ICD-10 Code for Transaminitis: A Comprehensive Guide for Medical Professionals
Navigating the complexities of medical coding can be challenging, especially when dealing with specific conditions like transaminitis. This comprehensive guide delves into the ICD-10 code for transaminitis, providing a deep understanding of its application, associated conditions, and best practices for accurate diagnosis and billing. We aim to equip healthcare professionals with the knowledge and resources necessary to confidently manage cases involving elevated liver enzymes, ensuring optimal patient care and streamlined administrative processes. This guide will provide a detailed explanation of the appropriate ICD-10 codes, related medical conditions, and the importance of accurate coding for reimbursement and data analysis. We will also cover common coding errors and how to avoid them, as well as provide resources for further learning and professional development.
Understanding Transaminitis and Its Significance
Transaminitis, characterized by elevated levels of liver enzymes (specifically alanine transaminase, ALT, and aspartate transaminase, AST) in the blood, indicates liver cell damage or inflammation. This condition is not a disease itself but rather a sign of an underlying issue affecting the liver. Accurately identifying and coding transaminitis is crucial for several reasons:
* **Diagnosis:** Transaminitis serves as a critical indicator for further investigation into potential liver disorders.
* **Treatment:** Accurate coding allows for appropriate treatment strategies based on the underlying cause of the elevated enzymes.
* **Billing and Reimbursement:** Proper coding ensures accurate billing practices and facilitates reimbursement from insurance providers.
* **Data Analysis:** Consistent and precise coding contributes to valuable data analysis for epidemiological studies and healthcare management.
Transaminitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
* **Viral Hepatitis:** Hepatitis A, B, and C are common causes of liver inflammation and elevated liver enzymes.
* **Alcoholic Liver Disease:** Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to liver damage and transaminitis.
* **Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD):** This condition, often associated with obesity and diabetes, can cause liver inflammation and elevated enzymes.
* **Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI):** Certain medications, both prescription and over-the-counter, can damage the liver and cause transaminitis.
* **Autoimmune Hepatitis:** This condition occurs when the body’s immune system attacks the liver, leading to inflammation and elevated enzymes.
* **Other Conditions:** Less common causes of transaminitis include hemochromatosis, Wilson’s disease, alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, and biliary obstruction.
The ICD-10-CM Coding System: An Overview
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) is a standardized coding system used in the United States to classify and report diagnoses and procedures. It is essential for healthcare providers, coders, and billers to understand the ICD-10-CM system to ensure accurate coding and reporting. The ICD-10-CM system is updated annually, with new codes added, existing codes revised, and obsolete codes deleted. It is important to stay up-to-date with the latest changes to ensure accurate coding.
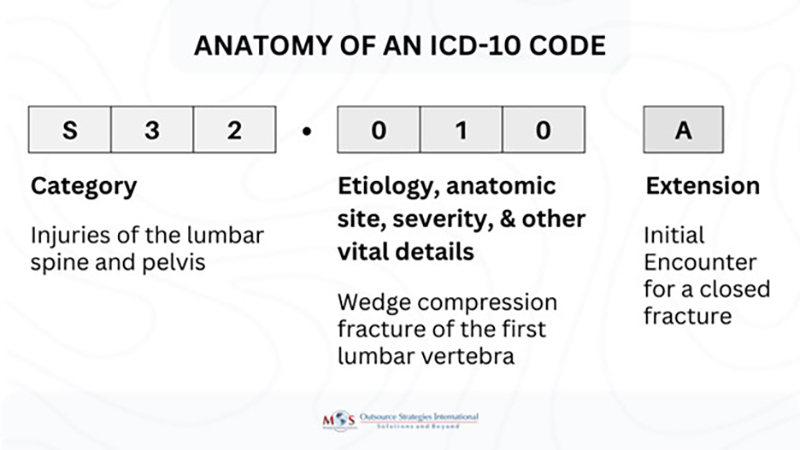
The ICD-10-CM codes are alphanumeric, consisting of three to seven characters. The first character is a letter, and the subsequent characters can be either letters or numbers. The codes are organized into chapters based on body system or disease type. Within each chapter, codes are further subdivided based on specific conditions and their manifestations. The ICD-10-CM system also includes various instructional notations, such as “includes,” “excludes1,” “excludes2,” and “code also,” which provide guidance on code selection and sequencing.
Decoding the ICD-10 Code for Transaminitis
While there isn’t a single, direct ICD-10 code specifically for “transaminitis,” the coding approach depends on identifying the underlying cause of the elevated liver enzymes. Here’s how to approach coding for transaminitis:
1. **Determine the Underlying Cause:** The most crucial step is to identify the underlying condition causing the transaminitis. This requires a thorough medical evaluation, including patient history, physical examination, and laboratory tests.
2. **Code the Underlying Condition:** Assign the appropriate ICD-10 code for the underlying condition. Examples include:
* **B15-B19:** Viral hepatitis (A, B, C, etc.)
* **K70:** Alcoholic liver disease
* **K76.0:** Nonalcoholic fatty liver (NAFL)
* **K75.81:** Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
* **K71:** Toxic liver disease (drug-induced)
* **K73:** Chronic hepatitis, not elsewhere classified
* **K75.4:** Autoimmune hepatitis
3. **Code Signs and Symptoms (If Necessary):** If the underlying cause is not yet determined, or if the transaminitis is a significant clinical finding, you may consider coding the signs and symptoms associated with liver dysfunction. However, this should be done cautiously to avoid duplicate coding when the underlying cause is known.
4. **Use Additional Codes:** Depending on the specific case, additional codes may be necessary to capture other relevant conditions or factors, such as comorbidities or risk factors.
**Example Scenario:** A patient presents with elevated ALT and AST levels. After further investigation, the physician diagnoses the patient with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). The appropriate ICD-10 code would be **K75.81** (Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)).
Common Coding Challenges and Solutions
Coding for transaminitis can present several challenges. Here are some common issues and how to address them:
* **Unspecified Cause:** If the underlying cause of the transaminitis is unknown, code the symptoms. Use codes like **R74.8** (Abnormal levels of transaminase and lactic acid dehydrogenase [LDH]) to indicate elevated liver enzymes when a definitive diagnosis is not yet established. Document thoroughly the steps taken to determine the underlying cause.
* **Multiple Possible Causes:** When multiple potential causes exist, the physician must determine the most likely cause based on clinical findings. If the cause remains uncertain, code the most probable condition, documenting the differential diagnoses considered.
* **Co-existing Conditions:** Accurately code all co-existing conditions that may contribute to or be affected by the transaminitis. For example, if a patient with alcoholic liver disease also has diabetes, code both conditions.
* **Documentation Inconsistencies:** Ensure that the medical record clearly and consistently documents the diagnosis, treatment, and relevant clinical information. Coding should be based on the physician’s documentation.
The Role of Laboratory Testing in Diagnosing Transaminitis
Laboratory testing plays a crucial role in diagnosing transaminitis and determining its underlying cause. Liver function tests (LFTs), including ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase (ALP), bilirubin, and albumin, are essential for assessing liver health. ALT and AST are the most commonly used markers for detecting liver cell damage. Elevated levels of these enzymes indicate liver inflammation or injury.
In addition to LFTs, other laboratory tests may be necessary to identify the specific cause of transaminitis. These tests may include:
* **Viral Hepatitis Serologies:** To detect hepatitis A, B, and C infections.
* **Autoimmune Markers:** To assess for autoimmune hepatitis.
* **Iron Studies:** To evaluate for hemochromatosis.
* **Ceruloplasmin:** To assess for Wilson’s disease.
* **Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Level:** To evaluate for alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
* **Lipid Profile:** To assess for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
* **Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP):** A broader panel that includes LFTs, electrolytes, glucose, and kidney function tests.
Imaging Modalities for Evaluating Transaminitis
Imaging studies can provide valuable information about the structure and function of the liver, helping to identify the underlying cause of transaminitis. Common imaging modalities used in the evaluation of transaminitis include:
* **Ultrasound:** A non-invasive imaging technique that can detect liver enlargement, masses, and other abnormalities.
* **Computed Tomography (CT) Scan:** A more detailed imaging technique that can provide cross-sectional images of the liver and surrounding structures.
* **Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):** An even more detailed imaging technique that can provide high-resolution images of the liver and biliary system.
* **Liver Biopsy:** In some cases, a liver biopsy may be necessary to obtain a tissue sample for microscopic examination. This can help to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of liver damage.
The Impact of Transaminitis on Patient Outcomes
The impact of transaminitis on patient outcomes depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the liver damage. In some cases, transaminitis may be mild and self-limiting, resolving without specific treatment. However, in other cases, transaminitis can be a sign of a serious liver condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Chronic liver diseases, such as chronic hepatitis B and C, alcoholic liver disease, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, can lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer. Early detection and treatment of these conditions can improve patient outcomes and prevent complications.
Best Practices for Accurate Coding and Documentation
To ensure accurate coding and documentation for transaminitis, follow these best practices:
* **Thorough Documentation:** Ensure that the medical record includes a detailed patient history, physical examination findings, laboratory results, imaging studies, and the physician’s assessment and plan.
* **Specificity:** Code to the highest level of specificity possible. Use the most specific ICD-10 code that accurately reflects the patient’s condition.
* **Accurate Sequencing:** Sequence codes correctly, with the underlying cause coded first, followed by any associated conditions or manifestations.
* **Compliance:** Adhere to coding guidelines and regulations, including the Official ICD-10-CM Coding Guidelines.
* **Continuing Education:** Stay up-to-date with the latest coding changes and guidelines through continuing education and professional development.
The Future of ICD-10 Coding for Liver Diseases
The ICD-10-CM coding system is continuously evolving to reflect advances in medical knowledge and technology. As new diagnostic and treatment modalities emerge for liver diseases, the ICD-10-CM system will likely be updated to incorporate these changes. Future updates may include more specific codes for different types of liver injury, such as drug-induced liver injury and autoimmune hepatitis. Additionally, there may be new codes for emerging liver diseases, such as metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), formerly known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Staying informed about these updates is essential for accurate coding and reporting.
Expert Insights on Managing Transaminitis
Based on expert consensus and clinical experience, managing transaminitis requires a comprehensive approach that includes:
* **Identifying and Addressing the Underlying Cause:** The primary goal is to identify and treat the underlying condition causing the elevated liver enzymes. This may involve lifestyle modifications, medications, or other interventions.
* **Monitoring Liver Function:** Regular monitoring of liver function tests is essential to assess the response to treatment and detect any signs of disease progression.
* **Lifestyle Modifications:** Lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss, exercise, and avoiding alcohol, can improve liver health and reduce the risk of complications.
* **Vaccination:** Vaccination against hepatitis A and B is recommended for individuals at risk of these infections.
* **Medications:** Medications may be necessary to treat specific liver conditions, such as viral hepatitis and autoimmune hepatitis.
Q&A: Addressing Common Questions About ICD-10 Coding for Transaminitis
**Q1: What is the most common ICD-10 code used for transaminitis when the cause is unknown?**
A: When the underlying cause of transaminitis is not yet determined, **R74.8** (Abnormal levels of transaminase and lactic acid dehydrogenase [LDH]) is often used to indicate elevated liver enzymes. However, efforts should continue to identify the underlying cause.
**Q2: How do I code transaminitis in a patient with both alcoholic liver disease and hepatitis C?**
A: Code both conditions. First, code **B18.2** (Chronic hepatitis C) to address the Hepatitis C, followed by **K70.30** (Alcoholic cirrhosis of liver without ascites), or another appropriate K70 code based on the specific manifestations of the alcoholic liver disease.
**Q3: What if the physician documents “elevated liver enzymes” but doesn’t specify ALT or AST?**
A: Query the physician for clarification. Accurate coding requires specific documentation of the elevated enzymes. If clarification cannot be obtained, use **R74.8** (Abnormal levels of transaminase and lactic acid dehydrogenase [LDH]).
**Q4: Is it appropriate to code transaminitis as the primary diagnosis if the patient is being seen for a routine check-up?**
A: It depends. If the elevated liver enzymes are a new finding discovered during the routine check-up, code the underlying cause if known. If the cause is unknown, code **R74.8** as the primary diagnosis, as it prompted further investigation.
**Q5: How often should I review updates to the ICD-10-CM coding system?**
A: At least annually. The ICD-10-CM system is updated every October 1st. Staying informed about these updates is crucial for accurate coding and compliance.
**Q6: What resources are available to help me improve my ICD-10 coding skills?**
A: Several resources are available, including coding manuals, online courses, professional organizations (such as AHIMA and AAPC), and coding conferences.
**Q7: How do I code drug-induced liver injury (DILI) causing transaminitis?**
A: Use code **K71** (Toxic liver disease) and specify the drug causing the injury. An additional code from categories **T36-T50** should be used to identify the specific drug.
**Q8: Can nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) cause transaminitis?**
A: Yes, NAFLD can cause transaminitis. Code **K76.0** (Nonalcoholic fatty liver (NAFL)) or **K75.81** (Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)), depending on the specific diagnosis.
**Q9: What is the difference between an “excludes1” and an “excludes2” note in the ICD-10-CM coding system?**
A: An “excludes1” note indicates that the excluded condition should never be coded together with the code above the note. An “excludes2” note indicates that the excluded condition is not part of the condition represented by the code above the note, but it may be acceptable to code both conditions if the patient has both.
**Q10: What is the role of a Certified Professional Coder (CPC) in managing transaminitis coding?**
A: A CPC plays a critical role in ensuring accurate and compliant coding for transaminitis. They review medical documentation, assign appropriate ICD-10 codes, and stay up-to-date with coding changes and guidelines. Their expertise helps healthcare providers receive appropriate reimbursement and avoid coding errors.
Conclusion: Mastering ICD-10 Coding for Transaminitis
Accurate ICD-10 coding for transaminitis is essential for effective diagnosis, treatment, billing, and data analysis. By understanding the underlying causes of transaminitis, following coding guidelines, and staying informed about coding updates, healthcare professionals can ensure accurate and compliant coding practices. This comprehensive guide provides a foundation for mastering ICD-10 coding for transaminitis and improving patient care. We encourage you to share your experiences with ICD-10 coding for transaminitis in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to liver disease diagnosis and treatment, and contact our experts for a consultation on complex coding scenarios.
