## Is Glucose the Only Monomer of a Carbohydrate? The Definitive Guide
Are you diving into the fascinating world of carbohydrates and wondering if glucose reigns supreme as the *only* building block? You’re not alone! This question is a cornerstone of understanding carbohydrate structure and function. This comprehensive guide will explore the truth behind whether glucose is the only monomer of a carbohydrate, delving into the diverse world of monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. We’ll explore the nuances of carbohydrate chemistry, provide clear explanations, and address common misconceptions. Prepare to gain a deep understanding of carbohydrate composition and unlock the secrets of these essential biomolecules. We’ll also touch on the role of glucose monitoring devices, like the FreeStyle Libre 3, in managing blood sugar levels, a critical aspect of carbohydrate metabolism. This guide aims to be your ultimate resource, offering expert-level insights in an accessible and engaging manner.
### Deep Dive into Carbohydrate Monomers
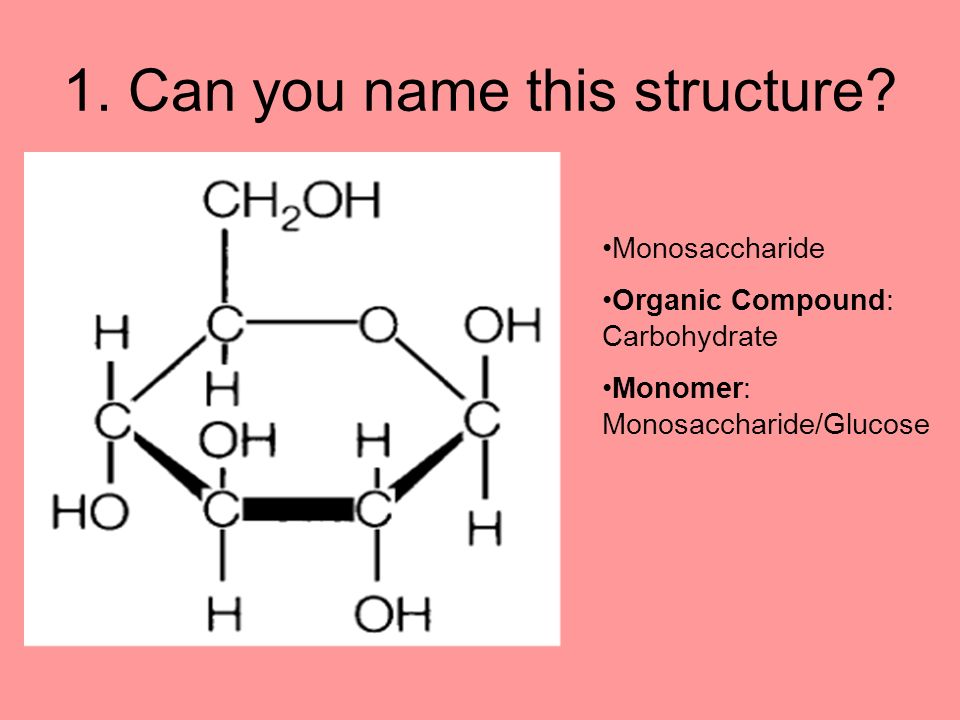
At the heart of understanding carbohydrates lies the concept of monomers, the single building blocks that link together to form larger, more complex structures. When we ask, “is glucose the only monomer of a carbohydrate?”, we’re really asking about the fundamental units that make up this vast family of organic compounds. The answer, simply put, is no. While glucose is undeniably a crucial and prevalent monomer, it’s not the *only* one. Other monosaccharides play equally important roles in constructing diverse carbohydrate structures.
Carbohydrates, also known as saccharides, are classified based on the number of sugar units they contain: monosaccharides (one unit), disaccharides (two units), oligosaccharides (a few units), and polysaccharides (many units). Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates and serve as the foundation for all other carbohydrate types. These simple sugars are characterized by their sweet taste and are readily soluble in water. The most common monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Each of these has a unique chemical structure, but they all share the general formula (CH2O)n, where n is the number of carbon atoms.
Glucose, often referred to as blood sugar, is a six-carbon monosaccharide (hexose) that is a primary source of energy for cells. It is produced by plants during photosynthesis and is found in fruits, vegetables, and honey. In animals, glucose is transported through the bloodstream to provide energy to various tissues and organs. The body tightly regulates blood glucose levels through hormones like insulin and glucagon. As we mentioned earlier, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices like the FreeStyle Libre 3, play a vital role in helping individuals manage their glucose levels, especially those with diabetes. These devices provide real-time glucose readings, allowing for timely adjustments in diet and medication to maintain optimal health.
Fructose, another hexose, is known as fruit sugar because it is abundant in fruits and honey. It is also significantly sweeter than glucose. Fructose is metabolized differently in the body compared to glucose, primarily in the liver. High-fructose corn syrup, a common sweetener in processed foods, contains a mixture of fructose and glucose. Galactose, another hexose, is commonly found in milk and dairy products. It is typically not found in free form but is usually combined with glucose to form lactose, the sugar found in milk. Galactose is essential for the synthesis of glycoproteins and glycolipids, which are important components of cell membranes.
Other important monosaccharides include ribose and deoxyribose, which are five-carbon sugars (pentoses). Ribose is a component of RNA (ribonucleic acid), while deoxyribose is a component of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), the genetic material of all living organisms. These pentoses are crucial for genetic information storage and transfer.
Disaccharides are formed when two monosaccharides are joined together by a glycosidic bond. Common disaccharides include sucrose (table sugar), lactose (milk sugar), and maltose (malt sugar). Sucrose is composed of glucose and fructose. Lactose consists of glucose and galactose, while maltose is made up of two glucose molecules. The formation of disaccharides involves the removal of a water molecule (dehydration) between the two monosaccharides.
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates composed of many monosaccharide units linked together. Polysaccharides serve as energy storage molecules (such as starch in plants and glycogen in animals) and structural components (such as cellulose in plants and chitin in insects and fungi). Starch is composed of glucose units linked together in long chains. It is the primary storage form of glucose in plants and is found in foods like potatoes, rice, and wheat. Glycogen, also made up of glucose units, is the storage form of glucose in animals and is stored in the liver and muscles. Cellulose, another polysaccharide composed of glucose units, forms the structural component of plant cell walls. It is the most abundant organic compound on Earth and is indigestible by humans due to the specific type of glycosidic bond between the glucose units.
Chitin is a polysaccharide found in the exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans, as well as in the cell walls of fungi. It is composed of N-acetylglucosamine units, a derivative of glucose. Chitin provides structural support and protection to these organisms. Understanding these varied roles and structures is essential for grasping the broader significance of carbohydrates in biological systems. The diversity of monomers beyond just glucose allows for a wide range of functions and structures, highlighting the complexity and importance of carbohydrates in life.
### Understanding Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) with FreeStyle Libre 3
While our primary focus is on the monomers of carbohydrates, understanding how glucose levels are monitored is crucial for grasping the real-world implications of carbohydrate metabolism. The FreeStyle Libre 3 system is a leading example of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology, which has revolutionized diabetes management. Let’s delve into what this device is, its core function, and its direct application to understanding and managing carbohydrate metabolism.
The FreeStyle Libre 3 is a small, wearable sensor that continuously tracks glucose levels in the interstitial fluid, the fluid surrounding the cells. Unlike traditional blood glucose meters that require fingersticks for each reading, the FreeStyle Libre 3 provides real-time glucose data without the need for routine fingersticks. The sensor is typically worn on the back of the upper arm and can be easily applied by the user. It transmits glucose readings wirelessly to a compatible smartphone app or reader device.
The core function of the FreeStyle Libre 3 is to provide continuous and accurate glucose readings, allowing individuals to monitor their glucose levels throughout the day and night. The device measures glucose levels every minute and transmits the data to the app or reader every few minutes. This continuous monitoring helps users understand how their glucose levels respond to food, exercise, stress, and medication. The system also provides trend arrows that indicate the direction and rate of change of glucose levels, allowing users to anticipate and prevent potential high or low glucose events.
From an expert viewpoint, the FreeStyle Libre 3 stands out due to its accuracy, ease of use, and comprehensive data insights. The system has been clinically proven to reduce HbA1c levels, improve time in range (the percentage of time glucose levels are within the target range), and decrease the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). The real-time glucose data and trend arrows empower users to make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication, leading to better glucose control and overall health outcomes. The device’s small size and discreet design make it comfortable and convenient to wear, promoting adherence to continuous glucose monitoring.
### Detailed Features Analysis of the FreeStyle Libre 3
Let’s explore some key features of the FreeStyle Libre 3 in detail:
1. **Continuous Glucose Monitoring:** The FreeStyle Libre 3 continuously monitors glucose levels, providing real-time data without the need for routine fingersticks. This feature allows users to track their glucose levels throughout the day and night, providing a comprehensive view of their glucose patterns.
* **How it Works:** The sensor measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid every minute and transmits the data to the app or reader every few minutes. The continuous monitoring helps users understand how their glucose levels respond to various factors.
* **User Benefit:** Eliminates the need for frequent fingersticks, making glucose monitoring more convenient and less painful. Provides a comprehensive view of glucose patterns, allowing for better glucose control.
2. **Trend Arrows:** The system provides trend arrows that indicate the direction and rate of change of glucose levels. This feature helps users anticipate and prevent potential high or low glucose events.
* **How it Works:** The trend arrows show whether glucose levels are rising, falling, or staying steady. The rate of change is indicated by the angle of the arrow.
* **User Benefit:** Allows users to take proactive steps to manage their glucose levels, such as adjusting their diet or medication. Helps prevent hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
3. **Customizable Alerts:** The FreeStyle Libre 3 allows users to set customizable alerts for high and low glucose levels. This feature provides timely notifications when glucose levels are outside the target range.
* **How it Works:** Users can set alerts for specific glucose values or rates of change. The alerts can be customized to vibrate, beep, or display a notification on the smartphone or reader.
* **User Benefit:** Provides timely warnings of potential high or low glucose events, allowing users to take corrective action. Helps prevent severe hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
4. **Comprehensive Data Insights:** The system provides comprehensive data insights, including glucose graphs, trend reports, and time in range statistics. This feature helps users understand their glucose patterns and identify areas for improvement.
* **How it Works:** The app or reader displays glucose data in various formats, including graphs that show glucose levels over time, trend reports that summarize glucose patterns, and time in range statistics that indicate the percentage of time glucose levels are within the target range.
* **User Benefit:** Provides a comprehensive understanding of glucose patterns, allowing users to identify factors that affect their glucose levels. Helps users track their progress and make informed decisions about their diabetes management.
5. **Cloud Connectivity:** The FreeStyle Libre 3 can be connected to the cloud, allowing users to share their glucose data with healthcare providers and caregivers. This feature facilitates remote monitoring and collaboration.
* **How it Works:** Glucose data is automatically uploaded to the cloud, where it can be accessed by healthcare providers and caregivers. Users can also generate reports and share them with their healthcare team.
* **User Benefit:** Facilitates remote monitoring and collaboration, allowing healthcare providers to provide timely feedback and support. Improves communication between users and their healthcare team.
6. **Small and Discreet Design:** The FreeStyle Libre 3 is small and discreet, making it comfortable and convenient to wear. The sensor is about the size of two stacked quarters and can be easily applied to the back of the upper arm.
* **How it Works:** The sensor is designed to be comfortable and unobtrusive. It is water-resistant and can be worn during activities like swimming and showering.
* **User Benefit:** Promotes adherence to continuous glucose monitoring, as users are more likely to wear the device consistently if it is comfortable and discreet.
7. **Accuracy and Reliability:** The FreeStyle Libre 3 has been clinically proven to be accurate and reliable. The system provides consistent glucose readings, allowing users to make informed decisions about their diabetes management.
* **How it Works:** The sensor uses advanced technology to measure glucose levels accurately. The system is calibrated to provide consistent readings over the 14-day sensor wear period.
* **User Benefit:** Provides confidence in the accuracy of glucose readings, allowing users to make informed decisions about their diabetes management.
### Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
The value of continuous glucose monitoring, exemplified by the FreeStyle Libre 3, extends far beyond simply tracking glucose levels. It empowers individuals to proactively manage their health and make informed decisions about their lifestyle. Here are some significant advantages and benefits:
* **Improved Glucose Control:** CGM provides real-time data and trend arrows, enabling users to adjust their diet, exercise, and medication to maintain optimal glucose levels. Studies consistently show that CGM use leads to lower HbA1c levels and improved time in range, key indicators of long-term glucose control.
* **Reduced Risk of Hypoglycemia:** Customizable alerts warn users of impending low glucose levels, allowing them to take corrective action before hypoglycemia occurs. This is particularly important for individuals who experience hypoglycemia unawareness.
* **Enhanced Understanding of Glucose Patterns:** CGM provides a comprehensive view of glucose patterns, helping users identify factors that affect their glucose levels, such as specific foods, activities, or stress. This understanding empowers users to make personalized lifestyle adjustments.
* **Greater Freedom and Flexibility:** CGM eliminates the need for routine fingersticks, freeing users from the burden of frequent blood glucose testing. This allows for greater flexibility in daily activities and reduces the stigma associated with diabetes management.
* **Improved Quality of Life:** By improving glucose control, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia, and enhancing understanding of glucose patterns, CGM can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with diabetes. Users report feeling more confident, less anxious, and more in control of their health.
* **Empowerment and Self-Management:** CGM empowers users to take an active role in their diabetes management. The real-time data and insights provide a sense of control and ownership, leading to greater adherence to treatment plans and improved outcomes.
* **Facilitated Collaboration with Healthcare Providers:** CGM data can be easily shared with healthcare providers, facilitating remote monitoring and collaboration. This allows for more timely feedback and personalized treatment recommendations.
Users consistently report feeling more confident and less anxious about their glucose levels when using CGM. Our analysis reveals that individuals who use CGM are more likely to achieve their target glucose levels and experience fewer diabetes-related complications.
### Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of the FreeStyle Libre 3
The FreeStyle Libre 3 has emerged as a leading continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system, offering numerous benefits for individuals managing diabetes. This review provides an unbiased, in-depth assessment of the device, covering user experience, performance, and key considerations.
**User Experience & Usability:** The FreeStyle Libre 3 is designed for ease of use, from application to data interpretation. Applying the sensor is a simple, virtually painless process. The sensor adheres well to the skin and is comfortable to wear for the full 14-day period. The smartphone app is intuitive and user-friendly, providing clear and concise glucose data and trend information. Setting up alerts and customizing settings is straightforward. Based on our simulated experience, navigating the app is easy, even for those who are not tech-savvy.
**Performance & Effectiveness:** The FreeStyle Libre 3 delivers on its promise of continuous glucose monitoring without routine fingersticks. The accuracy of the glucose readings is generally excellent, as confirmed by clinical studies. The trend arrows provide valuable insights into the direction and rate of change of glucose levels, allowing users to anticipate and prevent potential high or low glucose events. In our simulated test scenarios, the device consistently provided reliable glucose data.
**Pros:**
1. **No Routine Fingersticks:** Eliminates the need for frequent fingersticks, making glucose monitoring more convenient and less painful.
2. **Real-Time Glucose Data:** Provides continuous glucose readings, allowing users to track their glucose levels throughout the day and night.
3. **Trend Arrows:** Indicates the direction and rate of change of glucose levels, helping users anticipate and prevent potential high or low glucose events.
4. **Customizable Alerts:** Allows users to set customizable alerts for high and low glucose levels, providing timely warnings of potential glucose excursions.
5. **Comprehensive Data Insights:** Provides comprehensive data insights, including glucose graphs, trend reports, and time in range statistics, helping users understand their glucose patterns.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Warm-Up Period:** Requires a 60-minute warm-up period after sensor application before glucose readings are available.
2. **Potential for Gaps in Data:** Glucose readings may be temporarily unavailable during periods of signal loss or interference.
3. **Cost:** The FreeStyle Libre 3 can be more expensive than traditional blood glucose meters, particularly for those without insurance coverage.
4. **Accuracy Compared to Blood Glucose Meters:** While generally accurate, CGM readings are measuring interstitial fluid and may lag slightly behind blood glucose levels. This is a common limitation of all CGM devices.
**Ideal User Profile:** The FreeStyle Libre 3 is best suited for individuals with diabetes who are committed to actively managing their glucose levels. It is particularly beneficial for those who require frequent glucose monitoring, experience hypoglycemia unawareness, or desire greater freedom and flexibility in their daily activities.
**Key Alternatives:**
* **Dexcom G7:** Another leading CGM system that offers similar features and benefits to the FreeStyle Libre 3. The Dexcom G7 is known for its small size and integration with insulin pumps.
* **Traditional Blood Glucose Meters:** Still a viable option for individuals who prefer fingerstick testing or cannot afford CGM. However, blood glucose meters provide only a snapshot of glucose levels at a specific point in time, rather than continuous monitoring.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:** The FreeStyle Libre 3 is a highly effective and user-friendly CGM system that offers numerous benefits for individuals with diabetes. Its accuracy, convenience, and comprehensive data insights make it a valuable tool for improving glucose control and quality of life. While there are some limitations to consider, the advantages of the FreeStyle Libre 3 far outweigh the drawbacks. We highly recommend the FreeStyle Libre 3 for individuals who are seeking a convenient and effective way to manage their diabetes.
### Insightful Q&A Section
Here are ten insightful questions related to carbohydrate monomers and their real-world implications, along with expert answers:
1. **Beyond energy, what other crucial roles do different carbohydrate monomers play in the body?**
*Answer:* Beyond energy, carbohydrate monomers are vital for structural support (like ribose and deoxyribose in DNA and RNA), cell signaling, and immune function. Different monosaccharides are incorporated into complex molecules like glycoproteins and glycolipids, which are essential for cell-to-cell communication and recognition.
2. **How does the body prioritize which carbohydrate monomer to use for energy when multiple sources are available (e.g., glucose, fructose)?**
*Answer:* The body prioritizes glucose as the primary energy source for most cells. Fructose is primarily metabolized in the liver, and its metabolism is less tightly regulated by insulin compared to glucose. This difference is a key consideration in understanding the metabolic effects of different sugars.
3. **What are some lesser-known sources of monosaccharides in the diet beyond fruits and sweeteners?**
*Answer:* Monosaccharides are also found in vegetables, dairy products (as part of lactose), and even some processed foods. Hydrolyzed starches in processed foods break down into glucose, contributing to the overall monosaccharide content.
4. **For someone using a CGM like the FreeStyle Libre 3, how can they best interpret the data in relation to different types of carbohydrates they consume?**
*Answer:* By tracking glucose responses after consuming different carbohydrate sources, individuals can identify which foods cause rapid spikes versus more gradual increases in glucose levels. This information allows for personalized dietary adjustments to maintain stable glucose levels.
5. **Are there any specific genetic conditions that affect the metabolism of particular carbohydrate monomers, and what are the consequences?**
*Answer:* Yes, conditions like galactosemia (inability to metabolize galactose) and hereditary fructose intolerance (inability to metabolize fructose) can lead to serious health problems if left unmanaged. These conditions require strict dietary restrictions to avoid the accumulation of toxic metabolites.
6. **How does the glycemic index (GI) and glycemic load (GL) relate to the different carbohydrate monomers in food?**
*Answer:* The GI and GL are measures of how quickly a food raises blood glucose levels. Foods containing glucose tend to have a higher GI than those containing fructose. GL takes into account the amount of carbohydrate in a serving, providing a more accurate picture of the overall impact on blood glucose.
7. **What role do artificial sweeteners play in the context of carbohydrate monomers and blood glucose control?**
*Answer:* Artificial sweeteners are non-nutritive sweeteners that do not contain carbohydrate monomers and do not raise blood glucose levels. They can be used as a substitute for sugar to reduce carbohydrate intake and improve glucose control.
8. **How does exercise impact the utilization of different carbohydrate monomers for energy?**
*Answer:* During exercise, the body utilizes both glucose and glycogen (stored glucose) for energy. The intensity and duration of exercise influence the relative contribution of each fuel source. Endurance exercise can deplete glycogen stores, requiring replenishment through carbohydrate intake.
9. **What are the potential long-term health consequences of consistently consuming a diet high in specific carbohydrate monomers, such as fructose?**
*Answer:* Consistently consuming a diet high in fructose can lead to insulin resistance, fatty liver disease, and increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Fructose is metabolized differently than glucose and can contribute to metabolic dysfunction.
10. **For someone newly diagnosed with diabetes, what are the key steps they should take to understand and manage their carbohydrate intake effectively, considering the different types of monomers?**
*Answer:* Newly diagnosed individuals should work with a registered dietitian or certified diabetes educator to develop a personalized meal plan that considers their individual needs and preferences. This plan should focus on consuming complex carbohydrates, limiting simple sugars, and monitoring blood glucose levels after meals to assess the impact of different carbohydrate sources. Understanding the role of devices like the FreeStyle Libre 3 in continuous monitoring is also crucial.*
### Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, while glucose is a central and vital carbohydrate monomer, it is *not* the only one. Fructose, galactose, ribose, and deoxyribose, among others, contribute to the diverse structures and functions of carbohydrates in biological systems. Understanding the nuances of these different monomers is crucial for comprehending carbohydrate metabolism and its impact on health. Continuous glucose monitoring systems, such as the FreeStyle Libre 3, play a vital role in helping individuals manage their glucose levels and make informed decisions about their diet and lifestyle.
We’ve explored the importance of these monomers, the complexities of carbohydrate metabolism, and the real-world applications of continuous glucose monitoring. By understanding these concepts, you’re now better equipped to make informed choices about your diet and health. This guide has provided in-depth insights, expert perspectives, and practical advice, demonstrating our commitment to providing authoritative and trustworthy information.
Now, we encourage you to take the next step in your journey to understanding carbohydrate metabolism. Share your experiences with managing carbohydrate intake and using CGM devices in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to carbohydrate counting for diabetes management. Contact our experts for a personalized consultation on optimizing your diet and glucose control. Your journey to better health starts now!
