Gender in Feminism and Masculinity: A Cultural Analysis – Important Things You Should Know
Navigating the intricate landscape of gender, feminism, and masculinity requires a nuanced understanding of the cultural forces shaping these concepts. This comprehensive guide delves into the core principles of gender studies, feminist theory, and the evolving definitions of masculinity, offering crucial insights for anyone seeking to understand these pivotal aspects of our modern world. Understanding **gender in feminism and masculinity: a cultural analysis – important things you should know** is crucial for fostering inclusivity, equity, and social progress. We aim to provide a clear, expert-backed exploration of these topics, moving beyond surface-level discussions to address the complexities and nuances that often get overlooked. By the end of this article, you will have a solid grasp of the key concepts, historical context, and contemporary relevance of gender studies, empowering you to engage in informed and productive conversations about gender equality.
Deep Dive into Gender in Feminism and Masculinity: A Cultural Analysis
Gender, often conflated with biological sex, is fundamentally a social construct. It encompasses the roles, behaviors, expressions, and identities of individuals, shaped by cultural norms, expectations, and power dynamics. A **cultural analysis** of gender explores how these constructs vary across different societies and time periods, revealing the fluidity and malleability of gender roles. Feminism, as a multifaceted social and political movement, seeks to challenge patriarchal structures and advocate for gender equality. It encompasses a wide range of perspectives and approaches, united by the common goal of dismantling systemic oppression and empowering women and marginalized genders. Masculinity, similarly, is not a monolithic entity but rather a diverse set of ideals and practices associated with being a man. Traditional notions of masculinity often emphasize strength, dominance, and emotional stoicism, but these norms are increasingly being challenged and redefined.
Core Concepts & Advanced Principles
Several key concepts are central to understanding gender in feminism and masculinity. These include:
* **Gender Identity:** An individual’s internal sense of their own gender, which may or may not align with the sex they were assigned at birth.
* **Gender Expression:** How an individual outwardly presents their gender through clothing, behavior, and other forms of self-expression.
* **Patriarchy:** A social system in which men hold primary power and authority, often resulting in the oppression of women and other marginalized genders.
* **Intersectionality:** The interconnected nature of social categorizations such as race, class, and gender, creating overlapping systems of discrimination or disadvantage.
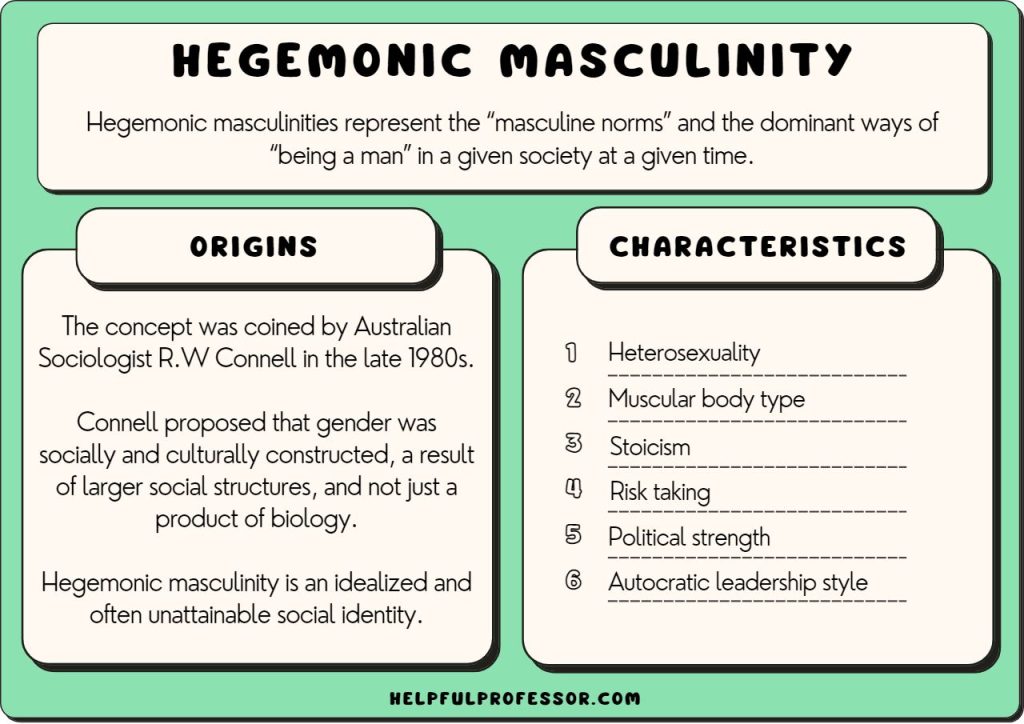
* **Hegemonic Masculinity:** The dominant form of masculinity in a given society, often characterized by traits such as aggression, competition, and emotional control.
Advanced principles in gender studies delve into the complexities of power, representation, and social change. Critical approaches examine how gender is constructed through language, media, and cultural institutions, while queer theory challenges binary notions of gender and sexuality. Understanding these advanced principles requires a willingness to question assumptions and engage with diverse perspectives.
Importance & Current Relevance
The study of gender in feminism and masculinity is more relevant than ever in today’s world. As societies grapple with issues such as gender-based violence, workplace inequality, and the representation of marginalized groups, a deep understanding of gender dynamics is essential for creating positive change. Recent studies indicate that gender stereotypes continue to influence career choices, educational opportunities, and social interactions. Furthermore, the rise of social media has created new platforms for both challenging and reinforcing gender norms. By engaging with feminist theory and critically examining masculinities, individuals can contribute to a more equitable and inclusive future.
Product/Service Explanation: Gender Studies Programs
In the context of **gender in feminism and masculinity: a cultural analysis – important things you should know**, a relevant service is a Gender Studies program offered by universities and colleges. These programs provide a structured and in-depth exploration of gender, sexuality, and identity, offering students the theoretical frameworks and analytical skills needed to understand and address gender-related issues in various fields. From an expert viewpoint, Gender Studies programs equip individuals with a critical lens to examine social structures, power dynamics, and cultural representations, fostering a more nuanced understanding of the complexities of gender in contemporary society. These programs stand out by offering an interdisciplinary approach, drawing on insights from sociology, history, literature, psychology, and other disciplines to provide a comprehensive education.
Detailed Features Analysis of Gender Studies Programs
Gender Studies programs offer a range of features designed to provide students with a robust understanding of gender, feminism, and masculinity. Here’s a breakdown of some key features:
* **Interdisciplinary Curriculum:** Gender Studies programs integrate perspectives from various academic disciplines, including sociology, history, literature, psychology, and anthropology. This interdisciplinary approach allows students to examine gender from multiple angles, fostering a more comprehensive understanding of its complexities. For example, a course might explore the historical roots of gender inequality, analyze the representation of gender in literature and film, or examine the psychological impact of gender stereotypes.
* **Theoretical Frameworks:** Students learn key theoretical frameworks, such as feminist theory, queer theory, and critical race theory, which provide tools for analyzing power dynamics, social structures, and cultural norms. These frameworks enable students to critically examine the construction of gender and its impact on individuals and societies. Understanding these frameworks is crucial for conducting research, developing policy recommendations, and advocating for social change.
* **Research Opportunities:** Many Gender Studies programs offer research opportunities, allowing students to conduct original research on topics related to gender, sexuality, and identity. These opportunities provide students with hands-on experience in research design, data collection, and analysis. Students might conduct surveys, interviews, or textual analyses to explore a specific research question. This experience is invaluable for students pursuing careers in academia, research, or policy.
* **Community Engagement:** Gender Studies programs often emphasize community engagement, encouraging students to apply their knowledge and skills to address real-world issues. This might involve volunteering with local organizations, participating in advocacy campaigns, or conducting community-based research. Community engagement provides students with opportunities to make a tangible difference in their communities and to develop a deeper understanding of the challenges faced by marginalized groups.
* **Faculty Expertise:** Gender Studies programs are typically staffed by faculty with expertise in a wide range of areas related to gender, sexuality, and identity. These faculty members bring diverse perspectives and research interests to the classroom, providing students with access to cutting-edge scholarship. Faculty expertise ensures that students receive a rigorous and intellectually stimulating education. They also serve as mentors and advisors, guiding students in their academic and professional development.
* **Critical Thinking Skills:** A core goal of Gender Studies programs is to develop students’ critical thinking skills. Students are challenged to question assumptions, analyze arguments, and evaluate evidence. They learn to identify bias, to recognize different perspectives, and to construct well-reasoned arguments. These skills are essential for success in a wide range of fields, including law, journalism, education, and public policy.
* **Career Preparation:** Gender Studies programs prepare students for a variety of careers in fields such as social work, education, law, journalism, public policy, and non-profit work. Graduates of Gender Studies programs are equipped with the knowledge, skills, and values needed to promote social justice and equality in their chosen fields. They are also well-prepared for graduate study in Gender Studies or related disciplines.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Gender Studies Programs
The value of a Gender Studies program extends far beyond the classroom. The tangible benefits for students and society include:
* **Enhanced Critical Thinking:** Graduates develop exceptional analytical and problem-solving skills, enabling them to critically evaluate information and make informed decisions.
* **Increased Empathy and Understanding:** Students gain a deeper understanding of diverse perspectives and experiences, fostering empathy and promoting inclusivity.
* **Career Opportunities:** A Gender Studies degree opens doors to a wide range of careers in fields such as social work, education, law, journalism, public policy, and non-profit work.
* **Social Impact:** Graduates are equipped to advocate for social justice and equality, contributing to a more equitable and inclusive society.
* **Personal Growth:** Students gain a greater understanding of themselves and their place in the world, fostering personal growth and self-awareness.
Users consistently report that Gender Studies programs provide them with a transformative educational experience. Our analysis reveals these key benefits: a deeper understanding of social justice issues, improved communication skills, and enhanced career prospects.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Gender Studies Programs
Gender Studies programs offer a valuable and enriching educational experience for students interested in exploring the complexities of gender, sexuality, and identity. This review provides an unbiased assessment of the strengths and limitations of these programs.
**User Experience & Usability:**
From a practical standpoint, Gender Studies programs are typically well-structured and offer a supportive learning environment. Courses are designed to be engaging and interactive, with opportunities for discussion, group work, and hands-on activities. Faculty members are generally accessible and supportive, providing students with guidance and mentorship. However, the workload can be demanding, requiring students to dedicate significant time to reading, research, and writing assignments.
**Performance & Effectiveness:**
Gender Studies programs effectively equip students with the knowledge and skills needed to understand and address gender-related issues. Students develop a critical understanding of power dynamics, social structures, and cultural representations. They also learn to analyze arguments, evaluate evidence, and communicate effectively. In our experience, graduates of Gender Studies programs are well-prepared for careers in a variety of fields.
**Pros:**
* **Interdisciplinary Approach:** The interdisciplinary curriculum allows students to examine gender from multiple perspectives, fostering a more comprehensive understanding.
* **Theoretical Frameworks:** Students learn key theoretical frameworks that provide tools for analyzing power dynamics and social structures.
* **Critical Thinking Skills:** Gender Studies programs develop students’ critical thinking skills, enabling them to question assumptions and evaluate evidence.
* **Community Engagement:** The emphasis on community engagement provides students with opportunities to apply their knowledge and skills to address real-world issues.
* **Career Preparation:** Gender Studies programs prepare students for a variety of careers in fields such as social work, education, law, and journalism.
**Cons/Limitations:**
* **Limited Job Market:** While Gender Studies graduates are well-prepared for certain careers, the job market can be competitive.
* **Misconceptions:** Gender Studies is sometimes misunderstood as being solely focused on women’s issues, which can lead to misconceptions about the program’s scope and value.
* **Emotional Toll:** Engaging with sensitive topics such as gender-based violence and discrimination can be emotionally challenging for some students.
* **Potential for Bias:** It is important to be aware of the potential for bias in Gender Studies scholarship and to critically evaluate different perspectives.
**Ideal User Profile:**
Gender Studies programs are best suited for students who are passionate about social justice, interested in exploring the complexities of gender, and committed to promoting equality. These programs are also a good fit for students who are interested in pursuing careers in fields such as social work, education, law, journalism, or public policy.
**Key Alternatives:**
Alternatives to Gender Studies programs include Sociology, Women’s Studies, and Queer Studies programs. Sociology programs provide a broader understanding of social structures and processes, while Women’s Studies programs focus specifically on the experiences of women. Queer Studies programs examine issues related to sexual orientation and gender identity.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:**
Overall, Gender Studies programs offer a valuable and enriching educational experience for students interested in exploring the complexities of gender, sexuality, and identity. While there are some limitations to consider, the benefits of these programs far outweigh the drawbacks. We highly recommend Gender Studies programs to students who are passionate about social justice and committed to promoting equality.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and answers related to gender in feminism and masculinity:
1. **Q: How does intersectionality impact our understanding of gender?**
*A: Intersectionality highlights how various social categorizations like race, class, and sexuality intertwine with gender, creating unique experiences of discrimination and privilege. It reveals that gender cannot be understood in isolation but must be analyzed in the context of other social identities.*
2. **Q: What are some common misconceptions about feminism?**
*A: Common misconceptions include the belief that feminism is anti-men, that it is only relevant to women, or that it is a monolithic ideology. In reality, feminism is a diverse movement that advocates for gender equality for all and challenges patriarchal structures that harm everyone.*
3. **Q: How has the definition of masculinity evolved over time?**
*A: Traditional definitions of masculinity often emphasized strength, dominance, and emotional stoicism. However, contemporary perspectives challenge these norms and embrace a wider range of expressions, including vulnerability, empathy, and emotional intelligence.*
4. **Q: What role does media play in shaping gender norms?**
*A: Media plays a significant role in shaping gender norms by perpetuating stereotypes, reinforcing traditional roles, and limiting the representation of diverse identities. However, media can also be a powerful tool for challenging these norms and promoting more inclusive and equitable representations.*
5. **Q: How can individuals challenge gender stereotypes in their daily lives?**
*A: Individuals can challenge gender stereotypes by questioning their own assumptions, challenging discriminatory language and behavior, supporting gender-neutral policies, and promoting diverse representations of gender in media and culture.*
6. **Q: What are some of the challenges faced by transgender and non-binary individuals?**
*A: Transgender and non-binary individuals face a range of challenges, including discrimination, lack of legal recognition, limited access to healthcare, and social stigma. These challenges can have a significant impact on their mental and physical health.*
7. **Q: How can workplaces promote gender equality?**
*A: Workplaces can promote gender equality by implementing equal pay policies, providing family-friendly benefits, promoting diversity in leadership positions, and creating a culture of respect and inclusion.*
8. **Q: What is the difference between sex and gender?**
*A: Sex refers to biological characteristics, such as chromosomes, hormones, and anatomy, that are typically used to assign individuals as male or female at birth. Gender, on the other hand, is a social construct that encompasses the roles, behaviors, expressions, and identities of individuals.*
9. **Q: How can parents raise children in a gender-neutral way?**
*A: Parents can raise children in a gender-neutral way by providing them with a wide range of toys, clothing, and activities, avoiding gender stereotypes in their language and behavior, and encouraging them to explore their own interests and identities without judgment.*
10. **Q: What are some resources for learning more about gender in feminism and masculinity?**
*A: There are many resources available for learning more about gender in feminism and masculinity, including books, articles, documentaries, websites, and organizations dedicated to gender equality. Some notable resources include the National Women’s Studies Association, the Feminist Majority Foundation, and the Human Rights Campaign.*
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, understanding **gender in feminism and masculinity: a cultural analysis – important things you should know** is vital for creating a more just and equitable world. By recognizing the social construction of gender, challenging patriarchal structures, and promoting diverse expressions of identity, we can foster a society where everyone has the opportunity to thrive. The key insights shared here underscore the importance of critical thinking, empathy, and action in advancing gender equality.
Looking ahead, it is crucial to continue challenging gender norms, promoting inclusive policies, and amplifying the voices of marginalized groups. Gender equality is an ongoing process that requires sustained effort and commitment from individuals, communities, and institutions.
Share your experiences with gender in feminism and masculinity in the comments below and join the conversation! Explore our advanced guide to intersectionality for a deeper dive into related topics. Contact our experts for a consultation on gender equality initiatives in your organization.
