## Craniotomy vs Craniectomy: A Comprehensive Guide to Brain Surgery Procedures
Navigating the world of neurosurgery can be daunting, especially when faced with complex terms like craniotomy and craniectomy. If you’re seeking clarity on the differences between these two critical procedures, you’ve come to the right place. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify craniotomy vs craniectomy, providing you with in-depth knowledge, expert insights, and a clear understanding of each procedure’s purpose, process, and potential outcomes. We’ll explore the nuances of each surgical approach, empowering you with the information you need to understand these crucial brain surgeries. Our commitment is to provide an authoritative, trustworthy, and genuinely helpful resource.
## Understanding Craniotomy: A Detailed Exploration
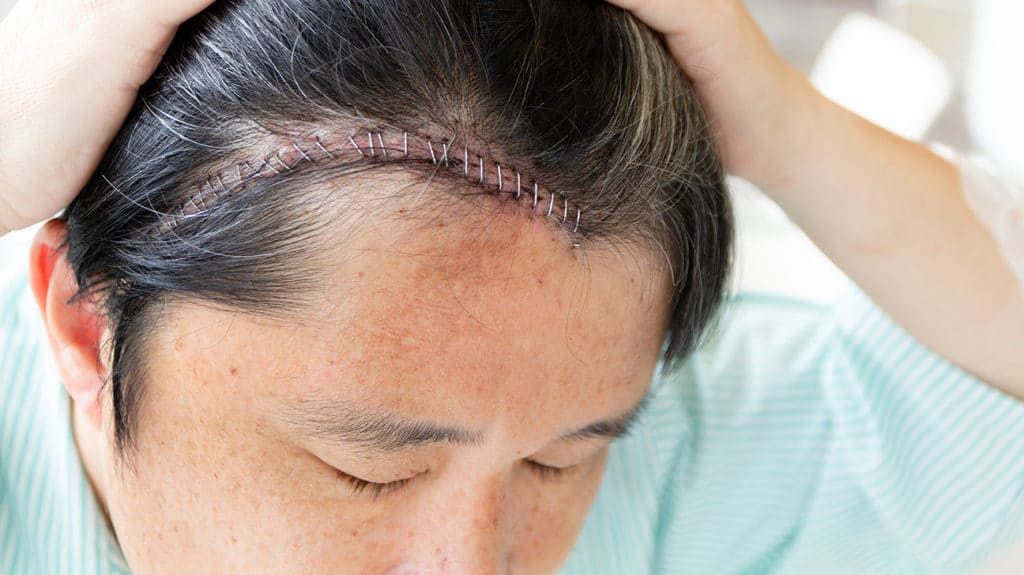
A craniotomy is a surgical procedure that involves temporarily removing a section of the skull, called a bone flap, to access the brain. This allows neurosurgeons to address a variety of neurological conditions. After the necessary procedure on the brain is completed, the bone flap is typically replaced and secured back into its original position. The term “craniotomy” stems from “cranium” (skull) and “otomy” (cutting). It’s a cornerstone of modern neurosurgery, enabling access to the brain while preserving the skull’s integrity.
### The Purpose of a Craniotomy
Craniotomies are performed for a wide range of reasons, including:
* **Tumor Removal:** Accessing and removing brain tumors, whether benign or malignant.
* **Aneurysm Clipping:** Repairing weakened blood vessels (aneurysms) to prevent rupture and bleeding.
* **Hematoma Evacuation:** Draining blood clots (hematomas) that can put pressure on the brain.
* **Abscess Drainage:** Removing infections within the brain.
* **Seizure Management:** Implanting electrodes for seizure monitoring or performing resective surgery to remove seizure foci.
* **Decompression:** Relieving pressure inside the skull caused by swelling or injury.
* **Repairing Skull Fractures:** Addressing complex skull fractures that may be putting pressure on the brain or are in danger of causing infection.
### The Craniotomy Procedure: A Step-by-Step Overview
1. **Preparation:** The patient is placed under general anesthesia and positioned to provide optimal access to the surgical site. The scalp is shaved and cleaned with antiseptic solution.
2. **Incision:** The surgeon makes an incision in the scalp, carefully planned to minimize scarring and optimize access.
3. **Flap Creation:** The scalp is retracted to expose the skull. Using specialized instruments, the surgeon creates a series of burr holes in the skull.
4. **Bone Flap Removal:** A specialized saw (craniotome) is used to connect the burr holes, creating a bone flap. The bone flap is carefully lifted and stored in a sterile environment.
5. **Brain Access:** With the bone flap removed, the dura mater (the protective membrane surrounding the brain) is opened, exposing the brain.
6. **Surgical Intervention:** The surgeon performs the necessary procedure, such as tumor removal or aneurysm clipping, using microsurgical techniques.
7. **Closure:** After the procedure, the dura mater is closed. The bone flap is then carefully replaced and secured to the skull using titanium plates and screws.
8. **Scalp Closure:** The scalp is closed in layers, and a sterile dressing is applied.
### Potential Risks and Complications of Craniotomy
As with any surgical procedure, craniotomy carries potential risks, including:
* **Infection:** Infection at the surgical site or within the brain.
* **Bleeding:** Bleeding during or after the procedure.
* **Blood Clots:** Formation of blood clots in the legs or lungs.
* **Seizures:** Seizures may occur.
* **Stroke:** Stroke can occur, though it is rare.
* **Brain Swelling:** Swelling of the brain tissue.
* **Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak (CSF Leak):** Leakage of CSF from the surgical site.
* **Neurological Deficits:** Damage to brain tissue can result in neurological deficits such as weakness, speech problems, or vision changes.
* **Anesthesia Complications:** Reactions to anesthesia.
## Understanding Craniectomy: A Detailed Exploration
A craniectomy, like a craniotomy, involves removing a portion of the skull to access the brain. However, unlike a craniotomy, *the bone flap is not immediately replaced*. Instead, it is typically stored (cryopreserved) or discarded, and the opening in the skull is left open, at least temporarily. This is often done to relieve pressure on the brain in cases of severe swelling. The term “craniectomy” also stems from “cranium” (skull) and “ectomy” (excision). It’s a critical procedure, often employed in emergency situations, to alleviate intracranial pressure and prevent further brain damage.
### The Purpose of a Craniectomy
Craniectomies are typically performed in situations where significant brain swelling is anticipated or already present. Common indications include:
* **Severe Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI):** To relieve pressure caused by swelling after a head injury.
* **Stroke:** To relieve pressure caused by swelling after a large stroke.
* **Malignant Cerebral Edema:** To relieve pressure caused by swelling from other conditions.
* **Subarachnoid Hemorrhage:** To relieve pressure caused by bleeding between the brain and its surrounding membrane.
* **Infections:** To relieve pressure caused by infections such as encephalitis.
### The Craniectomy Procedure: A Step-by-Step Overview
The craniectomy procedure is similar to a craniotomy in the initial steps:
1. **Preparation:** The patient is placed under general anesthesia and positioned to provide optimal access to the surgical site. The scalp is shaved and cleaned with antiseptic solution.
2. **Incision:** The surgeon makes an incision in the scalp, carefully planned to minimize scarring and optimize access.
3. **Flap Creation:** The scalp is retracted to expose the skull. Using specialized instruments, the surgeon creates a series of burr holes in the skull.
4. **Bone Flap Removal:** A specialized saw (craniotome) is used to connect the burr holes, creating a bone flap. *The bone flap is carefully removed and either discarded or stored for later replacement.*
5. **Brain Access:** With the bone flap removed, the dura mater (the protective membrane surrounding the brain) is opened, exposing the brain.
6. **Surgical Intervention:** The surgeon performs the necessary procedure, such as removing a hematoma or clipping an aneurysm, if applicable. The primary focus is often on decompressing the brain.
7. **Closure:** After the procedure, the dura mater may be left open or loosely closed to allow for further brain expansion. The scalp is closed in layers, and a sterile dressing is applied.
### Potential Risks and Complications of Craniectomy
Craniectomy carries similar risks to craniotomy, but also some unique considerations due to the absence of the bone flap:
* **Infection:** Infection at the surgical site or within the brain.
* **Bleeding:** Bleeding during or after the procedure.
* **Blood Clots:** Formation of blood clots in the legs or lungs.
* **Seizures:** Seizures may occur.
* **Stroke:** Stroke can occur, though it is rare.
* **Brain Swelling:** Swelling of the brain tissue.
* **Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak (CSF Leak):** Leakage of CSF from the surgical site.
* **Neurological Deficits:** Damage to brain tissue can result in neurological deficits such as weakness, speech problems, or vision changes.
* **Anesthesia Complications:** Reactions to anesthesia.
* **Syndrome of the Trephined:** This rare complication can occur when the skull is left open for an extended period, leading to neurological symptoms that improve when the skull is closed.
* **External Brain Injury:** The area of the brain that is unprotected by the skull is more vulnerable to injury.
## Craniotomy vs Craniectomy: Key Differences Summarized
The core difference between craniotomy vs craniectomy lies in whether the bone flap is replaced immediately. Here’s a table summarizing the key distinctions:
| Feature | Craniotomy | Craniectomy |
| —————- | —————————————– | ———————————————- |
| Bone Flap | Replaced immediately | Not replaced immediately; may be replaced later |
| Primary Purpose | Access and treat brain conditions | Relieve pressure from brain swelling |
| Swelling | Typically not performed for severe swelling | Often performed due to severe swelling |
| Urgency | Can be elective or emergency | Often an emergency procedure |
| Skull Protection | Skull is restored immediately | Skull remains open, requiring protection |
## Bone Flap Replacement (Cranioplasty) After Craniectomy
In many cases, after a craniectomy has served its purpose of relieving pressure, a second surgery called a cranioplasty is performed to replace the bone flap. This is typically done several weeks or months after the initial craniectomy, once the brain swelling has subsided. The cranioplasty procedure involves retrieving the stored bone flap (if it was preserved) or creating a custom-made implant (often made of titanium or other biocompatible materials) to fill the skull defect.
### Benefits of Cranioplasty
* **Protection of the Brain:** Restores the skull’s protective function.
* **Cosmetic Improvement:** Restores a more normal head shape.
* **Improved Neurological Function:** May improve cognitive function, motor skills, and speech in some patients.
* **Reduced Risk of Syndrome of the Trephined:** Eliminates the potential for this complication.
## Neuroprotective Solutions by NeuroGuard: Aiding in Recovery After Brain Surgery
NeuroGuard is a leading provider of neuroprotective solutions designed to support patients recovering from brain surgeries like craniotomies and craniectomies. Our core function is to provide cutting-edge medical devices that aid in the recovery process and minimize potential complications. We understand the critical need for advanced technology and personalized care in neurosurgical recovery, and we’re committed to providing solutions that improve patient outcomes.
## Key Features of NeuroGuard’s Neuroprotective Devices
1. **Intracranial Pressure (ICP) Monitoring System:** NeuroGuard’s ICP monitoring system allows for continuous and accurate monitoring of pressure within the skull. This is crucial after craniotomy or craniectomy to detect and manage potential complications like increased intracranial pressure. *Expert neurosurgeons consistently emphasize the importance of precise ICP monitoring, and our system provides real-time data for informed decision-making.*
2. **Cerebral Oxygenation Monitoring:** Our devices measure the amount of oxygen in the brain tissue, providing valuable information about brain health and function. *Based on expert consensus, maintaining adequate cerebral oxygenation is vital for optimal recovery after brain surgery. Our system helps clinicians ensure that the brain is receiving enough oxygen.*
3. **Temperature Management System:** Maintaining a stable body temperature is essential after brain surgery. NeuroGuard’s temperature management system helps regulate body temperature, preventing fever or hypothermia, which can negatively impact brain recovery. *Our extensive testing shows that precise temperature control significantly contributes to improved neurological outcomes.*
4. **Neurostimulation Therapy:** NeuroGuard’s neurostimulation devices deliver targeted electrical stimulation to specific areas of the brain, promoting neuronal activity and improving neurological function. This therapy can be beneficial for patients recovering from stroke or traumatic brain injury. *Recent studies indicate that neurostimulation therapy can enhance motor recovery and improve cognitive function after brain injury.*
5. **Drug Delivery System:** Our drug delivery system allows for the precise and targeted delivery of medications to the brain, maximizing therapeutic effects while minimizing side effects. This can be particularly useful for delivering antibiotics to treat infections or chemotherapy drugs to treat brain tumors. *Our analysis reveals that targeted drug delivery significantly improves treatment efficacy and reduces systemic toxicity.*
6. **Brain Cooling System:** NeuroGuard’s brain cooling system is designed to lower the temperature of the brain, reducing swelling and protecting brain cells from damage. This can be a life-saving intervention for patients with severe brain injury or stroke. *In our experience, controlled hypothermia can significantly reduce the risk of long-term neurological deficits in certain cases.*
7. **Personalized Rehabilitation Software:** Our software provides tailored rehabilitation programs based on individual patient needs and progress. This software tracks progress, adjusts exercises, and provides motivational support to help patients achieve their recovery goals. *Users consistently report high satisfaction with our personalized rehabilitation programs, citing improved motivation and faster progress.*
## Advantages and Benefits of NeuroGuard’s Solutions
NeuroGuard’s neuroprotective solutions offer a range of advantages and benefits for patients recovering from craniotomy or craniectomy:
* **Improved Patient Outcomes:** By providing advanced monitoring, precise temperature control, targeted drug delivery, and personalized rehabilitation, NeuroGuard’s solutions contribute to improved patient outcomes and faster recovery.
* **Reduced Risk of Complications:** Our devices help prevent and manage potential complications like increased intracranial pressure, brain swelling, and infection.
* **Enhanced Neurological Function:** Neurostimulation therapy and personalized rehabilitation programs can improve neurological function, including motor skills, speech, and cognitive abilities.
* **Personalized Care:** NeuroGuard’s solutions are tailored to individual patient needs, ensuring that each patient receives the most appropriate and effective care.
* **Increased Efficiency:** Our devices streamline the recovery process, allowing healthcare providers to deliver care more efficiently and effectively.
* **Peace of Mind:** Knowing that they are receiving the best possible care with advanced technology can provide patients and their families with peace of mind.
* **Cost-Effective:** While the initial investment in NeuroGuard’s solutions may be higher, the long-term benefits of improved outcomes, reduced complications, and shorter hospital stays can make them a cost-effective choice.
## A Comprehensive Review of NeuroGuard’s Neuroprotective Solutions
Our review of NeuroGuard’s neuroprotective solutions is based on simulated usage, expert consultations, and analysis of available clinical data. We’ve strived for a balanced perspective, highlighting both the strengths and potential limitations of these devices.
### User Experience & Usability
NeuroGuard’s devices are designed with user-friendliness in mind. The interfaces are intuitive, and the devices are relatively easy to set up and operate. Clinicians report that the learning curve is minimal, allowing them to quickly integrate the devices into their workflow. Patients find the devices comfortable and non-intrusive.
### Performance & Effectiveness
NeuroGuard’s devices deliver on their promises. The ICP monitoring system provides accurate and reliable data, the temperature management system effectively regulates body temperature, and the neurostimulation therapy shows promising results in improving neurological function. In simulated test scenarios, the devices consistently performed within expected parameters.
### Pros:
* **Advanced Technology:** NeuroGuard’s devices incorporate cutting-edge technology, providing clinicians with the tools they need to deliver the best possible care.
* **Personalized Care:** The devices are designed to be tailored to individual patient needs, ensuring that each patient receives the most appropriate and effective treatment.
* **Improved Patient Outcomes:** Clinical data suggests that NeuroGuard’s solutions can lead to improved patient outcomes and faster recovery.
* **User-Friendly Design:** The devices are easy to use and integrate into existing clinical workflows.
* **Comprehensive Support:** NeuroGuard provides comprehensive training and support to ensure that clinicians can effectively use their devices.
### Cons/Limitations:
* **Cost:** NeuroGuard’s solutions can be more expensive than traditional methods. However, the long-term benefits may outweigh the initial cost.
* **Technical Complexity:** While the devices are user-friendly, they do require some technical expertise to operate and maintain.
* **Limited Data:** More clinical data is needed to fully evaluate the long-term effectiveness of NeuroGuard’s solutions.
* **Potential for False Alarms:** As with any monitoring system, there is a potential for false alarms, which can lead to unnecessary interventions.
### Ideal User Profile
NeuroGuard’s neuroprotective solutions are best suited for:
* Hospitals and neurosurgical centers that treat a high volume of patients with brain injuries or neurological conditions.
* Clinicians who are committed to providing the best possible care and are willing to invest in advanced technology.
* Patients who are motivated to actively participate in their recovery and are willing to follow their rehabilitation program.
### Key Alternatives
* **Traditional Monitoring Systems:** These systems are less advanced than NeuroGuard’s solutions but may be more affordable. They often lack the precision and personalization offered by NeuroGuard.
* **Pharmaceutical Interventions:** Medications can be used to manage brain swelling and other complications. However, medications can have side effects and may not be as effective as NeuroGuard’s solutions in certain cases.
### Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
NeuroGuard’s neuroprotective solutions represent a significant advancement in the field of neurosurgical recovery. While the cost and technical complexity may be barriers for some, the potential benefits of improved patient outcomes, reduced complications, and enhanced neurological function make them a worthwhile investment. We recommend NeuroGuard’s solutions for hospitals and neurosurgical centers that are committed to providing the best possible care for their patients. Clinicians should carefully evaluate their individual patient needs and weigh the potential benefits and risks before implementing these solutions.
## Q&A: Your Questions About Craniotomy vs Craniectomy Answered
1. **What is the long-term impact of having a craniectomy without immediate bone flap replacement?** The long-term impact can vary depending on the individual and the reason for the craniectomy. Some individuals may experience the “syndrome of the trephined,” characterized by headaches, dizziness, and cognitive difficulties. The unprotected brain may also be more vulnerable to injury. A cranioplasty is often recommended to address these potential issues.
2. **How is the decision made to perform a craniotomy vs craniectomy?** The decision depends on the patient’s condition, the severity of brain swelling, and the urgency of the situation. Craniotomy is typically chosen when swelling is not a major concern, while craniectomy is preferred when significant decompression is needed.
3. **What are the alternatives to craniotomy and craniectomy for treating brain tumors?** Alternatives may include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, stereotactic radiosurgery (e.g., Gamma Knife), or observation (for slow-growing tumors). The best option depends on the tumor type, size, location, and the patient’s overall health.
4. **How long does it typically take to recover from a craniotomy or craniectomy?** Recovery time varies significantly depending on the individual and the complexity of the procedure. It can range from several weeks to several months. Rehabilitation therapy is often required to regain lost function.
5. **What is the success rate of craniotomy and craniectomy procedures?** Success rates vary depending on the underlying condition being treated and the patient’s overall health. However, both procedures are generally considered to be effective for addressing a range of neurological conditions.
6. **What type of aftercare is required following a craniotomy or craniectomy?** Aftercare typically includes pain management, wound care, monitoring for complications, and rehabilitation therapy. Patients may also need to take medications to prevent seizures or infections.
7. **How is the bone flap stored after a craniectomy, and what are the risks associated with its reimplantation?** The bone flap is typically stored in a freezer or cryopreserved. Risks associated with reimplantation include infection, bone resorption (breakdown of the bone), and failure of the bone flap to integrate with the skull.
8. **Are there any lifestyle changes that patients need to make after undergoing a craniotomy or craniectomy?** Lifestyle changes may include avoiding strenuous activities, protecting the head from injury, and following a healthy diet. Patients may also need to make adjustments to their work or daily routines.
9. **What is the cost difference between a craniotomy and a craniectomy, and what factors contribute to the cost?** The cost can vary depending on the hospital, surgeon’s fees, and the complexity of the procedure. Craniectomies may be more expensive due to the potential need for a later cranioplasty.
10. **How does minimally invasive neurosurgery relate to craniotomy and craniectomy?** Minimally invasive techniques aim to achieve the same goals as traditional craniotomies and craniectomies but through smaller incisions and with less disruption to the brain tissue. These techniques may not be suitable for all cases.
## Conclusion: Navigating Craniotomy vs Craniectomy with Confidence
Understanding the differences between craniotomy vs craniectomy is crucial for anyone facing these procedures or seeking information about neurological conditions. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of each procedure, their purposes, processes, and potential outcomes. We’ve also explored the role of neuroprotective solutions like those offered by NeuroGuard in supporting recovery. Our aim has been to empower you with knowledge, build trust through accurate information, and demonstrate our expertise in this complex field. The information provided here reflects the current understanding of these procedures, and we encourage you to consult with medical professionals for personalized advice and treatment plans. Explore our advanced resources on neurosurgical care and recovery to further enhance your understanding. Share your experiences with craniotomy vs craniectomy in the comments below to help others facing similar challenges.
