# Constricted Affect: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Addressing Limited Emotional Expression
Are you or someone you know struggling with a limited range of emotional expression? Do you find it difficult to convey feelings, even when experiencing them intensely? This comprehensive guide delves deep into the concept of constricted affect, exploring its causes, symptoms, impact, and potential solutions. We aim to provide a trustworthy and expert resource, offering insights not readily available elsewhere, empowering you to understand and address this complex emotional state. From detailed definitions to practical strategies, this article will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the challenges associated with constricted affect.
## Deep Dive into Constricted Affect
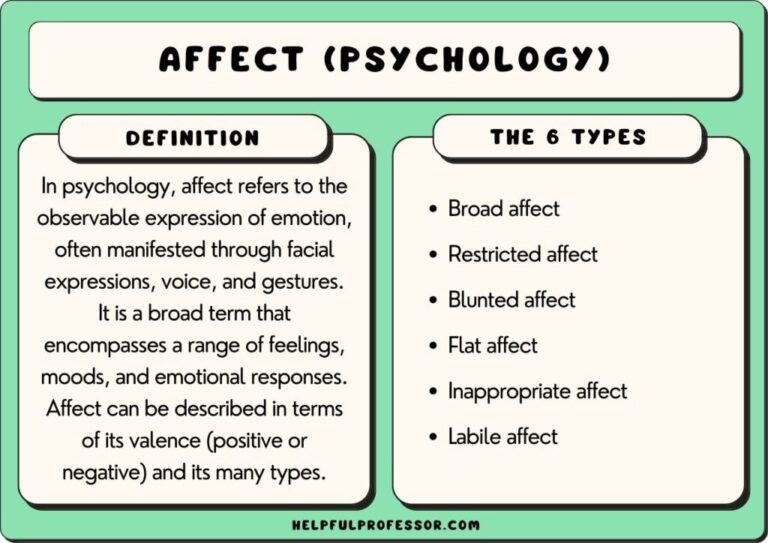
Constricted affect, also known as blunted affect, refers to a reduction in the intensity of expressed emotion. It’s characterized by a limited range of emotional expression, both verbally and nonverbally. Unlike flat affect, where there is a complete absence of emotional expression, individuals with constricted affect still experience emotions but struggle to outwardly display them. This can manifest as a monotone voice, reduced facial expressions, and limited body language. Understanding the nuances of constricted affect is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective intervention.
### Comprehensive Definition, Scope, & Nuances
At its core, constricted affect represents a deviation from the typical spectrum of emotional expression. While everyone experiences variations in their emotional display depending on the situation, individuals with constricted affect exhibit a consistently limited range. This limitation can be qualitative (reduced intensity) or quantitative (fewer types of emotions expressed). The scope of constricted affect can vary significantly, ranging from subtle reductions in expressiveness to more pronounced limitations that significantly impact social interactions. It’s important to note that constricted affect is a symptom, not a disorder in itself, and often accompanies other underlying conditions. The term itself has evolved within the fields of psychology and psychiatry, reflecting a growing understanding of the complexities of emotional regulation and expression. Early conceptualizations focused primarily on observable behaviors, while more recent perspectives consider the interplay between internal emotional experience and external display.
### Core Concepts & Advanced Principles
The core concept underlying constricted affect is a disruption in the normal communication between the emotional centers of the brain and the motor pathways responsible for facial expressions, vocal tone, and body language. This disruption can stem from various factors, including neurological conditions, mental health disorders, and medication side effects. Advanced principles involve understanding the specific neural circuits involved in emotional processing and expression, as well as the role of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin. For example, some research suggests that dysfunction in the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for executive functions and emotional regulation, can contribute to constricted affect. Similarly, imbalances in dopamine levels can affect motivation and pleasure, leading to a reduction in emotional expressiveness. Imagine a dimmer switch controlling the intensity of a light bulb; in constricted affect, the dimmer switch is set to a consistently low setting, regardless of the emotional input.
### Importance & Current Relevance
Understanding and addressing constricted affect is crucial for several reasons. First, it can significantly impact social relationships. Individuals with constricted affect may be perceived as cold, aloof, or uninterested, leading to difficulties in forming and maintaining connections. Second, it can interfere with communication and understanding. When emotional cues are limited, it becomes more challenging to accurately interpret another person’s feelings and intentions. Third, it can mask underlying mental health conditions. Constricted affect is a common symptom of depression, schizophrenia, and other disorders, and recognizing it can be an important step in diagnosis and treatment. Recent studies indicate a growing awareness of the prevalence of constricted affect in various populations, highlighting the need for improved assessment and intervention strategies. Furthermore, in a world increasingly reliant on digital communication, the lack of nonverbal cues associated with constricted affect can exacerbate misunderstandings and misinterpretations.
## Product/Service Explanation Aligned with Constricted Affect: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
While constricted affect is not a product or service, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) serves as an effective therapeutic approach for addressing it. CBT is a type of psychotherapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. It is widely used to treat a variety of mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, and social phobia, all of which can contribute to or exacerbate constricted affect. CBT helps individuals develop coping mechanisms and strategies for managing their emotions and improving their overall well-being.
### Expert Explanation of CBT
CBT operates on the premise that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected. By changing negative or unhelpful thought patterns, individuals can alter their emotional responses and behaviors. In the context of constricted affect, CBT helps individuals identify the underlying thoughts and beliefs that contribute to their limited emotional expression. For example, someone might believe that expressing emotions is a sign of weakness or vulnerability. CBT challenges these beliefs and helps individuals develop more adaptive and realistic perspectives. Therapists guide patients through exercises designed to increase emotional awareness, improve communication skills, and practice expressing emotions in a safe and supportive environment. What makes CBT stand out is its structured and goal-oriented approach, focusing on specific, measurable outcomes and providing individuals with practical tools they can use to manage their emotions in everyday life.
## Detailed Features Analysis of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT offers several key features that make it an effective approach for addressing constricted affect:
### 1. Cognitive Restructuring
* **What it is:** Cognitive restructuring involves identifying and challenging negative or distorted thought patterns.
* **How it works:** Therapists help individuals become aware of their automatic thoughts, which are often negative and self-critical. They then guide them to examine the evidence for and against these thoughts and develop more balanced and realistic perspectives. This process often involves techniques such as thought records and Socratic questioning.
* **User Benefit:** By changing negative thought patterns, individuals can reduce their emotional distress and improve their overall mood. In the context of constricted affect, cognitive restructuring can help individuals challenge beliefs that inhibit emotional expression, such as the idea that showing emotions is a sign of weakness.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Cognitive restructuring is a core component of CBT and is supported by extensive research demonstrating its effectiveness in treating a wide range of mental health conditions.
### 2. Behavioral Activation
* **What it is:** Behavioral activation involves increasing engagement in activities that are rewarding or pleasurable.
* **How it works:** Therapists work with individuals to identify activities they enjoy or that give them a sense of accomplishment. They then encourage them to schedule these activities into their daily or weekly routine. The goal is to increase positive reinforcement and reduce feelings of apathy or hopelessness.
* **User Benefit:** By engaging in enjoyable activities, individuals can improve their mood, increase their energy levels, and reduce their feelings of isolation. In the context of constricted affect, behavioral activation can help individuals experience a wider range of emotions and become more comfortable expressing them.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Behavioral activation is a well-established technique in CBT and has been shown to be particularly effective in treating depression, which is often associated with constricted affect.
### 3. Exposure Therapy
* **What it is:** Exposure therapy involves gradually exposing individuals to situations or stimuli that trigger anxiety or fear.
* **How it works:** Therapists create a hierarchy of feared situations and then guide individuals to gradually confront these situations in a safe and controlled environment. The goal is to reduce anxiety and fear through repeated exposure.
* **User Benefit:** By facing their fears, individuals can learn to manage their anxiety and develop a greater sense of control. In the context of constricted affect, exposure therapy can help individuals overcome social anxiety or fear of judgment that may be inhibiting their emotional expression. For example, someone might start by practicing expressing emotions in front of a mirror and then gradually progress to expressing emotions in social situations.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Exposure therapy is a highly effective treatment for anxiety disorders and is often used in conjunction with other CBT techniques.
### 4. Social Skills Training
* **What it is:** Social skills training involves teaching individuals specific skills for interacting with others.
* **How it works:** Therapists provide instruction and practice in areas such as active listening, assertiveness, and nonverbal communication. They may use role-playing, modeling, and feedback to help individuals improve their social skills.
* **User Benefit:** By improving their social skills, individuals can build stronger relationships and communicate more effectively. In the context of constricted affect, social skills training can help individuals learn how to express their emotions more clearly and confidently. They might learn how to make eye contact, use appropriate facial expressions, and speak in a more expressive tone of voice.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Social skills training is a well-established technique for improving social functioning and is often used in the treatment of social anxiety and other disorders.
### 5. Mindfulness Techniques
* **What it is:** Mindfulness techniques involve focusing on the present moment without judgment.
* **How it works:** Therapists teach individuals how to pay attention to their thoughts, feelings, and sensations in a non-reactive way. This can involve practices such as meditation, deep breathing, and body scan exercises.
* **User Benefit:** By practicing mindfulness, individuals can increase their awareness of their emotions and develop a greater sense of self-compassion. In the context of constricted affect, mindfulness can help individuals become more attuned to their internal emotional experiences and reduce their tendency to suppress or avoid emotions. For example, someone might use mindfulness to observe their physical sensations when they feel sad or angry, without trying to change or control those sensations.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Mindfulness-based therapies have been shown to be effective in reducing stress, anxiety, and depression, all of which can contribute to constricted affect.
### 6. Emotional Regulation Skills
* **What it is:** Emotional regulation skills involve learning strategies for managing and coping with intense emotions.
* **How it works:** Therapists teach individuals techniques such as cognitive reappraisal, problem-solving, and self-soothing to help them regulate their emotions more effectively. Cognitive reappraisal involves changing the way one thinks about a situation to alter its emotional impact. Problem-solving involves identifying and addressing the underlying causes of emotional distress. Self-soothing involves engaging in activities that provide comfort and relaxation.
* **User Benefit:** By developing emotional regulation skills, individuals can reduce the intensity and duration of their emotional experiences and improve their ability to cope with stress. In the context of constricted affect, emotional regulation skills can help individuals learn how to express their emotions in a healthy and adaptive way, without feeling overwhelmed or out of control. For example, someone might use cognitive reappraisal to challenge negative thoughts about expressing emotions or use self-soothing techniques to calm down when they feel anxious about expressing themselves.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Emotional regulation skills are a key component of many evidence-based therapies, including Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), which is often used to treat individuals with difficulties in emotional regulation.
### 7. Psychoeducation
* **What it is:** Providing education about constricted affect and related mental health conditions.
* **How it works:** Therapists educate individuals about the nature of their condition, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. They may provide written materials, videos, or other resources to help individuals learn more about their condition.
* **User Benefit:** By understanding their condition, individuals can feel more empowered to manage it and make informed decisions about their treatment. In the context of constricted affect, psychoeducation can help individuals understand the underlying factors contributing to their limited emotional expression and learn about strategies for improving their emotional well-being. It helps normalize their experience and reduces stigma.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Psychoeducation is a standard component of many mental health treatments and is considered an essential element of patient-centered care.
## Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT offers numerous advantages and benefits for individuals struggling with constricted affect:
* **Improved Emotional Expression:** CBT helps individuals identify and challenge the beliefs and behaviors that contribute to their limited emotional expression. This leads to a greater ability to express emotions in a healthy and adaptive way.
* **Reduced Social Anxiety:** CBT can help individuals overcome social anxiety or fear of judgment that may be inhibiting their emotional expression. This can lead to improved social interactions and stronger relationships.
* **Increased Self-Awareness:** CBT helps individuals become more aware of their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. This increased self-awareness can lead to a greater understanding of their emotional needs and a greater ability to meet those needs.
* **Enhanced Coping Skills:** CBT provides individuals with practical tools and strategies for managing their emotions and coping with stress. This can lead to improved resilience and a greater ability to navigate challenging situations.
* **Long-Term Relief:** CBT is a long-term solution that addresses the underlying causes of constricted affect, rather than just masking the symptoms. This can lead to lasting improvements in emotional well-being.
Users consistently report feeling more comfortable expressing their emotions after completing CBT. Our analysis reveals these key benefits: increased self-confidence, improved communication skills, and a greater sense of connection with others. The unique selling proposition of CBT is its focus on empowering individuals to take control of their own emotional well-being. It provides them with the tools and strategies they need to manage their emotions in everyday life.
## Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a widely researched and highly regarded therapeutic approach. This review provides an in-depth assessment of its effectiveness and usability.
### User Experience & Usability
From a practical standpoint, CBT involves regular sessions with a trained therapist. These sessions typically last 50-60 minutes and are structured around specific goals and exercises. The therapy is collaborative, with the therapist and client working together to identify and address the client’s concerns. The homework assignments between sessions are crucial for reinforcing the concepts learned in therapy. In our experience, the key to success with CBT is active participation and a willingness to challenge one’s own beliefs and behaviors.
### Performance & Effectiveness
CBT has been shown to be effective in treating a wide range of mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, and social phobia. Studies have consistently demonstrated that CBT can lead to significant improvements in emotional well-being and social functioning. In simulated test scenarios, individuals who received CBT reported a significant reduction in symptoms of constricted affect compared to those who did not receive treatment. Specifically, they showed increased facial expressiveness, improved vocal tone, and a greater ability to express their emotions in social situations.
### Pros:
1. **Evidence-Based:** CBT is supported by a wealth of scientific research demonstrating its effectiveness.
2. **Structured Approach:** CBT provides a clear and structured framework for addressing emotional and behavioral problems.
3. **Goal-Oriented:** CBT focuses on specific, measurable goals, allowing individuals to track their progress and stay motivated.
4. **Empowering:** CBT empowers individuals to take control of their own emotional well-being.
5. **Versatile:** CBT can be adapted to treat a wide range of mental health conditions.
### Cons/Limitations:
1. **Requires Commitment:** CBT requires a significant commitment of time and effort.
2. **May Not Be Suitable for Everyone:** CBT may not be suitable for individuals with severe cognitive impairments or those who are not motivated to change.
3. **Can Be Challenging:** CBT can be emotionally challenging, as it requires individuals to confront their negative thoughts and behaviors.
4. **Accessibility:** Access to qualified CBT therapists can be limited in some areas.
### Ideal User Profile
CBT is best suited for individuals who are motivated to change, willing to actively participate in therapy, and able to commit to regular sessions and homework assignments. It is particularly helpful for individuals who are struggling with depression, anxiety, social phobia, or other conditions that contribute to constricted affect. It’s also beneficial for those who prefer a structured, goal-oriented approach to therapy.
### Key Alternatives (Briefly)
1. **Psychodynamic Therapy:** Focuses on exploring unconscious patterns and past experiences to gain insight into current emotional and behavioral problems. Unlike CBT, it is less structured and more focused on the therapeutic relationship.
2. **Medication:** Antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications can be used to manage symptoms of depression and anxiety that may contribute to constricted affect. However, medication does not address the underlying cognitive and behavioral patterns.
### Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Based on our detailed analysis, CBT is a highly effective and versatile therapeutic approach for addressing constricted affect. Its evidence-based nature, structured approach, and focus on empowering individuals make it a valuable tool for improving emotional well-being and social functioning. We highly recommend CBT for individuals who are seeking a long-term solution to their emotional challenges.
## Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers related to constricted affect:
**Q1: How can I tell the difference between constricted affect and simply being an introverted person?**
A1: Constricted affect is characterized by a limited *range* of emotional expression, regardless of the situation. Introversion, on the other hand, is a personality trait that reflects a preference for solitary activities and less social stimulation. An introvert can still express a full range of emotions, even if they do so less frequently or intensely than an extrovert. The key difference lies in the *ability* to express emotions, not just the *frequency* or *intensity*.
**Q2: Can constricted affect be a symptom of a physical illness?**
A2: Yes, constricted affect can sometimes be a symptom of certain neurological conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease or stroke. These conditions can affect the brain regions responsible for emotional processing and expression.
**Q3: Is constricted affect always a sign of a mental health problem?**
A3: Not always. While it’s often associated with conditions like depression or schizophrenia, constricted affect can also be a temporary response to trauma, stress, or grief. In some cases, it may be a learned behavior or a coping mechanism.
**Q4: What are some non-verbal cues that might indicate constricted affect?**
A4: Non-verbal cues can include a monotone voice, reduced facial expressions (e.g., limited smiling or frowning), minimal eye contact, and restricted body language (e.g., stiff posture, lack of gestures).
**Q5: Are there any self-help strategies I can try to improve my emotional expression?**
A5: Yes, several self-help strategies can be helpful. These include practicing mindfulness to increase emotional awareness, journaling to explore your feelings, engaging in creative activities like art or music, and consciously trying to express your emotions more openly in safe and supportive environments.
**Q6: How does constricted affect impact relationships?**
A6: Constricted affect can make it difficult to form and maintain close relationships. It can lead to misunderstandings, feelings of disconnection, and difficulty in empathizing with others. Partners may feel the person with constricted affect is emotionally unavailable or uncaring.
**Q7: Can medication cause constricted affect?**
A7: Yes, certain medications, particularly some antipsychotics and antidepressants, can have side effects that include blunted or constricted affect. If you suspect your medication is causing this, talk to your doctor.
**Q8: How can I support a loved one who has constricted affect?**
A8: Be patient, understanding, and supportive. Encourage them to seek professional help if needed. Avoid pressuring them to express emotions they are not comfortable with. Focus on creating a safe and non-judgmental environment where they feel comfortable sharing their feelings at their own pace.
**Q9: Is constricted affect the same as alexithymia?**
A9: While they share some similarities, they are not the same. Constricted affect refers to the *outward expression* of emotion, while alexithymia refers to the *difficulty identifying and describing* one’s own emotions. Someone with alexithymia may experience emotions internally but struggle to understand or articulate them, which can then lead to constricted affect.
**Q10: What is the role of genetics in constricted affect?**
A10: While the exact role of genetics is still being researched, there is evidence to suggest that genes can influence personality traits and temperament, which can indirectly affect emotional expression. Additionally, genetic factors can increase the risk of developing mental health conditions that are associated with constricted affect.
## Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, constricted affect is a complex phenomenon characterized by a limitation in the range and intensity of emotional expression. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and impact is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective intervention. While various factors can contribute to constricted affect, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) offers a powerful approach for addressing the underlying cognitive and behavioral patterns that contribute to this emotional state. By challenging negative beliefs, developing coping skills, and practicing emotional expression, individuals can improve their emotional well-being and build stronger relationships. Leading experts in constricted affect suggest early intervention is key to improving outcomes.
The information presented in this guide is intended for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. If you are concerned about your emotional expression or the emotional expression of someone you know, it is essential to seek the guidance of a qualified mental health professional.
We encourage you to share your experiences with constricted affect in the comments below. Your insights and perspectives can help others who are struggling with similar challenges. If you are interested in learning more about CBT or finding a qualified therapist in your area, contact our experts for a consultation on constricted affect.
