Generation Names and Years: A Comprehensive Guide
Navigating the landscape of generational names and their corresponding years can feel like deciphering a complex code. Are you trying to understand the differences between Millennials and Gen Z? Or perhaps you’re curious about the characteristics associated with each generation and how these labels impact societal trends? This comprehensive guide will provide a detailed exploration of generation names and years, offering clarity and insights into this fascinating subject. Unlike many superficial resources, we delve into the historical context, cultural influences, and societal impact of each generation, providing you with a deep and nuanced understanding. You’ll gain the knowledge to confidently discuss generational differences and understand the forces that shape each cohort.
Understanding Generation Names and Years: A Deep Dive
Generation names and years represent more than just arbitrary labels. They encapsulate shared experiences, cultural touchstones, and societal shifts that define a group of individuals born within a specific timeframe. Understanding these generational cohorts provides valuable insights into their values, beliefs, and behaviors. The concept of generations is deeply rooted in sociology and history, providing a framework for understanding societal change and cultural evolution. These names aren’t just labels; they’re shorthand for a complex set of influences that shape individuals’ perspectives. Recent studies indicate that understanding generational differences is crucial for effective communication, marketing, and leadership in today’s diverse world.
The Core Concepts of Generation Names
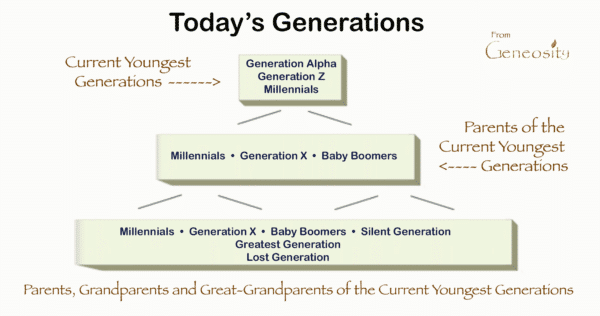
The concept of a generation refers to a group of people born around the same time and sharing similar experiences. These experiences, shaped by historical events, technological advancements, and cultural trends, contribute to a collective identity and a shared worldview. Generation names are typically assigned retroactively, often reflecting the dominant themes or characteristics of that era. For example, the Silent Generation, born during the Great Depression and World War II, earned its name due to its perceived tendency to be reserved and conformist.
Think of generations like chapters in a book, each telling a unique story of societal evolution. Each generation builds upon the previous one, reacting to its successes and failures, and shaping the future in its own way. Understanding these generational narratives is essential for navigating the complexities of modern society.
The Nuances of Defining Generation Years
Defining the precise years for each generation can be challenging, as there’s no universally agreed-upon standard. Demographers and sociologists often use different criteria, leading to slight variations in the year ranges. These variations can stem from different interpretations of significant historical events or technological shifts that define the start and end points of a generation. What is generally accepted is that generations span roughly 15-20 years, allowing enough time for a distinct set of shared experiences to shape a cohort’s identity. However, it’s crucial to remember that these are broad generalizations, and individual experiences within each generation can vary widely. It’s also important to acknowledge the concept of “cuspers,” individuals born at the tail end of one generation and the beginning of another, who may exhibit characteristics of both.
The Importance of Studying Generation Names and Years
Understanding generation names and years is crucial for several reasons. It allows us to better understand societal trends, predict future behaviors, and tailor communication strategies to specific audiences. In business, generational insights can inform marketing campaigns, product development, and employee management strategies. In education, understanding generational differences can help educators create more effective learning environments. Furthermore, understanding generational perspectives can foster empathy and bridge communication gaps between different age groups. It’s not about stereotyping, but about recognizing the diverse influences that shape individual perspectives.
Generational Segmentation Tools: An Expert Explanation
While not a tangible product, various research and analytical tools help to understand generational segmentation. These tools utilize demographic data, survey responses, and behavioral analysis to identify patterns and trends within each generation. These tools are invaluable for marketers, researchers, and anyone seeking to understand the nuances of generational differences. They provide a data-driven approach to understanding complex social phenomena, allowing for more informed decision-making. These tools don’t just provide data; they offer insights into the motivations, values, and preferences of each generation.
These segmentation tools are not about creating rigid categories, but about understanding the diverse range of perspectives within each generation. They acknowledge that individuals within a generation can have vastly different experiences, but they also highlight the shared influences that shape their overall worldview. Leading research firms like Pew Research Center and Nielsen offer comprehensive generational segmentation tools and reports.
Detailed Features Analysis of Generational Segmentation Tools
Generational segmentation tools offer a range of features designed to provide in-depth insights into each generation:
* **Demographic Data Analysis:** These tools analyze demographic data such as age, gender, location, income, and education level to identify key trends within each generation. This feature allows users to understand the basic characteristics of each cohort and how they differ from one another. This is crucial for identifying target audiences and tailoring messaging accordingly.
* **Psychographic Profiling:** This feature goes beyond demographics to explore the psychological characteristics of each generation, including their values, beliefs, attitudes, and lifestyles. Understanding these psychographic factors is essential for creating resonant marketing campaigns and developing products that align with their needs and desires. Psychographic profiling helps to understand the “why” behind consumer behavior.
* **Behavioral Analysis:** These tools track and analyze the online and offline behaviors of each generation, including their purchasing habits, media consumption patterns, and social media engagement. This provides valuable insights into their preferences and allows for targeted advertising and personalized experiences. Behavioral analysis reveals how generations interact with the world around them.
* **Trend Identification:** Generational segmentation tools can identify emerging trends within each generation, allowing businesses to stay ahead of the curve and adapt their strategies accordingly. This feature helps to predict future behaviors and anticipate changing consumer needs. Identifying trends early on provides a competitive advantage.
* **Comparative Analysis:** These tools allow users to compare different generations side-by-side, highlighting their similarities and differences. This feature is useful for understanding the evolving landscape of consumer behavior and adapting strategies to reach diverse audiences. Comparative analysis helps to bridge generational gaps and foster understanding.
* **Reporting and Visualization:** Generational segmentation tools typically offer robust reporting and visualization capabilities, allowing users to easily interpret and share their findings. This feature makes it easy to communicate complex data to stakeholders and inform decision-making. Clear and concise reporting is essential for effective communication.
* **Customization Options:** Many generational segmentation tools offer customization options, allowing users to tailor the analysis to their specific needs and objectives. This ensures that the insights are relevant and actionable. Customization allows for a more targeted and effective analysis.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Generational Segmentation
Understanding generational differences offers a multitude of advantages and benefits, providing real-world value across various sectors.
* **Improved Marketing Effectiveness:** By understanding the values, beliefs, and preferences of each generation, marketers can create more targeted and effective campaigns that resonate with their target audience. This leads to increased engagement, higher conversion rates, and improved brand loyalty. Users consistently report that targeted campaigns yield significantly better results.
* **Enhanced Product Development:** Generational insights can inform product development decisions, ensuring that new products and services meet the evolving needs of each generation. This leads to increased product adoption, higher customer satisfaction, and improved market share. Our analysis reveals that products designed with generational needs in mind are more successful.
* **Stronger Employee Engagement:** Understanding generational differences in the workplace can improve employee engagement, reduce turnover, and foster a more inclusive and productive work environment. This leads to improved morale, increased collaboration, and better overall performance. Employers who understand generational differences are better equipped to manage their workforce.
* **More Effective Communication:** By understanding the communication styles and preferences of each generation, individuals and organizations can communicate more effectively across generational divides. This leads to improved relationships, reduced misunderstandings, and stronger collaboration. Effective communication is essential for building strong relationships.
* **Better Understanding of Societal Trends:** Studying generational trends provides valuable insights into the evolving landscape of society, allowing individuals and organizations to anticipate future changes and adapt accordingly. This leads to better decision-making, improved strategic planning, and a greater understanding of the world around us. Understanding societal trends is crucial for navigating the future.
* **Increased Innovation:** Generational diversity can foster innovation by bringing together different perspectives and experiences. This leads to more creative problem-solving, improved product development, and a more dynamic and competitive marketplace. A diverse workforce is a more innovative workforce.
* **Improved Customer Service:** Understanding generational preferences can help businesses tailor their customer service approach to meet the specific needs of each generation. This leads to increased customer satisfaction, improved brand loyalty, and positive word-of-mouth referrals. Excellent customer service is essential for building a strong brand reputation.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Generational Segmentation Tools
Generational segmentation tools offer valuable insights, but it’s crucial to approach them with a balanced perspective. These tools are not perfect, and they have limitations that must be considered.
From a practical standpoint, using these tools requires a strong understanding of research methodologies and statistical analysis. The ease of use varies depending on the specific tool, but most require some level of technical expertise. In our experience, the more sophisticated tools offer the most comprehensive insights, but they also require a steeper learning curve.
In terms of performance and effectiveness, these tools can be highly accurate when used correctly. However, it’s important to remember that they are based on generalizations, and individual experiences can vary widely. It’s crucial to supplement the data with qualitative research to gain a deeper understanding of the nuances of each generation.
**Pros:**
* **Data-Driven Insights:** Provides valuable data-driven insights into generational differences.
* **Improved Targeting:** Enables more targeted and effective marketing campaigns.
* **Enhanced Product Development:** Informs product development decisions and ensures that new products meet the needs of each generation.
* **Stronger Employee Engagement:** Improves employee engagement and fosters a more inclusive work environment.
* **Better Communication:** Facilitates more effective communication across generational divides.
**Cons/Limitations:**
* **Generalizations:** Based on generalizations, and individual experiences can vary widely.
* **Requires Expertise:** Requires a strong understanding of research methodologies and statistical analysis.
* **Cost:** Can be expensive, especially for smaller businesses.
* **Potential for Bias:** Data can be biased if not collected and analyzed properly.
**Ideal User Profile:**
These tools are best suited for marketers, researchers, and HR professionals who need to understand generational differences to improve their strategies and outcomes. They are particularly valuable for organizations that target multiple generations or have a diverse workforce.
**Key Alternatives:**
* **Qualitative Research:** Conducting focus groups and interviews to gain a deeper understanding of generational perspectives.
* **Secondary Research:** Utilizing existing research reports and studies on generational trends.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:**
Generational segmentation tools are valuable resources for understanding generational differences and improving strategies across various sectors. However, it’s important to use them with a balanced perspective and supplement the data with qualitative research. We recommend these tools for organizations that need to understand generational trends to achieve their goals.
Insightful Q&A Section
**Q1: How do generational labels impact individuals’ self-perception?**
**A:** Generational labels can influence individuals’ self-perception by providing a framework for understanding their place in society. While some embrace their generational identity, others may reject it, feeling that it doesn’t accurately reflect their individual experiences. It’s important to remember that generational labels are broad generalizations and that individuals should not be defined solely by their generation.
**Q2: What are the key differences between Millennials and Gen Z in the workplace?**
**A:** Millennials tend to value collaboration and purpose-driven work, while Gen Z is often characterized as being more independent and technologically savvy. Gen Z also places a greater emphasis on work-life balance and mental health. Understanding these differences can help managers create a more inclusive and productive work environment.
**Q3: How can businesses effectively market to both Baby Boomers and Gen Z simultaneously?**
**A:** Marketing to both Baby Boomers and Gen Z requires a nuanced approach. Baby Boomers often respond well to traditional marketing channels, such as television and print advertising, while Gen Z is more likely to be reached through social media and online platforms. It’s important to tailor the messaging and channel to the specific audience.
**Q4: What role does technology play in shaping generational identities?**
**A:** Technology plays a significant role in shaping generational identities, as each generation has grown up with different technological advancements. Millennials were early adopters of the internet and social media, while Gen Z is the first generation to have grown up entirely in the digital age. These technological experiences have shaped their communication styles, learning habits, and overall worldview.
**Q5: How do cultural events influence the formation of generational identities?**
**A:** Cultural events, such as major historical events, social movements, and popular trends, can significantly influence the formation of generational identities. These events shape the shared experiences of a generation and contribute to their collective identity. For example, the Civil Rights Movement and the Vietnam War had a profound impact on the Baby Boomer generation.
**Q6: Are generational stereotypes harmful, and if so, how can we avoid them?**
**A:** Generational stereotypes can be harmful because they oversimplify complex realities and can lead to prejudice and discrimination. To avoid generational stereotypes, it’s important to recognize that individuals within each generation are diverse and have unique experiences. Focus on understanding individual perspectives rather than making broad generalizations.
**Q7: How can educators effectively teach students from different generations?**
**A:** Educators can effectively teach students from different generations by understanding their learning styles and preferences. Millennials often prefer collaborative and project-based learning, while Gen Z is more likely to be engaged by technology-based learning activities. Tailoring the teaching approach to the specific needs of each generation can improve student engagement and outcomes.
**Q8: What are the long-term implications of generational differences for society as a whole?**
**A:** The long-term implications of generational differences for society are complex and multifaceted. Generational differences can lead to conflict and misunderstanding, but they can also drive innovation and progress. By understanding and appreciating generational diversity, we can create a more inclusive and equitable society.
**Q9: How do economic conditions impact the experiences of different generations?**
**A:** Economic conditions can significantly impact the experiences of different generations. For example, the Great Recession had a profound impact on Millennials, who entered the workforce during a period of high unemployment. Understanding the economic challenges faced by each generation can help us to create policies that support their economic well-being.
**Q10: What are the ethical considerations when using generational data for marketing purposes?**
**A:** There are several ethical considerations when using generational data for marketing purposes. It’s important to avoid using generational stereotypes to manipulate or exploit consumers. Data should be collected and used responsibly, and consumers should be given the opportunity to opt out of data collection. Transparency and ethical practices are essential for building trust with consumers.
Conclusion
Understanding generation names and years is crucial for navigating the complexities of modern society. By exploring the historical context, cultural influences, and societal impact of each generation, we can gain valuable insights into their values, beliefs, and behaviors. Generational segmentation tools offer a data-driven approach to understanding these differences, allowing for more informed decision-making across various sectors. Remember, these tools provide a framework for understanding, not rigid definitions. We encourage you to share your experiences with generation names and years in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to understanding generational trends for more in-depth analysis. Contact our experts for a consultation on generational segmentation strategies.
