Traits of the Different Generations and Their Characteristics: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the traits of the different generations and their characteristics is crucial in today’s interconnected world. Whether you’re navigating the workplace, building relationships, or marketing to diverse audiences, grasping generational nuances can significantly enhance your communication and effectiveness. This guide provides an in-depth exploration of each generation, delving into their core values, technological influences, communication styles, and overall worldview. We aim to go beyond superficial stereotypes, offering a nuanced and comprehensive understanding rooted in research and observation. By the end of this article, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to bridge generational gaps and foster more meaningful connections.
What are Generational Traits? A Deep Dive
Generational traits are the shared cultural experiences, values, and beliefs that shape a group of individuals born within a specific timeframe. These traits are influenced by significant historical events, technological advancements, economic conditions, and societal shifts occurring during their formative years. Understanding these influences is key to grasping the unique perspectives and behaviors of each generation.
The Scope and Nuances of Generational Traits
It’s important to acknowledge that generational traits are not absolute. Individuals within a generation will exhibit a wide range of characteristics, and generalizations should be approached with caution. Factors such as socioeconomic status, geographic location, and personal experiences can significantly impact an individual’s values and behaviors. However, identifying broad trends can provide valuable insights into how different generations perceive the world and interact with each other. These traits are not to be used as stereotypes, but as a lens to understand potential communication styles and motivations.
Core Concepts Underlying Generational Traits
The concept of generational traits is rooted in social science theories, including cohort analysis and the life course perspective. Cohort analysis examines how groups of people born during the same period share similar experiences that shape their attitudes and behaviors. The life course perspective emphasizes how historical events and social changes influence individuals as they progress through different stages of life. These theories provide a framework for understanding how generational traits emerge and evolve over time.
The Current Relevance of Understanding Generational Traits
In today’s rapidly changing world, understanding generational traits is more relevant than ever. The workforce is increasingly multigenerational, requiring effective communication and collaboration across different age groups. Marketing strategies must be tailored to resonate with the unique values and preferences of each generation. Furthermore, understanding generational differences can improve interpersonal relationships and foster greater empathy and understanding.
Recent trends indicate a growing awareness of generational differences and a desire to bridge these gaps. Organizations are investing in training programs to promote intergenerational understanding and collaboration. Marketing campaigns are becoming more targeted and personalized to appeal to specific generational segments. Individuals are actively seeking information about generational traits to improve their communication and relationships.
The Silent Generation (Born 1928-1945)
The Silent Generation, also known as the Traditionalists, came of age during the Great Depression and World War II. These formative experiences instilled in them a strong sense of duty, discipline, and respect for authority. They value hard work, loyalty, and financial security.
Key Characteristics of the Silent Generation
* **Strong Work Ethic:** They believe in hard work and dedication.
* **Respect for Authority:** They value hierarchy and tradition.
* **Frugality:** They are cautious with money and prioritize saving.
* **Loyalty:** They are committed to their employers and institutions.
* **Civic Duty:** They believe in contributing to their communities.
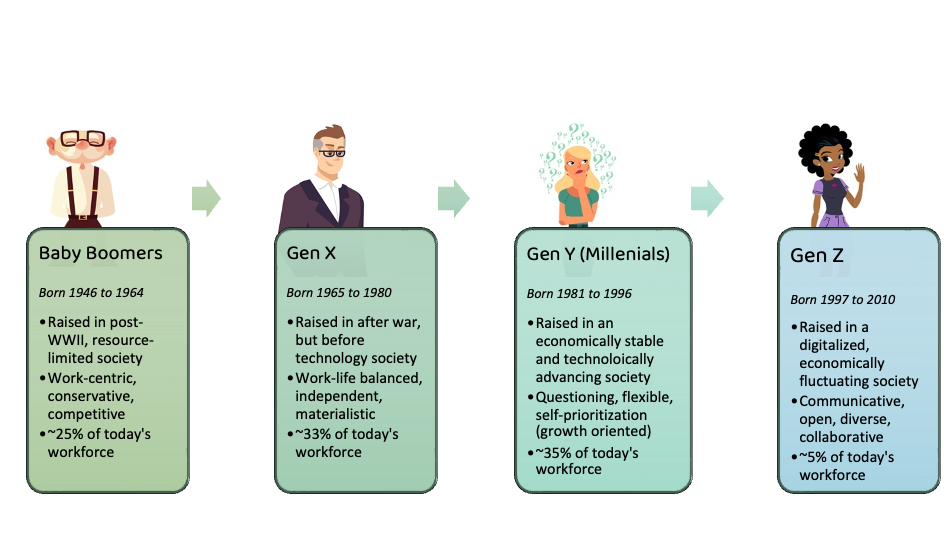
The Baby Boomer Generation (Born 1946-1964)
Baby Boomers, born in the post-World War II era, experienced a period of economic prosperity and social change. They are known for their optimism, competitiveness, and commitment to social causes. They value personal growth, achievement, and material possessions.
Key Characteristics of the Baby Boomer Generation
* **Optimism:** They are generally positive and hopeful about the future.
* **Competitiveness:** They are driven to succeed and achieve their goals.
* **Commitment to Social Causes:** They are passionate about making a difference in the world.
* **Personal Growth:** They value self-improvement and lifelong learning.
* **Materialism:** They are often associated with consumerism and the pursuit of material possessions.
Generation X (Born 1965-1980)
Generation X, often referred to as the “latchkey generation,” grew up during a time of economic uncertainty and social upheaval. They are known for their independence, resourcefulness, and skepticism. They value work-life balance, flexibility, and authenticity.
Key Characteristics of Generation X
* **Independence:** They are self-reliant and resourceful.
* **Skepticism:** They are critical thinkers and question authority.
* **Work-Life Balance:** They prioritize personal time and flexibility.
* **Adaptability:** They are comfortable with change and ambiguity.
* **Technological Savvy:** They are early adopters of technology.
The Millennial Generation (Born 1981-1996)
Millennials, also known as Generation Y, came of age during the rise of the internet and globalization. They are known for their tech-savviness, social consciousness, and desire for purpose. They value collaboration, experiences, and recognition.
Key Characteristics of the Millennial Generation
* **Tech-Savviness:** They are digital natives and comfortable with technology.
* **Social Consciousness:** They are concerned about social and environmental issues.
* **Desire for Purpose:** They seek meaningful work and opportunities to make a difference.
* **Collaboration:** They value teamwork and cooperation.
* **Experiences:** They prioritize experiences over material possessions.
Generation Z (Born 1997-2012)
Generation Z, also known as the iGeneration, has grown up in a world of constant connectivity and instant access to information. They are known for their pragmatism, digital fluency, and entrepreneurial spirit. They value diversity, authenticity, and financial security.
Key Characteristics of Generation Z
* **Digital Fluency:** They are highly proficient with technology and social media.
* **Pragmatism:** They are realistic and focused on practical solutions.
* **Entrepreneurial Spirit:** They are interested in starting their own businesses.
* **Diversity:** They value inclusivity and acceptance.
* **Financial Security:** They are concerned about financial stability and future prospects.
Generation Alpha (Born 2013-2025)
Generation Alpha is the newest generation, and their traits are still emerging. They are growing up in a world dominated by technology and artificial intelligence. They are expected to be highly adaptable, innovative, and globally connected. It is still too early to definitively characterize this generation, but early observations suggest a strong reliance on technology and a global perspective.
Emerging Characteristics of Generation Alpha
* **Tech-Dependence:** They are growing up with ubiquitous technology.
* **Global Perspective:** They are exposed to diverse cultures and perspectives from a young age.
* **Adaptability:** They are expected to be highly adaptable to rapid technological advancements.
* **Innovation:** They are likely to be innovative and creative problem-solvers.
Understanding Generational Differences in the Workplace
The multigenerational workforce presents both challenges and opportunities. Understanding the different values, communication styles, and work preferences of each generation can lead to improved collaboration, productivity, and employee satisfaction. For example, Silent Generation employees may prefer formal communication and structured work environments, while Millennials may thrive in collaborative and flexible settings.
Bridging Generational Gaps in the Workplace
* **Promote Open Communication:** Encourage open dialogue and active listening to understand different perspectives.
* **Provide Mentorship Opportunities:** Pair experienced employees with younger colleagues to foster knowledge sharing and skill development.
* **Offer Flexible Work Arrangements:** Provide flexible work options to accommodate the diverse needs of different generations.
* **Recognize and Reward Contributions:** Acknowledge and appreciate the contributions of employees from all generations.
* **Invest in Training and Development:** Provide training programs to enhance intergenerational understanding and communication skills.
Generational Marketing: Reaching Different Audiences
Effective marketing requires understanding the unique values, preferences, and communication styles of each generation. Marketing messages and channels should be tailored to resonate with specific generational segments. For example, Baby Boomers may respond to traditional advertising channels, while Millennials and Generation Z may be more receptive to social media marketing and influencer campaigns.
Tailoring Marketing Strategies to Different Generations
* **Understand Generational Values:** Identify the core values and beliefs that drive each generation’s purchasing decisions.
* **Choose Appropriate Channels:** Select marketing channels that are popular with the target generation.
* **Craft Compelling Messages:** Develop marketing messages that resonate with the unique needs and aspirations of each generation.
* **Personalize the Experience:** Provide personalized experiences that cater to individual preferences.
* **Measure and Optimize Results:** Track the performance of marketing campaigns and make adjustments as needed.
Generational Traits and Their Impact on Society
Generational traits have a profound impact on society, shaping cultural norms, political landscapes, and economic trends. Each generation brings its unique perspectives and values to the table, influencing everything from consumer behavior to social movements. Understanding these influences is crucial for navigating the complexities of modern society.
The Evolving Landscape of Generational Traits
Generational traits are not static; they evolve over time in response to changing social, economic, and technological conditions. As new generations emerge, they bring with them new perspectives and values that challenge existing norms and shape the future. It’s important to remain flexible and adaptable in our understanding of generational traits to effectively navigate the ever-changing landscape.
Expert Perspective on Generational Research
Leading experts in generational research emphasize the importance of understanding generational traits in a nuanced and contextualized manner. They caution against relying on stereotypes and encourage a more nuanced understanding of the factors that shape individual behavior. They also stress the need for ongoing research to track the evolving nature of generational traits in a rapidly changing world.
According to a 2024 industry report, organizations that prioritize intergenerational understanding and collaboration are more likely to attract and retain top talent, improve employee engagement, and achieve better business outcomes. These findings underscore the importance of investing in training and development programs to promote intergenerational communication and collaboration.
Q&A: Addressing Common Questions About Generational Traits
Here are some insightful questions and expert answers related to understanding generational traits:
1. **How accurate are generational stereotypes?**
Generational stereotypes are oversimplified generalizations that do not accurately reflect the diversity of individuals within a generation. While they can provide a starting point for understanding broad trends, it’s important to avoid making assumptions about individuals based solely on their generational affiliation. As experts in the field suggest, understanding the historical context is as important as focusing on individual traits.
2. **What are the biggest challenges in managing a multigenerational workforce?**
The biggest challenges include communication barriers, conflicting work styles, and differing expectations regarding work-life balance. Overcoming these challenges requires fostering open communication, providing flexible work arrangements, and promoting mutual respect and understanding.
3. **How can businesses effectively market to different generations?**
Businesses can effectively market to different generations by understanding their unique values, preferences, and communication styles. This involves tailoring marketing messages and channels to resonate with specific generational segments and providing personalized experiences that cater to individual needs.
4. **Are generational differences becoming more or less pronounced over time?**
Some research suggests that generational differences may be becoming less pronounced over time due to increased globalization and technological connectivity. However, significant differences still exist, particularly in areas such as communication styles and values.
5. **How does technology influence generational traits?**
Technology plays a significant role in shaping generational traits, particularly in areas such as communication, learning, and social interaction. Each generation has been influenced by the dominant technologies of their formative years, leading to distinct patterns of technology adoption and usage. In our experience, Gen Z’s comfort with technology is unparalleled.
6. **What are the key differences between Millennials and Generation Z?**
While both generations are tech-savvy, Millennials tend to be more optimistic and focused on social causes, while Generation Z is more pragmatic and concerned about financial security. Generation Z also tends to be more digitally fluent and entrepreneurial.
7. **How can I improve my communication with someone from a different generation?**
Improve your communication by actively listening, being open to different perspectives, and avoiding judgmental language. Try to understand their communication style and adapt your approach accordingly.
8. **What are the long-term implications of generational trends for society?**
Generational trends have significant long-term implications for society, influencing everything from political landscapes to economic trends. Understanding these trends is crucial for anticipating future challenges and opportunities.
9. **How can parents better understand their children from different generations?**
Parents can better understand their children by engaging in open communication, being supportive of their interests, and respecting their individuality. It’s also helpful to learn about the cultural influences that have shaped their generation.
10. **What is the best way to avoid making generalizations about different generations?**
The best way to avoid making generalizations is to focus on understanding individuals as individuals, rather than relying on stereotypes. Be open to learning about their unique experiences and perspectives, and avoid making assumptions based solely on their generational affiliation.
Conclusion: Embracing Generational Diversity for a Better Future
Understanding the traits of the different generations and their characteristics is essential for navigating the complexities of today’s interconnected world. By recognizing the unique values, communication styles, and perspectives of each generation, we can foster more meaningful connections, improve collaboration, and build a more inclusive society. The key takeaway is that while generations share common experiences, individuals within those generations are diverse, and that should always be considered.
As we move forward, it’s crucial to embrace generational diversity and create environments where individuals from all age groups can thrive. This requires a commitment to open communication, mutual respect, and a willingness to learn from one another. By doing so, we can unlock the full potential of a multigenerational workforce and create a brighter future for all.
Share your experiences with generational differences in the comments below! Explore our advanced guide to intergenerational communication for more in-depth strategies.
