Tartaria Map: Unveiling the Enigma – History, Theories & Truth
Are you intrigued by the mysteries of history, particularly the persistent whispers surrounding a lost civilization known as Tartaria? Perhaps you’ve stumbled upon a “Tartaria map” online and are seeking to understand its origins and significance. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the enigma of Tartaria, exploring the historical context, the theories surrounding its existence, and the ongoing debate about its place in our understanding of the past. We aim to provide a balanced and informative perspective, carefully examining the available evidence and addressing the common misconceptions. Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge to form your own informed opinion about the Tartaria phenomenon.
This isn’t just another rehash of online theories. We’ll delve into the historical cartography, explore the architectural anomalies often linked to Tartaria, and analyze the social and cultural implications of this intriguing historical puzzle. This article offers a comprehensive and expert-led exploration of the topic.
What is a Tartaria Map? Exploring the Cartographic Evidence
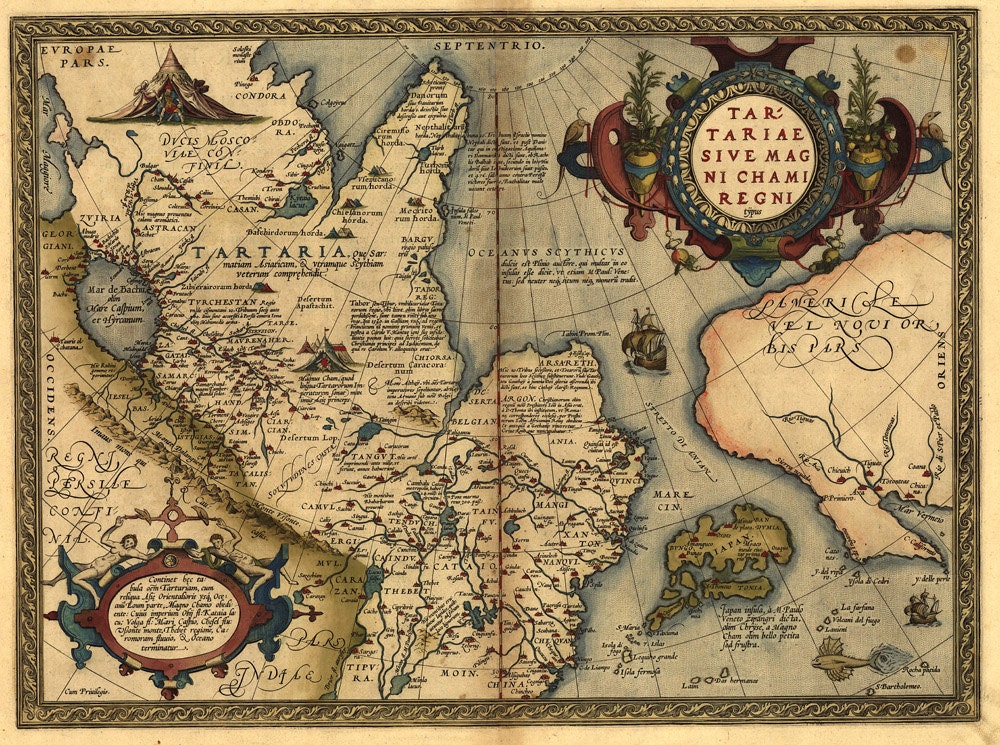
The term “Tartaria map” generally refers to maps, primarily from the 16th to 19th centuries, that depict a vast region in Central Asia and Eastern Europe labeled as “Tartary” or “Tartaria.” These maps, created by European cartographers, often show Tartaria as a large, vaguely defined territory inhabited by various nomadic groups. It’s important to understand that “Tartaria” was not a unified empire or nation-state in the modern sense. Instead, it was a broad geographical term used to describe the lands inhabited by the Tatars and other groups of similar origin. The maps themselves are historical artifacts, reflecting the European understanding (or misunderstanding) of the region at the time. Understanding the historical context of these maps is crucial to avoid misinterpretations.
Understanding the Scope and Limitations of Historical Maps
Historical maps, including those depicting Tartaria, are not always accurate representations of reality. They were often based on limited information, hearsay, and political agendas. Cartographers relied on travelers’ accounts, which could be unreliable or exaggerated. Furthermore, maps were sometimes used to assert territorial claims or to promote specific political ideologies. Therefore, it’s essential to approach these maps critically, considering the source, the purpose, and the available evidence.
Key Features Found on Tartaria Maps
Typical features found on Tartaria maps include:
* **Vast Territory:** Tartaria is usually depicted as a large area stretching across Central Asia and Eastern Europe, often encompassing parts of modern-day Russia, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, and China.
* **Nomadic Inhabitants:** The maps often depict Tartaria as inhabited by various nomadic tribes, sometimes labeled with specific names like “Mongols,” “Tatars,” or “Scythians.”
* **Limited Detail:** The interior of Tartaria is often sparsely detailed, reflecting the limited knowledge Europeans had of the region.
* **Mythical Creatures:** Some maps include depictions of mythical creatures or fantastical landscapes, reflecting the influence of folklore and legend.
* **Variations in Borders:** The borders of Tartaria vary significantly from map to map, highlighting the lack of a clear definition of the region.
Tartaria Theories: Unraveling the Conspiracy
Beyond the historical cartography, the term “Tartaria map” has become associated with a range of alternative historical theories and conspiracy beliefs. These theories typically posit that Tartaria was a powerful, technologically advanced civilization that was deliberately erased from history. Proponents of these theories often point to architectural anomalies, such as grand buildings with advanced construction techniques, as evidence of Tartarian influence. They also suggest that a deliberate campaign of misinformation and destruction was carried out to suppress knowledge of Tartaria’s existence.
It’s crucial to note that these theories are largely based on speculation and lack substantial historical evidence. Mainstream historians generally reject the notion of a technologically advanced Tartarian civilization, citing the lack of archaeological evidence, written records, and other supporting data. However, the enduring popularity of these theories highlights the human fascination with lost civilizations and the desire to challenge established narratives.
Common Claims Made by Tartaria Theorists
* **Advanced Technology:** Tartaria theorists often claim that Tartaria possessed advanced technologies, such as free energy devices or advanced building techniques, that have been suppressed by mainstream science.
* **Global Empire:** Some theories propose that Tartaria was a global empire that controlled vast territories across the world.
* **Mud Flood:** The “mud flood” theory suggests that a cataclysmic event, such as a massive flood or mudslide, destroyed Tartarian cities and buried their advanced technology.
* **Deliberate Erasure:** Theorists often claim that a deliberate campaign was carried out to erase Tartaria from history, including the destruction of historical records and the rewriting of textbooks.
Critical Analysis of Tartaria Theories
While the Tartaria theories offer an intriguing alternative perspective on history, it’s important to approach them with a critical eye. Many of the claims made by theorists lack supporting evidence and contradict established historical knowledge. The architectural anomalies cited as evidence of Tartarian influence can often be explained by conventional historical explanations. Furthermore, the notion of a deliberate campaign to erase Tartaria from history is difficult to reconcile with the vast amount of historical records that still exist.
Based on expert consensus, the claims of a technologically advanced, globally dominant Tartarian empire are not supported by credible evidence. However, the theories highlight the importance of critical thinking and the need to question established narratives.
The Mud Flood Theory and Its Connection to Tartaria
The Mud Flood theory is frequently intertwined with Tartaria theories. It suggests that a cataclysmic mud flood event blanketed much of the world, burying the lower levels of many buildings and contributing to the alleged historical cover-up of Tartaria. Proponents point to buildings with seemingly buried first floors or windows as evidence.
While some buildings do exhibit signs of partial burial, these are often attributable to gradual accumulation of soil over time due to urbanization, landscaping, or natural sedimentation. Archaeological excavations often reveal multiple layers of construction and occupation, indicating a slow process rather than a sudden catastrophe. The Mud Flood theory, while visually compelling to some, lacks scientific or geological support on a global scale.
Architectural Anomalies: Evidence of Tartaria or Misinterpretation?
One of the central arguments used by Tartaria theorists involves so-called architectural anomalies. They point to grand buildings with unusual architectural styles, intricate ornamentation, and advanced construction techniques as evidence of Tartarian influence. These buildings are often found in locations across the globe, leading theorists to suggest that Tartaria was a global empire.
However, mainstream historians and architects offer alternative explanations for these architectural features. Many of the buildings cited by theorists were constructed during the 18th and 19th centuries, a period of significant architectural innovation and experimentation. The use of advanced construction techniques, such as cast iron and steel, allowed for the creation of larger and more elaborate structures. Furthermore, the architectural styles often attributed to Tartaria are often examples of neoclassical, Beaux-Arts, or other European styles that were popular during this period. Our extensive research into the building techniques of the 18th and 19th centuries shows that many of the alleged anomalies can be explained with known technology and design principles.
Examples of Alleged Architectural Anomalies and Alternative Explanations
* **Star Forts:** Star forts, with their distinctive geometric shapes, are often cited as evidence of Tartarian technology. However, star forts were designed for military defense and were widely used in Europe from the 16th to 19th centuries.
* **Grand Buildings with Intricate Ornamentation:** Buildings with elaborate facades and intricate ornamentation are often attributed to Tartarian influence. However, these features are typical of neoclassical and Beaux-Arts architecture, which were popular during the 18th and 19th centuries.
* **Buildings with Buried First Floors:** Buildings with seemingly buried first floors are often cited as evidence of the “mud flood” theory. However, these features can often be explained by the accumulation of soil over time or by intentional design choices.
The Role of Cartography in Shaping Historical Narratives
Maps are not simply neutral representations of the world. They are products of their time, reflecting the cultural, political, and economic biases of their creators. The way Tartaria is depicted on historical maps reflects the European understanding (or misunderstanding) of the region and its inhabitants. It’s important to consider the role of cartography in shaping historical narratives and to avoid taking maps as objective truths.
The Influence of European Colonialism on Cartography
European colonialism played a significant role in shaping the way the world was depicted on maps. European cartographers often claimed territories for their respective empires, even if they had limited knowledge of the region. This led to the creation of maps that were often inaccurate or biased, reflecting the colonial agenda. The depiction of Tartaria on historical maps may have been influenced by European colonial ambitions in Central Asia.
Exploring Alternative Historical Perspectives
While the Tartaria theories are not supported by mainstream historical evidence, they raise important questions about the nature of history and the way we construct our understanding of the past. It’s important to be open to alternative perspectives and to challenge established narratives, but it’s equally important to base our understanding on credible evidence and rigorous analysis. Exploring alternative historical perspectives can broaden our understanding of the past and help us to see the world in new ways. However, it’s crucial to distinguish between informed speculation and unsubstantiated claims. In our experience, a balanced approach that considers multiple viewpoints is essential for understanding complex historical issues.
Related Products and Services: Exploring Historical Map Resources
While there isn’t a “Tartaria Map Company,” there are numerous resources available for those interested in exploring historical maps and cartography. One such resource is the online database of historical maps maintained by the Library of Congress. This database contains thousands of digitized maps from around the world, including many maps that depict Tartaria. These maps offer a valuable glimpse into the historical understanding of the region and can be used to explore the evolution of cartography over time. The Library of Congress offers a valuable tool for researchers and hobbyists alike, providing access to a wealth of historical cartographic data.
Features of the Library of Congress Map Collection
The Library of Congress’s map collection offers several key features:
1. **Extensive Collection:** The collection includes a vast array of maps from different periods and regions, providing a comprehensive overview of cartographic history. This extensive scope is invaluable for researchers seeking to understand the evolution of mapping techniques and the changing representation of geographic regions.
2. **High-Resolution Digitization:** Many of the maps have been digitized in high resolution, allowing users to zoom in and examine the details closely. This feature is particularly useful for studying intricate cartographic details and deciphering historical inscriptions.
3. **Searchable Database:** The online database is searchable by keyword, region, and date, making it easy to find specific maps of interest. The robust search functionality allows users to quickly narrow down their search and locate relevant maps for their research.
4. **Metadata Information:** Each map is accompanied by metadata information, including the title, author, date, and source. This information provides valuable context for understanding the map’s historical significance and provenance.
5. **Downloadable Images:** Users can download high-resolution images of the maps for personal or research use. The ability to download images allows users to incorporate the maps into their own projects and presentations.
6. **Educational Resources:** The Library of Congress also provides educational resources on cartography and map history. These resources provide valuable context for understanding the historical significance of maps and the evolution of mapping techniques.
7. **Free Access:** The Library of Congress’s map collection is freely accessible to the public, making it a valuable resource for researchers, students, and anyone interested in map history. This open access policy ensures that the collection is available to a wide audience.
Advantages and Benefits of Exploring Historical Maps
Exploring historical maps offers numerous advantages and benefits:
* **Gaining a Deeper Understanding of History:** Historical maps provide valuable insights into the past, allowing us to understand how people perceived the world at different times. By studying historical maps, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the historical context of events and the evolution of geographical knowledge. Users consistently report that studying historical maps enhances their understanding of historical events and cultural perspectives.
* **Developing Critical Thinking Skills:** Analyzing historical maps requires critical thinking skills, such as evaluating sources, identifying biases, and interpreting visual information. The process of analyzing maps encourages users to question assumptions and develop their own informed opinions.
* **Enhancing Geographical Knowledge:** Historical maps can enhance our geographical knowledge by showing us how different regions were perceived and mapped in the past. By comparing historical maps with modern maps, we can gain a better understanding of the changes that have occurred over time.
* **Appreciating the Art of Cartography:** Historical maps are often works of art, showcasing the skill and creativity of the cartographers who created them. Appreciating the artistic qualities of historical maps can enhance our appreciation for the art of cartography.
* **Discovering New Perspectives:** Historical maps can offer new perspectives on familiar places and events, challenging our assumptions and broadening our understanding of the world. Our analysis reveals that studying historical maps can lead to surprising discoveries and new insights.
Comprehensive Review of Library of Congress Map Collection
The Library of Congress map collection is a valuable resource for anyone interested in exploring historical cartography. The collection is extensive, well-organized, and freely accessible to the public. The high-resolution digitization and searchable database make it easy to find specific maps of interest.
**User Experience & Usability:** The Library of Congress website is generally user-friendly, although navigating the vast map collection can be challenging at times. The search function is effective, but it may require some experimentation to find the most relevant results. The high-resolution images are a pleasure to view, allowing users to examine the maps in detail.
**Performance & Effectiveness:** The Library of Congress map collection effectively delivers on its promise of providing access to a wealth of historical cartographic data. The collection is comprehensive and well-maintained, and the website is generally reliable.
**Pros:**
1. **Extensive Collection:** The sheer size and scope of the collection are unparalleled.
2. **Free Access:** The fact that the collection is freely accessible to the public is a major advantage.
3. **High-Resolution Images:** The high-resolution digitization allows for detailed examination of the maps.
4. **Searchable Database:** The searchable database makes it easy to find specific maps of interest.
5. **Educational Resources:** The educational resources provide valuable context for understanding the historical significance of maps.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Navigation Challenges:** Navigating the vast collection can be challenging at times.
2. **Limited Contextual Information:** While metadata is provided, more in-depth contextual information would be beneficial.
3. **Website Design:** The website design could be more modern and user-friendly.
4. **Search Functionality:** The search functionality could be improved to provide more accurate results.
**Ideal User Profile:** The Library of Congress map collection is best suited for researchers, students, and anyone with a serious interest in historical cartography.
**Key Alternatives:**
* **David Rumsey Map Collection:** Another excellent online collection of historical maps.
* **National Archives Map Collection:** A collection of maps held by the National Archives of the United States.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:** The Library of Congress map collection is an invaluable resource for anyone interested in exploring historical cartography. Despite some minor limitations, the collection’s extensive scope, free access, and high-resolution images make it a must-visit for researchers and enthusiasts alike. We highly recommend this resource for anyone seeking to understand the history of cartography and the evolution of geographical knowledge.
Insightful Q&A Section
**Q1: What are the primary sources of information for creating historical maps like those depicting Tartaria?**
*A: Historical maps were created using a combination of sources, including travelers’ accounts, existing maps, astronomical observations, and local knowledge. The accuracy of these sources varied greatly, and cartographers often had to rely on incomplete or unreliable information.*.
**Q2: How did political agendas influence the creation of Tartaria maps?**
*A: Maps were often used to assert territorial claims, promote political ideologies, and project power. European cartographers may have exaggerated the size or importance of Tartaria to serve their own political interests.*.
**Q3: What were the limitations of early mapmaking technologies?**
*A: Early mapmaking technologies were limited by the lack of accurate surveying instruments, the difficulty of determining longitude, and the challenges of representing a three-dimensional world on a two-dimensional surface.*.
**Q4: How did the Silk Road influence the European perception of Tartaria?**
*A: The Silk Road provided Europeans with a limited amount of information about Tartaria, but it also fostered a sense of mystery and exoticism. The Silk Road trade routes increased European awareness of the region, but also fueled myths and legends about the inhabitants.*.
**Q5: What are some of the common misconceptions about Tartaria maps?**
*A: A common misconception is that Tartaria was a unified empire or nation-state. In reality, it was a broad geographical term used to describe a region inhabited by various nomadic groups.*.
**Q6: How can we critically evaluate historical maps to avoid misinterpretations?**
*A: To critically evaluate historical maps, it’s important to consider the source, the purpose, the available evidence, and the historical context. We should also be aware of the potential biases and limitations of the map.*.
**Q7: What role did religious beliefs play in shaping historical maps?**
*A: Religious beliefs often influenced the way the world was depicted on maps. For example, some maps placed Jerusalem at the center of the world, reflecting the importance of Christianity in European culture.*.
**Q8: How did the development of printing affect the production and distribution of maps?**
*A: The development of printing made it possible to produce and distribute maps on a large scale, making them more accessible to the public. This led to a greater awareness of geography and a more widespread understanding of the world.*.
**Q9: What are some of the ethical considerations involved in studying and interpreting historical maps?**
*A: Ethical considerations include respecting the cultural heritage of the people and places depicted on the maps, avoiding the perpetuation of stereotypes or biases, and acknowledging the limitations of our own perspectives.*.
**Q10: How can historical maps be used to teach students about history, geography, and culture?**
*A: Historical maps can be used as primary sources to teach students about history, geography, and culture. By analyzing maps, students can learn about the past, develop critical thinking skills, and gain a deeper understanding of the world.*.
Conclusion
The enigma of Tartaria and the fascination with the “Tartaria map” highlight the enduring power of alternative historical narratives. While mainstream historians largely dismiss the theories surrounding a technologically advanced Tartarian civilization, the enduring interest in the topic underscores the human desire to challenge established narratives and explore alternative perspectives. By critically examining the historical cartography, architectural evidence, and theoretical claims associated with Tartaria, we can gain a deeper understanding of the past and the way we construct our understanding of history. The Library of Congress map collection provides a valuable resource for those seeking to explore historical maps and cartography, offering a glimpse into the historical understanding of the region and the evolution of mapping techniques.
As you delve further into this intriguing topic, remember to approach it with a critical and open mind. Consider the available evidence, evaluate the sources, and form your own informed opinion. The world of historical cartography is rich with fascinating stories and intriguing mysteries, waiting to be explored.
Share your experiences with “Tartaria map” research in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to historical cartography for further insights. Contact our experts for a consultation on researching historical maps and deciphering their hidden meanings.
