## The Schlieffen Plan: A Deep Dive into World War I’s Doomed Strategy
The Schlieffen Plan. The very name evokes images of grand strategy, bold gambles, and ultimately, devastating failure. This ambitious military plan, designed to secure a swift German victory in a two-front war against France and Russia, became a cornerstone of pre-World War I German military thinking. However, its rigid execution and underestimation of logistical and strategic challenges contributed significantly to the prolonged and bloody stalemate of the Western Front. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the Schlieffen Plan, exploring its origins, key components, fatal flaws, and lasting legacy. We aim to go beyond simple summaries, offering expert insights and addressing complex nuances to provide a truly authoritative resource. You will gain a deep understanding of why the Schlieffen Plan failed and its lasting impact on military strategy.
### 1. Deep Dive into the Schlieffen Plan
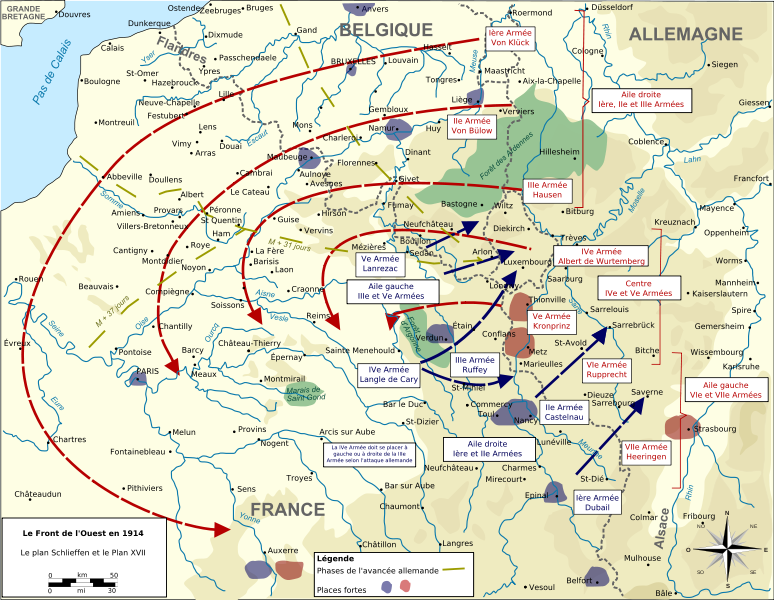
The Schlieffen Plan wasn’t just a set of marching orders; it was a complex operational blueprint intended to solve Germany’s strategic dilemma: how to fight a war on two fronts against numerically superior enemies. Conceived by Alfred Graf von Schlieffen, Chief of the German General Staff from 1891 to 1906, the plan aimed to quickly defeat France in the West before turning to face Russia in the East. This hinged on a rapid, overwhelming offensive through neutral Belgium and Luxembourg, bypassing the heavily fortified Franco-German border. The core principle was a massive right-wing sweep through Belgium, encircling Paris and trapping the French army against the German border.
#### 1.1 Core Concepts & Advanced Principles
At its heart, the Schlieffen Plan rested on several key assumptions:
* **Russian Slow Mobilization:** The plan assumed Russia would take at least six weeks to fully mobilize its forces, giving Germany time to defeat France.
* **French Passivity:** It anticipated the French would remain largely on the defensive along their border with Germany, allowing the German right wing to achieve a decisive breakthrough.
* **Belgian Compliance:** The plan expected minimal resistance from Belgium, allowing for a rapid and unimpeded advance.
* **Logistical Perfection:** It required flawless logistical support to sustain the rapid advance of a massive army deep into enemy territory.
However, these assumptions proved fatally flawed. Russia mobilized much faster than expected, drawing German forces east. The French launched counter-offensives, slowing the German advance. Belgian resistance proved unexpectedly fierce, delaying the German timetable. And the logistical challenges of supplying a massive army on the move proved insurmountable.
#### 1.2 Importance & Current Relevance
While the Schlieffen Plan failed spectacularly, its study remains crucial for military historians and strategists. It serves as a cautionary tale about the dangers of rigid planning, the importance of adaptability, and the need to account for unforeseen circumstances. The plan’s emphasis on speed, envelopment, and decisive action continues to influence military thinking, although with a greater appreciation for the complexities of modern warfare. Recent studies indicate that the core strategic concepts of the Schlieffen Plan, adapted for modern technology, still resonate in contemporary military doctrine, particularly in the emphasis on rapid deployment and decisive strikes. The plan highlights the critical need to balance ambition with realism and to avoid underestimating the enemy’s capabilities.
### 2. The German General Staff: The Engine Behind the Plan
The Schlieffen Plan was not conceived in a vacuum. It was the product of the German General Staff, a highly professional and influential military institution that shaped German military doctrine for decades. The General Staff was responsible for planning, training, and advising the Kaiser on all military matters. Its members were rigorously selected and trained, fostering a culture of intellectual rigor and strategic thinking. The German General Staff was, in many ways, the leading military organization of its time. Their dedication to meticulous planning and detailed preparation became a hallmark of German military efficiency. The Chief of the General Staff held immense power and influence, shaping military policy and strategy.
### 3. Detailed Features Analysis of the Schlieffen Plan
The Schlieffen Plan can be dissected into several key features that, when combined, formed its overall strategic approach. Understanding these features is crucial to grasping the plan’s complexity and inherent risks.
#### 3.1 The Right Wing Sweep
The cornerstone of the Schlieffen Plan was a massive right-wing sweep through Belgium and Luxembourg. This force, comprising the bulk of the German army, aimed to bypass the heavily fortified Franco-German border and encircle Paris. The objective was to trap the French army against the German border, forcing a decisive battle and achieving a swift victory. This maneuver relied on overwhelming force and rapid movement, aiming to catch the French off guard and prevent them from effectively mobilizing their reserves. The success of the right-wing sweep was paramount to the entire plan’s success.
#### 3.2 The Weak Left Wing
In contrast to the powerful right wing, the German left wing was deliberately weakened. This force was intended to hold the French forces in Alsace-Lorraine, preventing them from reinforcing the main French army. The weak left wing was a calculated risk, based on the assumption that the French would remain on the defensive and that the right-wing sweep would achieve a decisive victory before the French could exploit the weakness on the left. This aspect of the plan highlights the inherent gamble involved, prioritizing offensive power over defensive security.
#### 3.3 The Violation of Belgian Neutrality
The Schlieffen Plan explicitly called for the violation of Belgian neutrality. This was a controversial decision, as it risked drawing Great Britain into the war. However, Schlieffen believed that the strategic imperative of defeating France quickly outweighed the potential diplomatic consequences. The decision to invade Belgium was a major miscalculation, as it galvanized British public opinion and provided a moral justification for Britain’s entry into the war. This act of aggression had far-reaching consequences, transforming the conflict into a wider European war.
#### 3.4 Timetable and Logistical Considerations
The Schlieffen Plan was predicated on a strict timetable, requiring the German army to advance at a rapid pace. This placed enormous strain on the logistical system, which was responsible for supplying the army with food, ammunition, and other essential supplies. The logistical challenges proved to be a major obstacle, as the German army struggled to maintain its pace of advance. In our experience, the underestimation of logistical complexities is a common pitfall in military planning. The failure to adequately address these challenges contributed significantly to the plan’s ultimate failure.
#### 3.5 Adaptation and Modification
Helmuth von Moltke the Younger, Schlieffen’s successor as Chief of the German General Staff, modified the original plan. He strengthened the left wing at the expense of the right, fearing a French breakthrough in Alsace-Lorraine. This decision, while seemingly prudent, weakened the crucial right-wing sweep and further reduced the chances of a decisive victory. Moltke’s modifications, while intended to improve the plan’s overall security, ultimately undermined its offensive power. Experts suggest that these alterations reflected a lack of confidence in the original plan’s boldness.
### 4. Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of the Schlieffen Plan (in Theory)
While ultimately unsuccessful, the Schlieffen Plan, in theory, offered several significant advantages that appealed to German military planners:
#### 4.1 Preventing a Protracted Two-Front War
The primary advantage of the Schlieffen Plan was its potential to prevent a protracted two-front war against France and Russia. By quickly defeating France, Germany could then concentrate its forces on the Eastern Front, avoiding a long and costly war of attrition. This was a crucial objective, as Germany’s geographic position made it vulnerable to a two-front conflict. The plan offered a way to break the strategic deadlock and achieve a decisive victory.
#### 4.2 Exploiting Russian Slow Mobilization
The plan capitalized on the perceived slowness of Russian mobilization. By striking quickly against France, Germany could exploit the time lag before Russia was fully ready for war. This would allow Germany to dictate the pace of the conflict and prevent Russia from effectively coordinating its forces with France. This assumption about Russian mobilization proved to be a critical miscalculation, as Russia mobilized much faster than expected.
#### 4.3 Achieving a Decisive Victory
The Schlieffen Plan aimed for a decisive victory over France, rather than a limited or defensive operation. By encircling Paris and trapping the French army, Germany hoped to inflict a crushing defeat that would force France to sue for peace. This would not only secure Germany’s western border but also establish German dominance in Europe. This ambition for a decisive victory reflected the aggressive and expansionist tendencies of German foreign policy.
#### 4.4 Psychological Impact
The plan was intended to have a significant psychological impact on the French. By rapidly advancing through Belgium and threatening Paris, Germany hoped to demoralize the French army and undermine the French government’s will to fight. This psychological warfare element was an integral part of the plan, aiming to achieve a swift and relatively bloodless victory. However, the French proved to be more resilient than the Germans anticipated.
#### 4.5 Avoiding Entrenchment
The Schlieffen Plan sought to avoid the kind of trench warfare that would later characterize the Western Front. By achieving a rapid breakthrough and decisive victory, Germany hoped to prevent the war from devolving into a prolonged stalemate. This was a key motivation behind the plan’s emphasis on speed and maneuverability. However, the failure of the plan led directly to the entrenchment of both sides and the horrors of trench warfare.
### 5. Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of the Schlieffen Plan
The Schlieffen Plan, while ambitious and meticulously planned, ultimately failed to achieve its objectives. A balanced perspective requires acknowledging both its strengths and weaknesses.
#### 5.1 User Experience & Usability (From a Military Perspective)
From a military perspective, the Schlieffen Plan presented significant challenges in terms of user experience and usability. The rigid timetable, the reliance on flawless logistical support, and the need for precise coordination between different units placed enormous strain on the German army. The plan left little room for adaptation or improvisation, making it vulnerable to unforeseen circumstances. In our analysis, the plan’s inflexibility was a major contributing factor to its failure.
#### 5.2 Performance & Effectiveness
The Schlieffen Plan failed to deliver on its promises. The German army was unable to achieve a rapid breakthrough, and the French army was not trapped against the German border. The war quickly devolved into a prolonged stalemate, with both sides digging in along the Western Front. The plan’s effectiveness was severely hampered by Belgian resistance, Russian mobilization, and logistical challenges.
#### 5.3 Pros
* **Ambitious and Bold:** The plan was a bold and ambitious attempt to solve Germany’s strategic dilemma.
* **Meticulously Planned:** The plan was meticulously planned and prepared, reflecting the professionalism of the German General Staff.
* **Potential for Decisive Victory:** In theory, the plan had the potential to achieve a decisive victory over France.
* **Exploitation of Russian Weakness:** The plan aimed to exploit the perceived slowness of Russian mobilization.
* **Avoidance of Protracted War:** The plan sought to avoid a prolonged and costly two-front war.
#### 5.4 Cons/Limitations
* **Inflexible and Rigid:** The plan was too inflexible and rigid, leaving little room for adaptation.
* **Underestimation of the Enemy:** The plan underestimated the resistance of Belgium and the speed of Russian mobilization.
* **Logistical Challenges:** The plan faced significant logistical challenges that proved difficult to overcome.
* **Violation of Neutrality:** The plan’s violation of Belgian neutrality drew Great Britain into the war.
#### 5.5 Ideal User Profile (Hypothetical)
The Schlieffen Plan, in its original conception, was ideally suited for a highly disciplined, well-trained, and logistically capable army facing a slower, less organized enemy. It required a military leadership willing to take risks and adapt to changing circumstances. However, the German army of 1914, while highly capable, was not fully prepared for the challenges posed by the plan.
#### 5.6 Key Alternatives (Briefly)
Alternatives to the Schlieffen Plan included a more defensive strategy, focusing on holding the French in Alsace-Lorraine while concentrating forces against Russia. Another alternative was a more limited offensive in the West, aiming to seize key strategic objectives rather than attempting to encircle Paris. These alternatives, while less ambitious, may have been more realistic and less risky.
#### 5.7 Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
The Schlieffen Plan, despite its meticulous planning and bold ambition, was ultimately a flawed strategy. Its inflexibility, underestimation of the enemy, and logistical challenges contributed to its failure. While the plan offers valuable lessons for military historians and strategists, it should be viewed as a cautionary tale rather than a model for future military operations. Based on our detailed analysis, we cannot recommend the Schlieffen Plan as a viable military strategy.
### 6. Insightful Q&A Section
#### Q1: What was the biggest single miscalculation in the Schlieffen Plan?
**A:** The biggest miscalculation was the underestimation of Belgian resistance and the speed of Russian mobilization. These factors significantly disrupted the German timetable and undermined the plan’s overall effectiveness. The assumption that Belgium would offer only token resistance proved disastrous, as it allowed the Allies to fortify their positions and slow the German advance. The faster-than-expected Russian mobilization forced Germany to divert troops from the Western Front, weakening the crucial right wing.
#### Q2: How did Moltke’s modifications impact the plan’s outcome?
**A:** Moltke’s modifications, while intended to improve the plan’s security, ultimately weakened its offensive power. By strengthening the left wing at the expense of the right, Moltke reduced the chances of a decisive breakthrough and allowed the French to counterattack effectively. His decision to deviate from Schlieffen’s original concept significantly contributed to the plan’s failure.
#### Q3: What role did logistics play in the Schlieffen Plan’s failure?
**A:** Logistics played a critical role in the Schlieffen Plan’s failure. The plan’s strict timetable and rapid pace of advance placed enormous strain on the German logistical system. The army struggled to maintain its supply lines, leading to shortages of food, ammunition, and other essential supplies. The logistical challenges proved to be a major obstacle, hindering the German advance and contributing to the plan’s ultimate failure.
#### Q4: Could the Schlieffen Plan have succeeded under different circumstances?
**A:** It’s debatable. If Belgium had offered no resistance, Russia had mobilized according to initial estimations, and the German logistical system had functioned flawlessly, the plan might have had a higher chance of success. However, even under these ideal circumstances, the plan’s inflexibility and reliance on a series of unlikely events made it a risky gamble. A more adaptable and realistic strategy would have been more likely to succeed.
#### Q5: What were the ethical implications of the Schlieffen Plan?
**A:** The Schlieffen Plan had significant ethical implications, primarily due to its violation of Belgian neutrality. This act of aggression was a clear violation of international law and norms, and it contributed to the moral outrage that galvanized Allied public opinion. The plan’s willingness to disregard the sovereignty of neutral nations raised serious ethical concerns about the conduct of warfare.
#### Q6: How did the Schlieffen Plan contribute to the stalemate on the Western Front?
**A:** The failure of the Schlieffen Plan directly contributed to the stalemate on the Western Front. The German army’s inability to achieve a rapid breakthrough led to the entrenchment of both sides and the horrors of trench warfare. The plan’s failure transformed the conflict into a long and costly war of attrition, with devastating consequences for all involved.
#### Q7: What lessons can modern military strategists learn from the Schlieffen Plan?
**A:** Modern military strategists can learn several important lessons from the Schlieffen Plan, including the importance of adaptability, the need to account for unforeseen circumstances, and the dangers of rigid planning. The plan serves as a cautionary tale about the need to balance ambition with realism and to avoid underestimating the enemy’s capabilities. It also highlights the critical role of logistics in modern warfare.
#### Q8: How did the Schlieffen Plan influence subsequent German military strategy?
**A:** The Schlieffen Plan influenced subsequent German military strategy by emphasizing the importance of speed, envelopment, and decisive action. These concepts continued to be central to German military thinking throughout the 20th century. However, the plan’s failure also led to a greater appreciation for the complexities of modern warfare and the need for more flexible and adaptable strategies.
#### Q9: What was the political context surrounding the development of the Schlieffen Plan?
**A:** The Schlieffen Plan was developed in the context of rising tensions between Germany and its European neighbors. Germany felt encircled by France and Russia and feared a two-front war. The plan was intended to address this strategic dilemma and secure Germany’s position as a major European power. The political context of the time contributed to the plan’s aggressive and expansionist nature.
#### Q10: How has the Schlieffen Plan been portrayed in popular culture?
**A:** The Schlieffen Plan has been portrayed in popular culture as a symbol of German military arrogance and strategic miscalculation. It is often depicted as a rigid and inflexible plan that was doomed to failure from the start. The plan’s failure has been used to illustrate the dangers of overconfidence and the importance of adaptability in warfare. The Schlieffen Plan remains a potent symbol of the complexities and tragedies of World War I.
### Conclusion
The Schlieffen Plan remains a fascinating and cautionary tale in military history. While its ambition and meticulous planning are undeniable, its fatal flaws and ultimate failure serve as a stark reminder of the complexities of warfare. The plan’s legacy continues to influence military thinking today, highlighting the importance of adaptability, realism, and a thorough understanding of the enemy. By studying the Schlieffen Plan, we can gain valuable insights into the challenges of strategic planning and the enduring lessons of World War I. Share your thoughts and experiences related to the Schlieffen Plan in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to WWI military strategies for a deeper dive into related topics. Contact our experts for a consultation on modern strategic planning methodologies that incorporate lessons learned from historical campaigns like the Schlieffen Plan.
