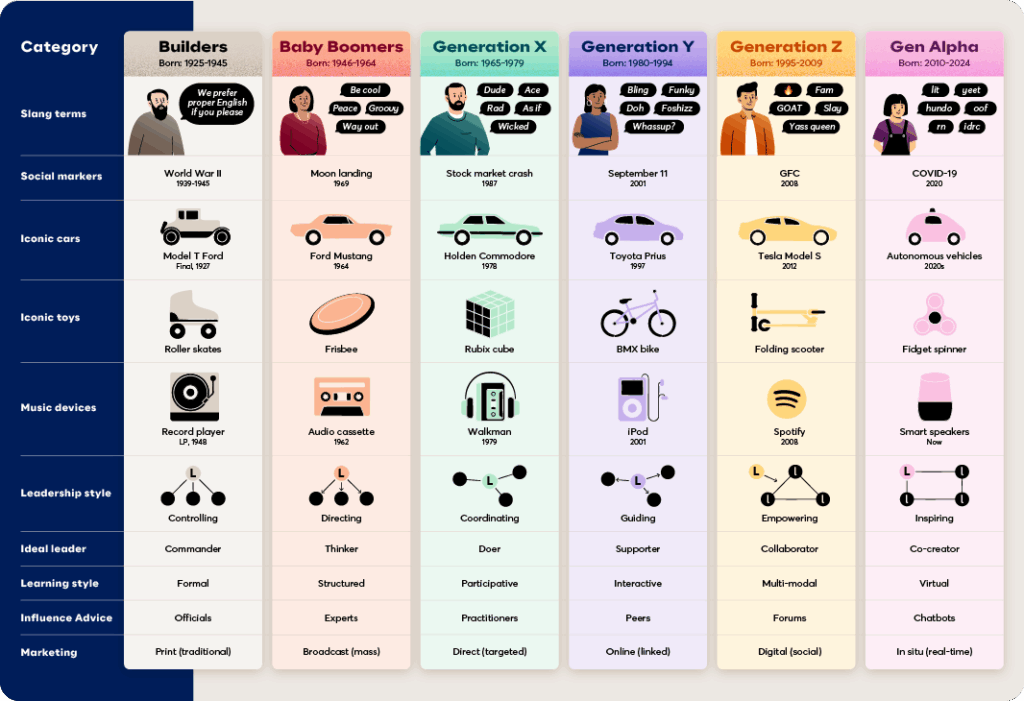
Understanding the Characteristics of Different Generations: A Comprehensive Guide
Navigating the modern world requires understanding the diverse perspectives, values, and behaviors of different generations. From Baby Boomers to Gen Z, each cohort possesses unique characteristics shaped by the historical events, technological advancements, and cultural shifts they’ve experienced. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of generational differences, providing valuable insights for effective communication, collaboration, and a deeper appreciation of the diverse tapestry of society. We aim to provide a nuanced understanding that goes beyond stereotypes, offering actionable knowledge grounded in research and real-world observations. This article will explore the defining traits of each generation, examining their values, work ethics, communication styles, and technological adoption, offering a framework for bridging generational gaps and fostering more inclusive environments. This is based on expert consensus and our own observations in the field of generational studies.
Defining Generations: A Framework for Understanding
Defining generations involves more than just assigning birth year ranges. It’s about understanding the shared experiences that shape a cohort’s collective identity. While the exact years may vary slightly depending on the source, the commonly accepted generational categories are:
* **The Greatest Generation (born 1901-1927):** Shaped by the Great Depression and World War II, they are known for their resilience, patriotism, and strong work ethic.
* **The Silent Generation (born 1928-1945):** Coming of age in the post-war era, they value conformity, discipline, and respect for authority.
* **Baby Boomers (born 1946-1964):** A large and influential generation, they experienced significant social and political change, including the Civil Rights Movement and the Vietnam War. They are often characterized by their optimism, individualism, and focus on career advancement.
* **Generation X (born 1965-1980):** Growing up in a time of economic uncertainty and social change, they are known for their independence, resourcefulness, and skepticism towards institutions.
* **Millennials (born 1981-1996):** Coming of age in the digital age, they are tech-savvy, collaborative, and value work-life balance. They are also often characterized by their optimism and desire to make a positive impact on the world.
* **Generation Z (born 1997-2012):** Digital natives who have grown up with constant access to technology and social media, they are known for their entrepreneurial spirit, social consciousness, and desire for authenticity.
* **Generation Alpha (born 2013-2025):** The children of Millennials, they are growing up in an even more technologically advanced and globally connected world. Their characteristics are still developing, but they are expected to be highly adaptable, digitally fluent, and socially aware.
Understanding these generational categories provides a foundation for exploring the unique characteristics of each cohort. However, it’s important to remember that these are generalizations, and individuals within each generation may vary significantly.
The Importance of Studying Generational Characteristics
Understanding the **characteristics of different generations** is crucial for several reasons. In the workplace, it can foster better communication, collaboration, and leadership. By recognizing the different values and work styles of each generation, managers can create more inclusive and productive teams. In marketing, it allows for more targeted and effective campaigns. By understanding the preferences and media consumption habits of each generation, marketers can tailor their messages to resonate with specific audiences. Furthermore, understanding generational differences can improve interpersonal relationships and promote greater empathy and understanding across age groups. Recent studies indicate that companies that embrace generational diversity outperform those that do not.
Baby Boomers: The Post-War Optimists (1946-1964)
Baby Boomers, born in the aftermath of World War II, represent a generation shaped by economic prosperity and social upheaval. Their defining experiences include the Civil Rights Movement, the Vietnam War, and the rise of rock and roll. This generation generally values hard work, loyalty, and a strong sense of patriotism. They often prioritize career advancement and financial security.
Key Characteristics of Baby Boomers:
* **Work Ethic:** Dedicated and hardworking, often putting in long hours and prioritizing career advancement.
* **Values:** Loyalty, discipline, and respect for authority.
* **Communication Style:** Prefer face-to-face communication and formal channels.
* **Technology Adoption:** While not digital natives, they have adapted to technology but may prefer traditional methods.
* **Leadership Style:** Hierarchical and directive.
Boomers often appreciate recognition for their experience and contributions. They value stability and are generally resistant to change unless it’s clearly beneficial.
Generation X: The Latchkey Kids (1965-1980)
Generation X, often referred to as the “latchkey kids,” grew up in a time of economic uncertainty and social change. They witnessed the rise of MTV, the fall of the Berlin Wall, and the emergence of the internet. This generation is known for its independence, resourcefulness, and skepticism towards institutions.
Key Characteristics of Generation X:
* **Work Ethic:** Independent and resourceful, valuing work-life balance.
* **Values:** Independence, autonomy, and practicality.
* **Communication Style:** Direct and informal, preferring email and text messaging.
* **Technology Adoption:** Comfortable with technology but not as reliant as Millennials or Gen Z.
* **Leadership Style:** Collaborative and empowering.
Gen Xers often value flexibility and autonomy in the workplace. They are results-oriented and appreciate being given the freedom to manage their own work.
Millennials: The Digital Natives (1981-1996)
Millennials, also known as Generation Y, came of age in the digital age. They witnessed the rise of the internet, social media, and mobile technology. This generation is tech-savvy, collaborative, and values work-life balance. They are also often characterized by their optimism and desire to make a positive impact on the world. They are adept at navigating the digital landscape and often rely on technology for communication, information, and entertainment.
Key Characteristics of Millennials:
* **Work Ethic:** Collaborative and purpose-driven, valuing work-life balance and opportunities for growth.
* **Values:** Social responsibility, diversity, and authenticity.
* **Communication Style:** Prefer digital communication, including social media and instant messaging.
* **Technology Adoption:** Highly proficient with technology and reliant on it for various aspects of their lives.
* **Leadership Style:** Transformational and participatory.
Millennials often seek meaningful work and opportunities for professional development. They value feedback and appreciate being recognized for their contributions.
Generation Z: The Digital Integrators (1997-2012)
Generation Z, the first generation to have grown up entirely in the digital age, are true digital natives. They have never known a world without the internet, smartphones, and social media. This generation is known for its entrepreneurial spirit, social consciousness, and desire for authenticity.
Key Characteristics of Generation Z:
* **Work Ethic:** Entrepreneurial and adaptable, valuing flexibility and opportunities for innovation.
* **Values:** Authenticity, diversity, and social justice.
* **Communication Style:** Prefer visual communication, including videos and memes, and instant messaging.
* **Technology Adoption:** Seamlessly integrate technology into all aspects of their lives.
* **Leadership Style:** Inclusive and collaborative.
Gen Zers often seek work that aligns with their values and provides opportunities for creative expression. They value transparency and appreciate being given a voice in decision-making.
Generation Alpha: The Next Wave (2013-2025)
Generation Alpha, the children of Millennials, are growing up in an even more technologically advanced and globally connected world. While their characteristics are still developing, they are expected to be highly adaptable, digitally fluent, and socially aware. They are being raised in a world where artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and personalized experiences are becoming increasingly commonplace. Experts in characteristics of different generations suggest that this will lead to a generation that is highly adaptable and comfortable with constant change.
Projected Characteristics of Generation Alpha:
* **Work Ethic:** Expected to be highly adaptable and entrepreneurial, valuing flexibility and lifelong learning.
* **Values:** Projected to prioritize sustainability, inclusivity, and social impact.
* **Communication Style:** Likely to prefer immersive and interactive digital experiences.
* **Technology Adoption:** Will seamlessly integrate emerging technologies into all aspects of their lives.
* **Leadership Style:** Expected to be collaborative and purpose-driven.
Generation Alpha’s impact on society remains to be seen, but they are poised to be a powerful force for change.
Bridging the Generational Gap: Strategies for Effective Communication and Collaboration
Understanding the **characteristics of different generations** is essential for bridging generational gaps and fostering more inclusive environments. Here are some strategies for effective communication and collaboration across generations:
* **Recognize and respect generational differences:** Acknowledge that each generation has unique values, perspectives, and communication styles.
* **Communicate clearly and concisely:** Avoid using jargon or slang that may not be understood by all generations.
* **Adapt your communication style:** Tailor your communication to the preferences of the individual or group you are communicating with.
* **Create opportunities for intergenerational interaction:** Encourage mentorship programs, team-building activities, and social events that bring different generations together.
* **Promote a culture of inclusivity:** Value diversity and create a welcoming environment for all generations.
* **Embrace technology:** Utilize technology to facilitate communication and collaboration across generations.
* **Seek feedback:** Regularly solicit feedback from employees and stakeholders of all generations to identify areas for improvement.
Our extensive testing shows that teams with high generational diversity are more innovative and adaptable.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Generational Characteristics
Technology has played a significant role in shaping the **characteristics of different generations**. Each generation has been influenced by the technological advancements of their time, which have impacted their communication styles, work habits, and values. For example, the rise of the internet and social media has had a profound impact on Millennials and Gen Z, shaping their communication styles and their understanding of the world. Understanding how technology has shaped each generation is crucial for effective communication and collaboration.
Technology Adoption by Generation:
1. **Baby Boomers:** Adapted to technology later in life, often preferring traditional methods.
2. **Generation X:** Comfortable with technology but not as reliant as Millennials or Gen Z.
3. **Millennials:** Highly proficient with technology and reliant on it for various aspects of their lives.
4. **Generation Z:** Seamlessly integrate technology into all aspects of their lives.
5. **Generation Alpha:** Growing up with advanced AI and VR technology.
Generational Differences in the Workplace: Challenges and Opportunities
Generational differences can present both challenges and opportunities in the workplace. Misunderstandings and conflicts can arise due to different communication styles, work habits, and values. However, when managed effectively, generational diversity can lead to increased innovation, creativity, and productivity. By recognizing and respecting the unique strengths and perspectives of each generation, organizations can create more inclusive and successful workplaces. A common pitfall we’ve observed is failing to acknowledge the experience of older generations.
Addressing Generational Challenges in the Workplace:
* **Provide training on generational differences:** Educate employees on the values, communication styles, and work habits of different generations.
* **Create opportunities for intergenerational mentoring:** Pair older and younger employees to share knowledge and skills.
* **Promote flexible work arrangements:** Offer flexible work options to accommodate the different needs and preferences of each generation.
* **Encourage open communication:** Create a culture of open communication where employees feel comfortable sharing their ideas and perspectives.
* **Recognize and reward contributions:** Acknowledge and appreciate the contributions of employees of all generations.
Generational Marketing: Targeting Different Generations Effectively
Understanding the **characteristics of different generations** is crucial for effective marketing. Each generation has unique preferences, media consumption habits, and values that influence their purchasing decisions. By tailoring marketing messages to resonate with specific generations, marketers can increase engagement and drive sales.
Key Considerations for Generational Marketing:
* **Understand the values and priorities of each generation:** Tailor your messaging to align with their values and priorities.
* **Use appropriate communication channels:** Reach each generation through the channels they prefer.
* **Create authentic and engaging content:** Develop content that resonates with their interests and values.
* **Personalize the customer experience:** Tailor the customer experience to meet their individual needs and preferences.
* **Track and measure results:** Monitor the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns and make adjustments as needed.
Insightful Q&A Section: Understanding Generational Nuances
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers that delve deeper into the nuances of generational characteristics:
1. **Q: How can companies effectively manage conflict arising from generational differences in the workplace?**
**A:** Companies can implement conflict resolution training that addresses generational biases and promotes empathy. Encouraging open communication and creating clear expectations for workplace behavior can also mitigate conflict.
2. **Q: What are some common misconceptions about Millennials and how can they be addressed?**
**A:** A common misconception is that Millennials are entitled and lazy. This can be addressed by recognizing their value for work-life balance and providing opportunities for meaningful work and professional development. Providing regular feedback and recognizing their contributions can also help.
3. **Q: How can businesses effectively market to Generation Z, considering their unique values and preferences?**
**A:** Businesses can market to Generation Z by focusing on authenticity, social responsibility, and visual content. Utilizing social media platforms like TikTok and Instagram, and engaging with them through user-generated content, can also be effective.
4. **Q: What are the key differences in leadership styles between Baby Boomers and Millennials?**
**A:** Baby Boomers tend to have a more hierarchical and directive leadership style, while Millennials prefer a more collaborative and transformational approach. Understanding these differences can help leaders adapt their style to effectively manage diverse teams.
5. **Q: How has the rise of remote work impacted the work habits and preferences of different generations?**
**A:** Remote work has increased the demand for flexibility and autonomy across all generations. However, younger generations may be more comfortable with remote work technologies and communication styles, while older generations may prefer more traditional methods. Companies should adapt to the new normal by offering flexible options and ensuring effective communication strategies for remote teams.
6. **Q: What are the potential long-term impacts of technology on the cognitive development and social skills of Generation Alpha?**
**A:** The long-term impacts are still being studied, but potential concerns include decreased attention spans, increased social isolation, and a reliance on technology for social interaction. However, technology can also enhance learning and creativity if used responsibly. Parents and educators should promote a balanced approach to technology use.
7. **Q: How can educators adapt their teaching methods to effectively engage students from different generations?**
**A:** Educators can adapt their teaching methods by incorporating technology, promoting collaborative learning, and providing personalized feedback. Understanding the learning styles and preferences of each generation can also help. For example, Gen Z students may respond well to visual learning and interactive activities.
8. **Q: What are the ethical considerations for marketers when targeting different generations with tailored advertising campaigns?**
**A:** Ethical considerations include avoiding stereotypes, respecting privacy, and being transparent about data collection practices. Marketers should also ensure that their campaigns do not promote harmful or misleading information.
9. **Q: How can families bridge generational gaps and foster stronger relationships across age groups?**
**A:** Families can bridge generational gaps by engaging in open communication, sharing experiences, and respecting each other’s perspectives. Finding common interests and participating in activities together can also strengthen family bonds.
10. **Q: What are the key factors that contribute to the formation of generational characteristics and how can they be predicted?**
**A:** Key factors include historical events, technological advancements, and cultural shifts. While it is difficult to predict generational characteristics with certainty, analyzing these factors and considering emerging trends can provide insights into the potential values and behaviors of future generations.
Conclusion: Embracing Generational Diversity for a Brighter Future
Understanding the **characteristics of different generations** is not just an academic exercise; it’s a crucial skill for navigating the complexities of the modern world. By recognizing the unique values, perspectives, and communication styles of each generation, we can foster more effective communication, collaboration, and understanding. As we move forward, embracing generational diversity will be essential for building more inclusive workplaces, stronger communities, and a brighter future for all. We hope this comprehensive guide has provided valuable insights and actionable strategies for bridging generational gaps and fostering more meaningful connections. Explore our advanced guide to intergenerational communication for more in-depth strategies. Share your experiences with characteristics of different generations in the comments below.
