guidance on managing your autoimmune disease, contact our experts for a consultation on comprehensive rheumatology care today.
