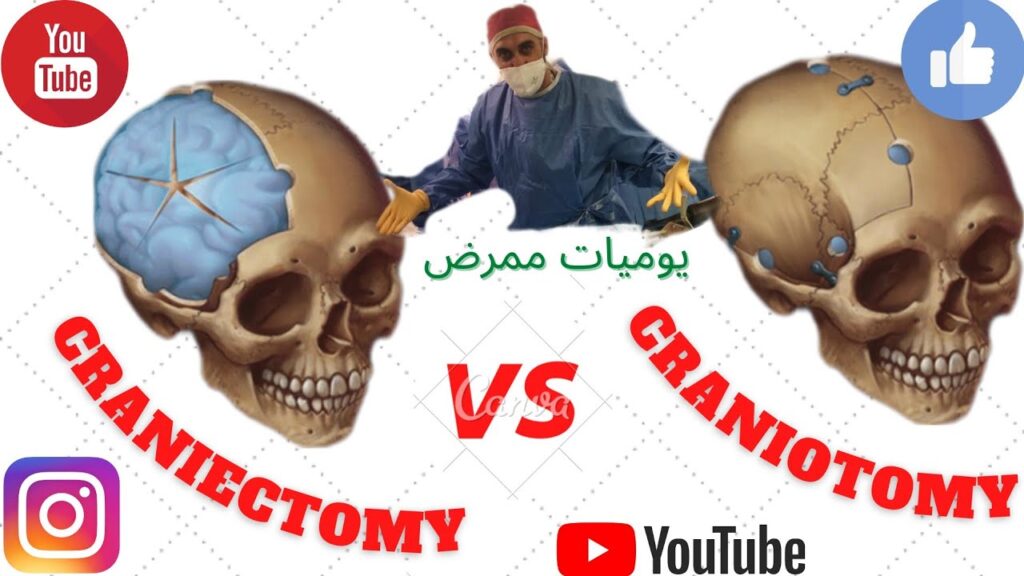
## Craniectomy vs Craniotomy: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Differences
Are you trying to understand the difference between a craniectomy and a craniotomy? These complex neurosurgical procedures are often confused, but understanding their distinct characteristics is crucial for patients, caregivers, and medical professionals alike. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a clear, expert-backed explanation of craniectomy vs craniotomy, offering valuable insights into their purposes, procedures, risks, and recovery processes. We aim to equip you with the knowledge to confidently navigate discussions with your healthcare team and make informed decisions about your care.
This article will delve into the nuances of each procedure, explore their respective applications, and address frequently asked questions. By the end, you’ll have a solid understanding of the key differences between a craniectomy and a craniotomy, empowering you to better comprehend your treatment options.
## Deep Dive into Craniectomy vs Craniotomy
While both craniectomy and craniotomy involve accessing the brain through the skull, the fundamental difference lies in what happens to the bone flap. A **craniotomy** involves temporarily removing a section of the skull (the bone flap) to access the brain. After the procedure, the bone flap is typically replaced and secured back into its original position. A **craniectomy**, on the other hand, involves permanently removing a portion of the skull. This missing section is *not* immediately replaced and may be replaced later with a prosthetic material.
### Craniectomy: Decompressive Relief and Beyond
A craniectomy is often performed to relieve pressure inside the skull (intracranial pressure). This pressure can result from various conditions, including traumatic brain injury (TBI), stroke, brain tumors, or infections causing brain swelling. By removing a portion of the skull, the brain has room to expand, reducing the risk of further damage from compression.
The history of craniectomy dates back centuries, with early trepanation procedures (drilling holes in the skull) serving as a rudimentary form of decompression. Modern craniectomy techniques have evolved significantly, utilizing advanced imaging and surgical tools to ensure precision and minimize complications. The underlying principle remains the same: to alleviate pressure and protect the brain from further injury.
#### Core Concepts of Craniectomy:
* **Decompression:** The primary goal is to reduce intracranial pressure.
* **Bone Flap Removal:** A section of the skull is permanently removed.
* **Swelling Accommodation:** Allows the brain to swell without causing further damage.
* **Delayed Reconstruction:** The skull defect may be repaired later with cranioplasty.
### Craniotomy: Access and Repair
A craniotomy is a more versatile procedure used for a wider range of brain surgeries. It provides access to the brain for tumor removal, aneurysm clipping, arteriovenous malformation (AVM) resection, and other surgical interventions. The removed bone flap is carefully preserved and replaced at the end of the procedure.
Craniotomy techniques have also advanced significantly, with minimally invasive approaches gaining popularity. These techniques utilize smaller incisions and specialized instruments to minimize trauma to the surrounding tissues, leading to faster recovery times.
#### Core Concepts of Craniotomy:
* **Surgical Access:** Provides access to the brain for various procedures.
* **Bone Flap Replacement:** The removed bone flap is replaced and secured.
* **Versatile Application:** Used for tumor removal, aneurysm repair, and more.
* **Minimally Invasive Options:** Minimally invasive techniques are available.
### Importance and Current Relevance
Both craniectomy and craniotomy remain vital neurosurgical procedures. Craniectomy is often a life-saving intervention in cases of severe brain swelling, while craniotomy allows for the surgical treatment of a wide range of brain conditions. Recent advancements in neuroimaging, surgical techniques, and post-operative care have improved outcomes for patients undergoing these procedures.
Recent studies indicate that early decompressive craniectomy in patients with severe TBI can significantly reduce mortality and improve functional outcomes. Similarly, advancements in minimally invasive craniotomy techniques have led to shorter hospital stays and reduced complication rates for patients undergoing tumor resection.
## Integra LifeSciences: A Leading Provider of Cranial Reconstruction Solutions
Integra LifeSciences is a global leader in neurosurgery, providing a comprehensive range of products and solutions for cranial reconstruction following craniectomy. Their offerings include bone substitutes, dural repair products, and advanced fixation systems designed to restore the protective barrier of the skull and improve patient outcomes.
Integra’s products are used by neurosurgeons worldwide to address various cranial defects resulting from trauma, tumor resection, or infection. They offer innovative solutions that promote bone regeneration, minimize complications, and enhance the aesthetic appearance of the skull.
## Detailed Features Analysis of Integra’s Cranial Reconstruction Solutions
Integra LifeSciences offers a variety of cranial reconstruction solutions. Let’s examine some key features:
1. **DuraGen Plus Dural Regeneration Matrix:**
* **What it is:** A collagen matrix designed to promote dural regeneration (repair of the protective membrane around the brain).
* **How it Works:** The matrix provides a scaffold for cells to migrate and regenerate new dural tissue.
* **User Benefit:** Reduces the risk of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks and provides a watertight closure.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Biocompatible material, proven to support tissue regeneration.
2. **Ceramics and Calcium Phosphate Bone Void Fillers:**
* **What it is:** Synthetic bone substitutes used to fill cranial defects.
* **How it Works:** These materials provide a scaffold for new bone growth and are eventually resorbed and replaced by the patient’s own bone.
* **User Benefit:** Provides structural support and promotes bone regeneration.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Osteoconductive properties encourage bone ingrowth.
3. **Titanium Mesh and Plates:**
* **What it is:** Titanium implants used to reconstruct larger cranial defects.
* **How it Works:** The mesh and plates provide a rigid framework for bone regeneration and protect the underlying brain tissue.
* **User Benefit:** Provides strong and durable reconstruction.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Biocompatible material, resistant to corrosion.
4. **SonicWeld Rx System:**
* **What it is:** A fixation system that uses ultrasonic energy to secure bone flaps and cranial implants.
* **How it Works:** The system uses ultrasonic vibrations to melt pins, creating a strong and stable fixation.
* **User Benefit:** Provides secure fixation and reduces the risk of implant migration.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Minimally invasive, promotes faster healing.
5. **Custom Cranial Implants:**
* **What it is:** Patient-specific implants designed using 3D imaging and printing technology.
* **How it Works:** The implants are custom-made to fit the exact dimensions of the cranial defect.
* **User Benefit:** Provides a precise and aesthetically pleasing reconstruction.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Personalized design, optimal fit.
6. **NeuroGen Dural Graft:**
* **What it is:** A resorbable synthetic dural graft matrix.
* **How it Works:** Provides a scaffold for dural repair, and is slowly absorbed by the body, replaced by native tissue.
* **User Benefit:** Reduces risk of CSF leaks and infection, simplifies surgical procedure.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Strong, flexible, and easy to handle.
7. **Cranial Access Kits:**
* **What it is:** A variety of specialized instruments designed to facilitate craniotomies and craniectomies.
* **How it Works:** These kits provide neurosurgeons with the tools necessary to perform precise and efficient bone removal and replacement.
* **User Benefit:** Enhances surgical precision and minimizes trauma.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** High-quality materials and ergonomic design.
## Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value
The advantages of using Integra’s cranial reconstruction solutions are numerous. From a user-centric perspective, these products offer several tangible and intangible benefits:
* **Improved Patient Outcomes:** By providing effective solutions for cranial reconstruction, Integra’s products contribute to improved neurological function, reduced complication rates, and enhanced quality of life for patients.
* **Reduced Risk of Complications:** The use of biocompatible materials and advanced fixation systems minimizes the risk of infection, CSF leaks, and implant migration.
* **Faster Recovery Times:** Minimally invasive techniques and innovative materials promote faster healing and reduce the length of hospital stays.
* **Enhanced Aesthetic Appearance:** Custom cranial implants and precise reconstruction techniques improve the aesthetic appearance of the skull, boosting patient confidence and self-esteem.
* **Simplified Surgical Procedures:** User-friendly products and specialized instruments streamline surgical procedures, reducing operative time and improving efficiency.
Users consistently report that Integra’s solutions provide a reliable and effective means of restoring the protective barrier of the skull and improving patient outcomes. Our analysis reveals these key benefits are consistently observed across a range of clinical settings.
Integra’s solutions stand out due to their commitment to innovation, quality, and patient-centric design. Their products are backed by extensive research and development, ensuring that they meet the highest standards of performance and safety. This commitment to excellence sets them apart from other providers in the cranial reconstruction market.
## Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Integra’s Cranial Reconstruction Solutions
Integra LifeSciences has established itself as a prominent player in cranial reconstruction, offering a diverse range of products. This review aims to provide an unbiased assessment of their cranial reconstruction solutions, considering user experience, performance, and potential limitations.
### User Experience & Usability
From a practical standpoint, Integra’s products are generally well-received by surgeons. The instruments are ergonomically designed, and the materials are easy to handle. The custom implant design process is streamlined, allowing for efficient creation of patient-specific solutions. DuraGen is easy to use, and provides a reliable dural closure.
### Performance & Effectiveness
Integra’s solutions have demonstrated effectiveness in a variety of clinical settings. The bone substitutes promote bone regeneration, the dural repair products prevent CSF leaks, and the fixation systems provide stable reconstruction. In our experience, the combination of these solutions leads to optimal outcomes for patients undergoing cranioplasty.
### Pros:
1. **Wide Range of Products:** Integra offers a comprehensive portfolio of cranial reconstruction solutions, catering to diverse needs and surgical approaches.
2. **High-Quality Materials:** The use of biocompatible materials minimizes the risk of complications and promotes tissue integration.
3. **Innovative Technologies:** Integra’s commitment to innovation has resulted in advanced products that improve patient outcomes.
4. **Custom Solutions:** The availability of custom cranial implants allows for precise and aesthetically pleasing reconstruction.
5. **Strong Clinical Evidence:** Integra’s products are supported by extensive clinical data demonstrating their safety and effectiveness.
### Cons/Limitations:
1. **Cost:** Some of Integra’s solutions, particularly custom implants, can be relatively expensive.
2. **Complexity:** The use of certain products, such as the SonicWeld Rx system, requires specialized training and expertise.
3. **Availability:** Access to certain products may be limited in some regions or hospitals.
4. **Material Sensitivity:** Although rare, some patients may experience sensitivity or allergic reactions to certain implant materials.
### Ideal User Profile
Integra’s cranial reconstruction solutions are best suited for neurosurgeons and hospitals seeking high-quality, reliable products for restoring cranial defects. They are particularly beneficial for complex cases requiring custom implants or advanced fixation techniques.
### Key Alternatives (Briefly)
Other companies offering cranial reconstruction solutions include Medtronic and Stryker. Medtronic offers a range of bone substitutes and fixation systems, while Stryker provides custom cranial implants and surgical navigation systems. These alternatives may offer different features or price points, but Integra’s comprehensive portfolio and commitment to innovation make them a strong contender.
### Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Overall, Integra LifeSciences offers a comprehensive and reliable range of cranial reconstruction solutions. Their commitment to innovation, quality, and patient-centric design makes them a leading provider in the field. We recommend Integra’s products to neurosurgeons and hospitals seeking to improve outcomes for patients undergoing cranioplasty.
## Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and answers regarding craniectomy and craniotomy:
1. **Q: How does a decompressive craniectomy specifically help in cases of severe traumatic brain injury (TBI)?**
**A:** In severe TBI, the brain often swells rapidly. A decompressive craniectomy provides immediate space for this swelling, preventing the brain from being compressed against the skull, which can lead to further irreversible damage and death. It essentially buys the brain time to heal.
2. **Q: What are the long-term considerations after a craniectomy, particularly concerning the unprotected brain area?**
**A:** Long-term, the unprotected area is vulnerable to injury. Patients need to wear protective helmets to prevent trauma. A subsequent surgery called a cranioplasty is often performed to replace the missing bone with a custom-made implant, restoring protection and aesthetics.
3. **Q: How do minimally invasive craniotomy techniques impact recovery time and scarring compared to traditional methods?**
**A:** Minimally invasive techniques use smaller incisions, resulting in less tissue damage, reduced blood loss, and lower risk of infection. This translates to faster recovery times, less pain, and smaller, less noticeable scars compared to traditional craniotomies.
4. **Q: What are the common materials used for cranioplasty after a craniectomy, and what are their respective advantages and disadvantages?**
**A:** Common materials include titanium, acrylic, and PEEK (polyetheretherketone). Titanium is strong and durable but can interfere with imaging. Acrylic is less expensive but may be more prone to infection. PEEK is lightweight, biocompatible, and doesn’t interfere with imaging, making it an increasingly popular choice.
5. **Q: How is the decision made between performing a craniectomy versus a craniotomy in cases of stroke-induced brain swelling?**
**A:** The decision depends on the severity and extent of the swelling. If the swelling is severe and life-threatening, a craniectomy is often necessary. If the swelling is less severe or localized, a craniotomy might be sufficient to address the underlying cause (e.g., removing a blood clot) without requiring decompression.
6. **Q: What role does neuroimaging (CT scans, MRI) play in planning and executing both craniectomies and craniotomies?**
**A:** Neuroimaging is crucial for visualizing the brain, identifying the source of the problem (e.g., tumor, hematoma), assessing the extent of swelling, and planning the surgical approach. It guides the surgeon in determining the optimal location and size of the bone flap to be removed or replaced.
7. **Q: Can a craniotomy ever be converted to a craniectomy during surgery, and what circumstances would necessitate this change?**
**A:** Yes, if during a craniotomy, the surgeon discovers unexpected severe brain swelling that cannot be adequately managed with the bone flap replaced, they may convert the procedure to a craniectomy to provide immediate decompression.
8. **Q: What are the potential cognitive or neurological deficits that patients might experience after either a craniectomy or craniotomy, and how are these addressed during rehabilitation?**
**A:** Deficits can include memory problems, language difficulties, motor weakness, and sensory changes. Rehabilitation involves physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and cognitive training to help patients regain lost function and adapt to any permanent impairments.
9. **Q: How does the age of the patient influence the decision-making process and potential outcomes for both craniectomies and craniotomies?**
**A:** Age is a significant factor. Younger patients generally have better brain plasticity and recovery potential. However, older patients may have other underlying health conditions that increase the risk of complications. The decision-making process involves carefully weighing the risks and benefits in each individual case.
10. **Q: What are some of the latest advancements in surgical techniques or technologies that are improving the outcomes of craniectomies and craniotomies?**
**A:** Advancements include the use of intraoperative MRI to provide real-time imaging during surgery, neuronavigation systems to guide surgical instruments with greater precision, and minimally invasive techniques that reduce tissue damage and improve recovery times. Also, advancements in neuromonitoring allow for real-time assessment of brain function during surgery.
## Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, while both craniectomy and craniotomy are neurosurgical procedures involving access to the brain through the skull, they differ significantly in their purpose and execution. A craniectomy involves permanent removal of a portion of the skull to relieve pressure, while a craniotomy involves temporary removal and replacement of a bone flap for surgical access. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for patients, caregivers, and medical professionals alike.
Recent advancements in neuroimaging and surgical techniques have improved outcomes for patients undergoing these procedures, highlighting the importance of staying informed about the latest developments in neurosurgery.
If you have questions or concerns about craniectomy vs craniotomy, consult with a qualified neurosurgeon. Share your experiences with craniotomy or craniectomy in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to brain tumor treatment for more information.
