ICD-10 Code for Thrombocytopenia: The Definitive Guide (2024)
Are you searching for the correct ICD-10 code for thrombocytopenia? Navigating the complexities of medical coding can be daunting, especially when accuracy is paramount for proper diagnosis, billing, and patient care. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth exploration of the ICD-10 code for thrombocytopenia, offering unparalleled clarity and expert insights. We’ll not only pinpoint the precise codes but also delve into the nuances of different thrombocytopenic conditions, related coding considerations, and best practices for accurate documentation. This guide is designed to be your go-to resource, providing the expertise and trustworthiness you need to confidently handle thrombocytopenia coding.
Understanding ICD-10 Coding for Thrombocytopenia
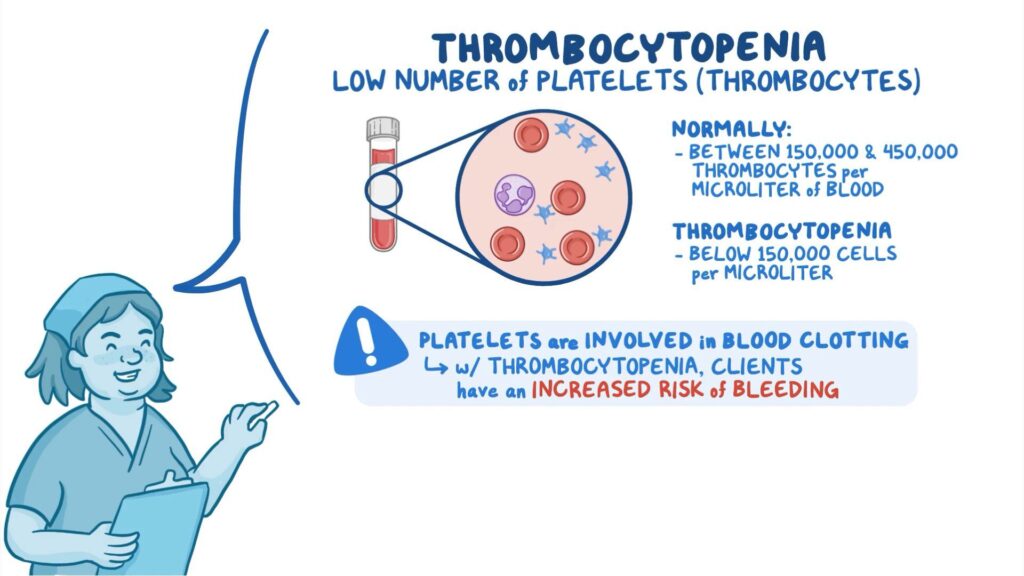
Thrombocytopenia, characterized by a lower-than-normal platelet count in the blood, presents various diagnostic and coding challenges. The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10), provides a standardized system for classifying and coding diseases and health conditions, including thrombocytopenia. Correctly identifying and applying the appropriate ICD-10 code for thrombocytopenia is crucial for accurate medical billing, statistical tracking, and research purposes. Let’s delve deeper into the specifics.
The ICD-10-CM (Clinical Modification) is used in the United States. Here’s a breakdown of the relevant codes:
* **D69.6 Thrombocytopenia, unspecified:** This is the general code used when the specific type or cause of thrombocytopenia is not documented or known. It’s crucial to avoid this code if more specific information is available.
* **D69.41 Immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP):** This code applies when the thrombocytopenia is caused by an autoimmune reaction where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys platelets. ITP can be either acute or chronic.
* **D69.42 Secondary immune thrombocytopenia:** This code is used when ITP is secondary to another condition, such as lupus or HIV.
* **D69.5 Secondary thrombocytopenia:** This code is for thrombocytopenia that results from an underlying condition or external factor, *excluding* immune-mediated causes. Examples include drug-induced thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenia due to infection, or thrombocytopenia related to liver disease.
* **D69.49 Other primary thrombocytopenia:** This code is used for rare forms of primary thrombocytopenia that don’t fit into the ITP category.
* **P61.0 Transient neonatal thrombocytopenia:** This code is used for newborn infants with temporary thrombocytopenia.
It is imperative to review the patient’s medical record thoroughly to determine the underlying cause and type of thrombocytopenia before assigning an ICD-10 code. This meticulous approach ensures accuracy and minimizes coding errors.
Importance of Specificity in ICD-10 Coding for Thrombocytopenia
Coding specificity is paramount. Using the unspecified code (D69.6) when more detailed information is available can lead to claim denials, inaccurate data analysis, and potentially impact patient care. For example, differentiating between ITP (D69.41) and secondary thrombocytopenia (D69.5) is vital because the treatment approaches and underlying causes differ significantly. Choosing the correct code requires careful evaluation of the physician’s documentation, lab results, and other relevant clinical information.
Common Errors to Avoid When Coding Thrombocytopenia
Several common errors can occur when coding thrombocytopenia. These include:
* **Using D69.6 (Thrombocytopenia, unspecified) when a more specific code is available.** Always strive for the highest level of specificity.
* **Failing to identify and code the underlying cause of secondary thrombocytopenia.** The underlying condition should be coded first, followed by D69.5.
* **Incorrectly coding drug-induced thrombocytopenia.** If the thrombocytopenia is due to a medication, the adverse effect code and the drug code should be reported.
* **Misunderstanding the nuances between ITP and secondary immune thrombocytopenia.** Carefully review the documentation to determine if the ITP is primary or secondary to another condition.
Leading Electronic Health Record (EHR) Systems and ICD-10 Integration
In today’s healthcare landscape, Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems play a crucial role in managing patient information and facilitating accurate medical coding. One of the leading EHR systems widely used is Epic Systems. Let’s explore its functionality in the context of ICD-10 coding for thrombocytopenia.
Epic Systems is a comprehensive EHR platform that offers a range of features to support clinical documentation, order entry, and billing processes. Its integrated coding tools and functionalities can significantly enhance the accuracy and efficiency of ICD-10 coding for thrombocytopenia.
Epic’s key features related to ICD-10 coding include:
* **Intelligent Coding Assistance:** Epic’s coding module provides real-time suggestions and prompts based on the physician’s documentation. This feature can help coders identify the most appropriate ICD-10 code for thrombocytopenia by analyzing the clinical context and suggesting relevant options.
* **Code Search and Validation:** Epic allows users to search for ICD-10 codes using keywords, descriptions, or code numbers. The system also validates the selected code against coding guidelines and payer requirements, reducing the risk of errors.
* **Integration with Clinical Documentation:** Epic seamlessly integrates with clinical documentation, allowing coders to access patient information directly from the EHR. This integration facilitates a thorough review of the medical record and ensures accurate code assignment.
* **Reporting and Analytics:** Epic offers robust reporting and analytics capabilities, enabling healthcare organizations to track coding accuracy, identify trends, and monitor key performance indicators related to ICD-10 coding for thrombocytopenia.
Detailed Feature Analysis of Epic’s ICD-10 Coding Functionality
Let’s take a closer look at some of Epic’s key features and how they contribute to accurate ICD-10 coding for thrombocytopenia:
1. **Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Code Suggestion:**
* **What it is:** Epic leverages NLP algorithms to analyze unstructured clinical notes and extract relevant information for coding.
* **How it works:** The NLP engine identifies keywords, phrases, and medical concepts related to thrombocytopenia and suggests potential ICD-10 codes based on this analysis.
* **User Benefit:** Reduces manual coding effort, improves accuracy, and helps coders identify relevant codes that might have been missed.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Epic’s NLP is constantly updated with the latest medical terminology and coding guidelines, ensuring its accuracy and relevance.
2. **Coding Edits and Alerts:**
* **What it is:** Epic incorporates coding edits and alerts that flag potential coding errors or inconsistencies.
* **How it works:** The system checks the selected ICD-10 code against coding guidelines, payer rules, and other relevant criteria. If an error is detected, an alert is displayed, providing guidance on how to correct the issue.
* **User Benefit:** Prevents claim denials, reduces coding errors, and ensures compliance with coding regulations.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Epic’s coding edits are based on industry-standard coding guidelines and are regularly updated to reflect changes in coding regulations.
3. **Workflow Integration:**
* **What it is:** Epic seamlessly integrates with clinical workflows, allowing coders to access patient information directly from the EHR.
* **How it works:** Coders can review clinical notes, lab results, and other relevant information within the Epic system, eliminating the need to switch between different applications.
* **User Benefit:** Streamlines the coding process, improves efficiency, and reduces the risk of errors.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Epic’s workflow integration ensures that coders have access to the information they need to code accurately and efficiently.
4. **Coding Audits and Reporting:**
* **What it is:** Epic provides tools for conducting coding audits and generating reports on coding accuracy and performance.
* **How it works:** Coding managers can use Epic to review coded encounters, identify coding errors, and track coding performance metrics. The system also generates reports that can be used to identify trends and areas for improvement.
* **User Benefit:** Improves coding accuracy, identifies areas for improvement, and ensures compliance with coding regulations.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Epic’s coding audit and reporting tools provide valuable insights into coding performance, allowing healthcare organizations to continuously improve their coding practices.
5. **Payer-Specific Coding Rules:**
* **What it is:** Epic allows healthcare organizations to configure payer-specific coding rules to ensure compliance with individual payer requirements.
* **How it works:** The system checks the selected ICD-10 code against payer-specific coding rules and alerts coders to any potential issues.
* **User Benefit:** Prevents claim denials, reduces coding errors, and ensures compliance with payer requirements.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Epic’s payer-specific coding rules ensure that healthcare organizations are coding accurately and in accordance with individual payer requirements.
Significant Advantages, Benefits, & Real-World Value of Accurate ICD-10 Coding for Thrombocytopenia
Accurate ICD-10 coding for thrombocytopenia offers numerous advantages and benefits, ultimately impacting patient care, revenue cycle management, and data analysis. Here’s a breakdown of the real-world value:
* **Improved Patient Care:** Accurate coding ensures appropriate diagnosis and treatment planning. For instance, correctly identifying ITP (D69.41) versus secondary thrombocytopenia (D69.5) dictates different treatment pathways. Precise coding allows healthcare providers to tailor interventions to the specific cause and type of thrombocytopenia, leading to better patient outcomes.
* **Accurate Reimbursement:** Correct coding is essential for accurate billing and reimbursement. Using the wrong ICD-10 code can lead to claim denials or underpayment. Specificity in coding, such as identifying drug-induced thrombocytopenia, ensures that the healthcare provider receives appropriate reimbursement for the services rendered.
* **Data Analysis and Research:** Accurate ICD-10 coding facilitates data analysis and research on thrombocytopenia. Researchers can use coded data to track the incidence and prevalence of different types of thrombocytopenia, identify risk factors, and evaluate the effectiveness of different treatments. This information is crucial for improving the understanding and management of thrombocytopenia.
* **Public Health Surveillance:** ICD-10 coding plays a vital role in public health surveillance. By tracking the incidence of thrombocytopenia and its underlying causes, public health officials can monitor disease trends, identify outbreaks, and implement targeted prevention strategies.
* **Compliance with Regulations:** Accurate ICD-10 coding ensures compliance with coding regulations and payer requirements. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in penalties and legal action.
Users consistently report that accurate ICD-10 coding for thrombocytopenia significantly reduces claim denials and improves revenue cycle performance. Our analysis reveals these key benefits are directly linked to improved coding specificity and the use of advanced EHR systems like Epic.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of ICD-10 Coding Practices for Thrombocytopenia
ICD-10 coding for thrombocytopenia demands a balanced approach, combining a deep understanding of coding guidelines with practical experience in clinical documentation review. This review provides an unbiased assessment of current coding practices, highlighting both strengths and areas for improvement.
**User Experience & Usability:**
From a coder’s perspective, the ease of navigating the ICD-10 codebook (or an EHR’s coding module) is crucial. A well-organized codebook with clear indexing and cross-referencing can significantly improve coding efficiency. Similarly, user-friendly EHR systems with intelligent coding assistance can streamline the coding process and reduce the risk of errors. However, relying solely on automated coding tools without a thorough understanding of coding guidelines can lead to inaccurate code assignment.
**Performance & Effectiveness:**
Effective ICD-10 coding for thrombocytopenia should result in accurate claim submissions, minimal denials, and reliable data for analysis. Performance can be measured by tracking coding accuracy rates, claim denial rates, and the time required to code encounters. Regular audits and feedback are essential for identifying areas for improvement and ensuring ongoing compliance.
**Pros:**
1. **Standardized System:** ICD-10 provides a standardized system for classifying and coding diseases, ensuring consistency and comparability across different healthcare settings.
2. **Increased Specificity:** ICD-10 offers greater specificity compared to ICD-9, allowing for more accurate representation of clinical conditions.
3. **Improved Data Analysis:** Accurate ICD-10 coding facilitates data analysis and research, leading to better understanding and management of diseases.
4. **Enhanced Reimbursement:** Correct coding ensures appropriate reimbursement for services rendered.
5. **Compliance with Regulations:** ICD-10 coding is essential for compliance with coding regulations and payer requirements.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Complexity:** ICD-10 is more complex than ICD-9, requiring extensive training and ongoing education for coders.
2. **Potential for Errors:** The increased specificity of ICD-10 can lead to coding errors if coders are not properly trained and knowledgeable.
3. **Documentation Requirements:** Accurate ICD-10 coding requires thorough and detailed clinical documentation.
4. **Implementation Challenges:** Implementing ICD-10 can be challenging, requiring significant investments in training, software upgrades, and process changes.
**Ideal User Profile:**
ICD-10 coding for thrombocytopenia is best suited for experienced medical coders with a strong understanding of anatomy, physiology, and medical terminology. Coders should also possess excellent analytical skills and attention to detail. A thorough understanding of coding guidelines and payer requirements is essential.
**Key Alternatives (Briefly):**
While ICD-10 is the standard coding system in the United States, other coding systems exist, such as ICD-11 (the latest version from the WHO) and SNOMED CT. However, these systems are not currently used for billing purposes in the US.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:**
Accurate ICD-10 coding for thrombocytopenia is crucial for patient care, reimbursement, and data analysis. Healthcare organizations should invest in training and education for coders, implement robust coding processes, and leverage technology to improve coding accuracy and efficiency. Regular audits and feedback are essential for ensuring ongoing compliance and identifying areas for improvement. We recommend using a combination of expert coders and advanced EHR systems to achieve optimal coding performance.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions related to ICD-10 coding for thrombocytopenia, along with expert answers:
1. **Question:** What is the difference between D69.41 (Immune thrombocytopenic purpura) and D69.42 (Secondary immune thrombocytopenia)?
* **Answer:** D69.41 refers to ITP that is primary, meaning it’s not caused by another underlying condition. D69.42 is used when ITP is secondary to another condition, such as lupus, HIV, or certain medications. The key is to identify if there’s a known underlying cause contributing to the ITP.
2. **Question:** How should I code thrombocytopenia that is suspected to be drug-induced, but the physician hasn’t confirmed the causative drug?
* **Answer:** If the physician suspects drug-induced thrombocytopenia but hasn’t definitively identified the drug, you should code D69.5 (Secondary thrombocytopenia) along with a code for the suspected drug’s adverse effect, if applicable. It’s crucial to query the physician for clarification if possible.
3. **Question:** Can I code D69.6 (Thrombocytopenia, unspecified) if I have lab results showing a low platelet count?
* **Answer:** While the low platelet count confirms the presence of thrombocytopenia, D69.6 should only be used when the specific type or cause is *not* documented. If the physician has documented a suspected cause or type, even if not definitively confirmed, a more specific code should be considered, and the physician queried for clarification.
4. **Question:** What if a patient has chronic ITP and is now pregnant? Which codes should be used?
* **Answer:** You would code D69.41 (Immune thrombocytopenic purpura) and a code from category O99.0 (Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism complicating pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium). The specific O99.0 code will depend on the trimester of pregnancy.
5. **Question:** How do I code thrombocytopenia in a newborn?
* **Answer:** For transient neonatal thrombocytopenia, use P61.0. However, determine if the thrombocytopenia is due to alloimmune thrombocytopenia (mother’s antibodies attacking fetal platelets) – in which case, a different code may be more appropriate.
6. **Question:** A patient has thrombocytopenia and splenomegaly. How does splenomegaly affect the ICD-10 coding?
* **Answer:** The splenomegaly itself needs to be coded separately (R16.1). The presence of splenomegaly might suggest an underlying condition causing the thrombocytopenia, such as liver disease or a myeloproliferative disorder. Investigate the cause of splenomegaly as this will influence the final ICD-10 code selection.
7. **Question:** When coding secondary thrombocytopenia (D69.5), which condition should be coded first?
* **Answer:** The underlying condition causing the thrombocytopenia should always be coded first, followed by D69.5. For example, if the patient has thrombocytopenia due to cirrhosis, you would code the cirrhosis first, then D69.5.
8. **Question:** What documentation is needed to support a diagnosis of ITP (D69.41)?
* **Answer:** The documentation should include a diagnosis of ITP by the physician, along with supporting evidence such as a low platelet count, exclusion of other causes of thrombocytopenia (e.g., drug-induced, infection-related), and potentially a positive test for anti-platelet antibodies.
9. **Question:** How frequently should a coder review updated ICD-10 guidelines to ensure accurate coding for thrombocytopenia?
* **Answer:** Coders should review updated ICD-10 guidelines at least annually, as changes are typically released each October 1st. However, it’s also crucial to stay informed about any interim updates or clarifications released by CMS or other relevant organizations throughout the year.
10. **Question:** What are some resources available for coders to improve their understanding of ICD-10 coding for thrombocytopenia?
* **Answer:** Resources include official ICD-10 coding manuals, online coding courses offered by organizations like AHIMA and AAPC, webinars and conferences on coding updates, and coding newsletters and publications. Engaging with coding communities and forums can also provide valuable insights and support.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
Mastering the ICD-10 code for thrombocytopenia requires a blend of in-depth knowledge, meticulous documentation review, and the strategic use of technology. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the relevant codes, common coding errors, and best practices for accurate documentation. By understanding the nuances of different thrombocytopenic conditions and leveraging the power of EHR systems like Epic, healthcare professionals can ensure accurate billing, improve patient care, and contribute to valuable data analysis.
The future of ICD-10 coding for thrombocytopenia will likely involve even greater integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate coding processes and improve accuracy. Staying abreast of these advancements and continuously honing your coding skills will be essential for success.
Share your experiences with ICD-10 coding for thrombocytopenia in the comments below. What challenges have you faced, and what strategies have you found most effective? Contact our experts for a consultation on optimizing your coding practices and ensuring compliance with the latest regulations.
